大根堆
大根堆:每个结点的值不大于他的父亲结点的值
分析如下:
假设对{ 27,15,19,18,28,34,65,49,25,37 }这样一个集合的数据创建成堆;
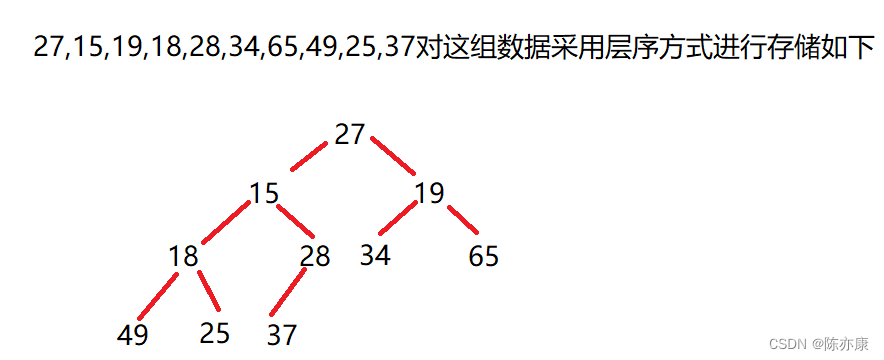
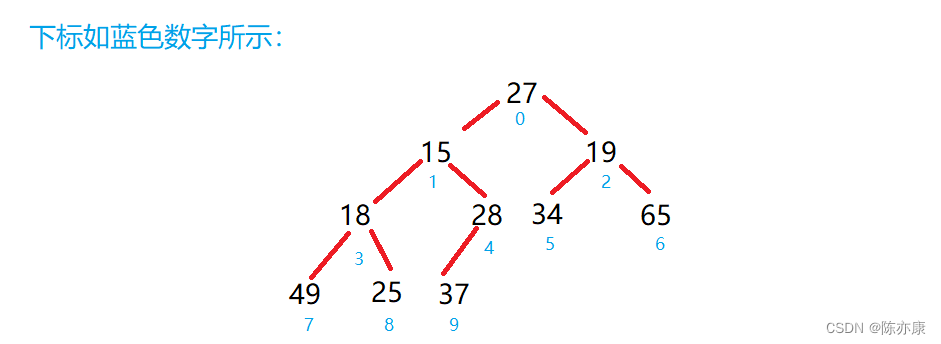
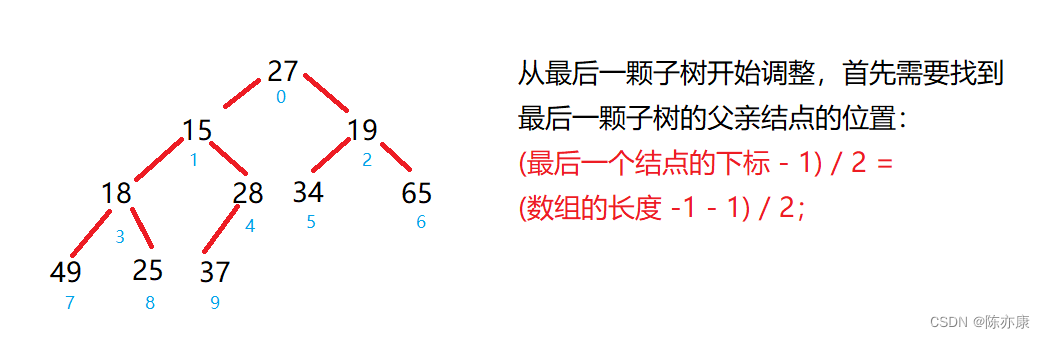
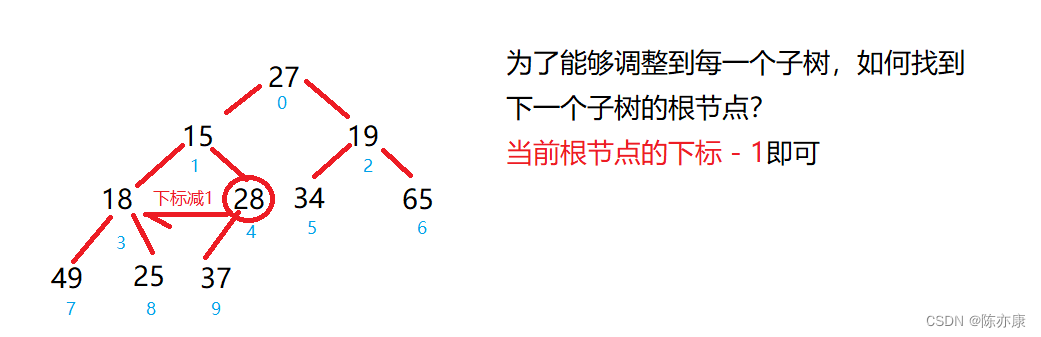
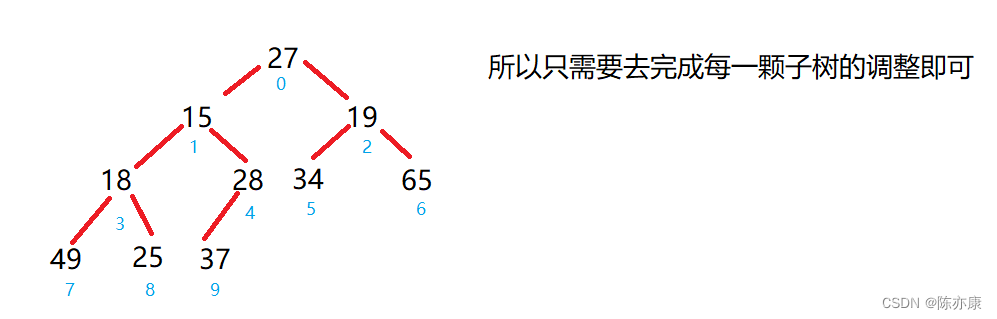

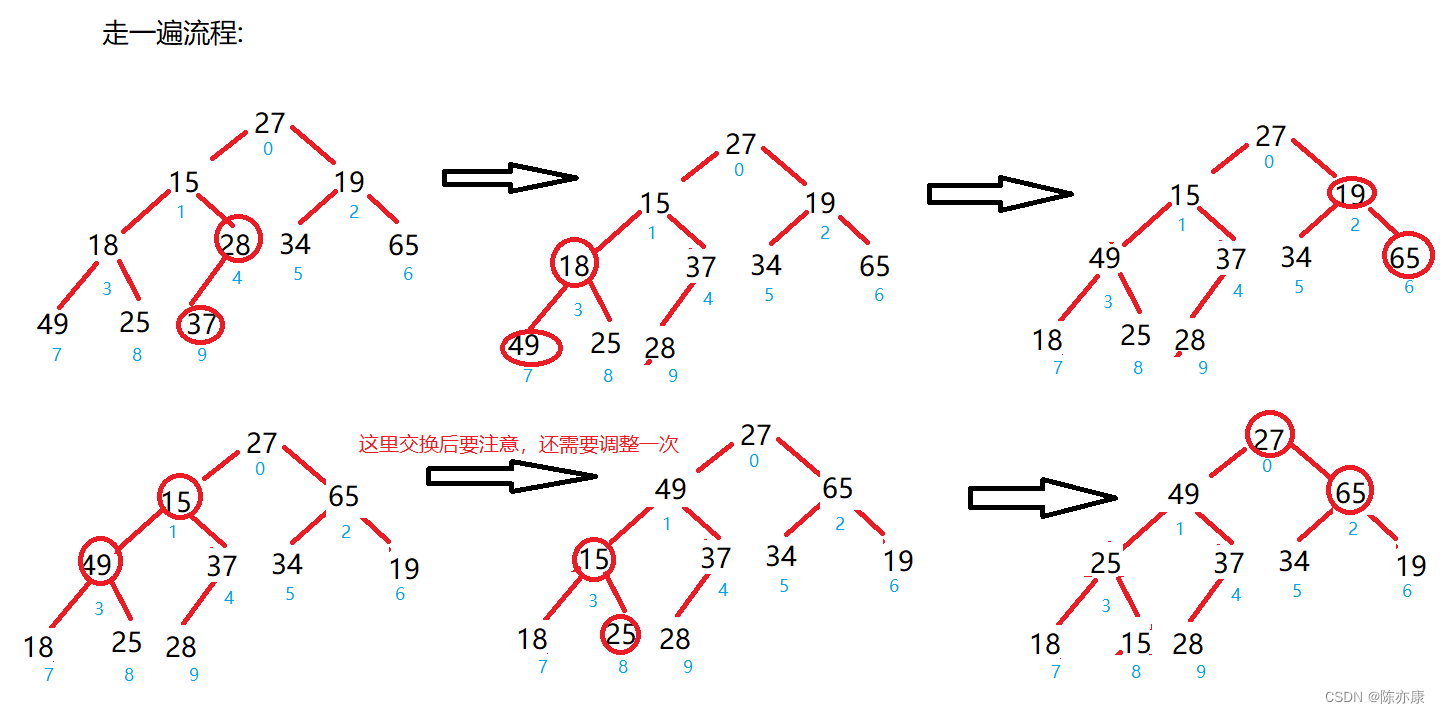
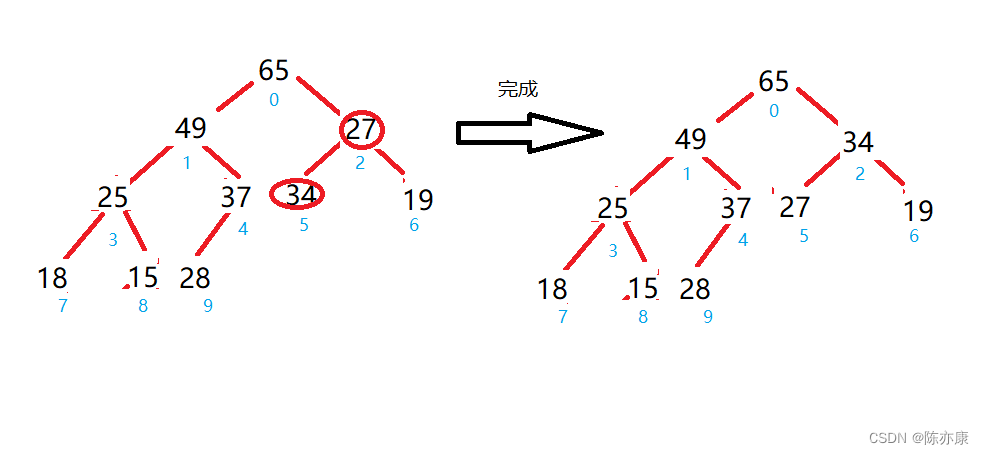
代码如下:
//建立大根堆
public class TestHeap{
public int[] array;
public int usedSize;//当前有效数组长度
public TestHeap(){
this.array = new int[10];
this.usedSize = 0;
}
//初始化数组
public void InitArray(int[] arrayClone){
array = Arrays.copyOf(arrayClone, arrayClone.length);
usedSize = array.length;
}
//创建大根堆
public void createHeap(){
for(int parent = (usedSize - 1 - 1) / 2; parent >= 0; parent--){
adjustment(parent, usedSize);
}
}
//调整
