题目:
给你一个整数 n ,对于 0 <= i <= n 中的每个 i ,计算其二进制表示中 1 的个数 ,返回一个长度为 n + 1 的数组 ans 作为答案。
示例 1:
输入:n = 2
输出:[0,1,1]
解释:
0 --> 0
1 --> 1
2 --> 10
示例 2:
输入:n = 5
输出:[0,1,1,2,1,2]
解释:
0 --> 0
1 --> 1
2 --> 10
3 --> 11
4 --> 100
5 --> 101
提示:
0 <= n <= 105
进阶:
很容易就能实现时间复杂度为 O(n log n) 的解决方案,你可以在线性时间复杂度 O(n) 内用一趟扫描解决此问题吗?
你能不使用任何内置函数解决此问题吗?(如,C++ 中的 __builtin_popcount )
如果没有加入限制可以使用java的内置函数
Integer.bitCount
思路一:
使用右移以及数多少个1的思路
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
bits[i] = countOnes(i);
}
return bits;
}
public int countOnes(int x) {
int ones = 0;
while (x > 0) {
ones+=x & 1;
x>>=1;
}
return ones;
}
}
或者将其并在一起
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
bits[i] = bits[i >> 1] + (i & 1);
}
return bits;
}
}
思路二:
进行位运算
有多少个1就执行多少次
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
bits[i] = countOnes(i);
}
return bits;
}
public int countOnes(int x) {
int ones = 0;
while (x > 0) {
x &= (x - 1);
ones++;
}
return ones;
}
}
但如果将其函数一起写入for之内
会显示超时限
具体原因好像是
局部变量在栈里面,全局在堆里面。一直循环,堆里面数据不gc只会更多那就会更卡,栈的话在循环的时候,编译器会自动释放,但是堆会越来越多