public void adjustment(int parent, int len){
//左子树结点下标
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
//调整
while(child < len){
//先判断有没有右孩子,如果右,找出最大值
if(child + 1 < len && array[child] < array[child + 1]){
child++;//如果右子树大,child++就指向他,如果左子树大,就不用管,直接进行下一步判断交换
}
//若左右子树的最大值大于父亲结点则交换
if(array[child] > array[parent]){
swap(array, child, parent);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
} else{
break;
}
}
}
//交换
public void swap(int[] array, int child, int parent){
int tmp = array[child];
array[child] = array[parent];
array[parent] = tmp;
}
}小根堆
小根堆:每个结点的值不小于他的父亲结点的值
分析与大根堆类似,只是比较出更小的进行替换
代码如下:
//建立大根堆
public class TestHeap{
public int[] array;
public int usedSize;//当前有效数组长度
public TestHeap(){
this.array = new int[10];
this.usedSize = 0;
}
//初始化数组
public void InitArray(int[] arrayClone){
array = Arrays.copyOf(arrayClone, arrayClone.length);
usedSize = array.length;
}
//创建大根堆
public void createHeap(){
for(int parent = (usedSize - 1 - 1) / 2; parent >= 0; parent--){
adjustment(parent, usedSize);
}
}
//调整
public void adjustment(int parent, int len){
//左子树结点下标
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
//调整
while(child < len){
//先判断有没有右孩子,如果右,找出最小值
if(child + 1 < len && array[child] > array[child + 1]){
child++;//如果右子树小,child++就指向他,如果左子树小,就不用管,直接进行下一步判断交换
}
//若左右子树的最大值小于父亲结点则交换
if(array[child] < array[parent]){
swap(array, child, parent);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
} else{
break;
}
}
}
//交换
public void swap(int[] array, int child, int parent){
int tmp = array[child];
array[child] = array[parent];
array[parent] = tmp;
}
}
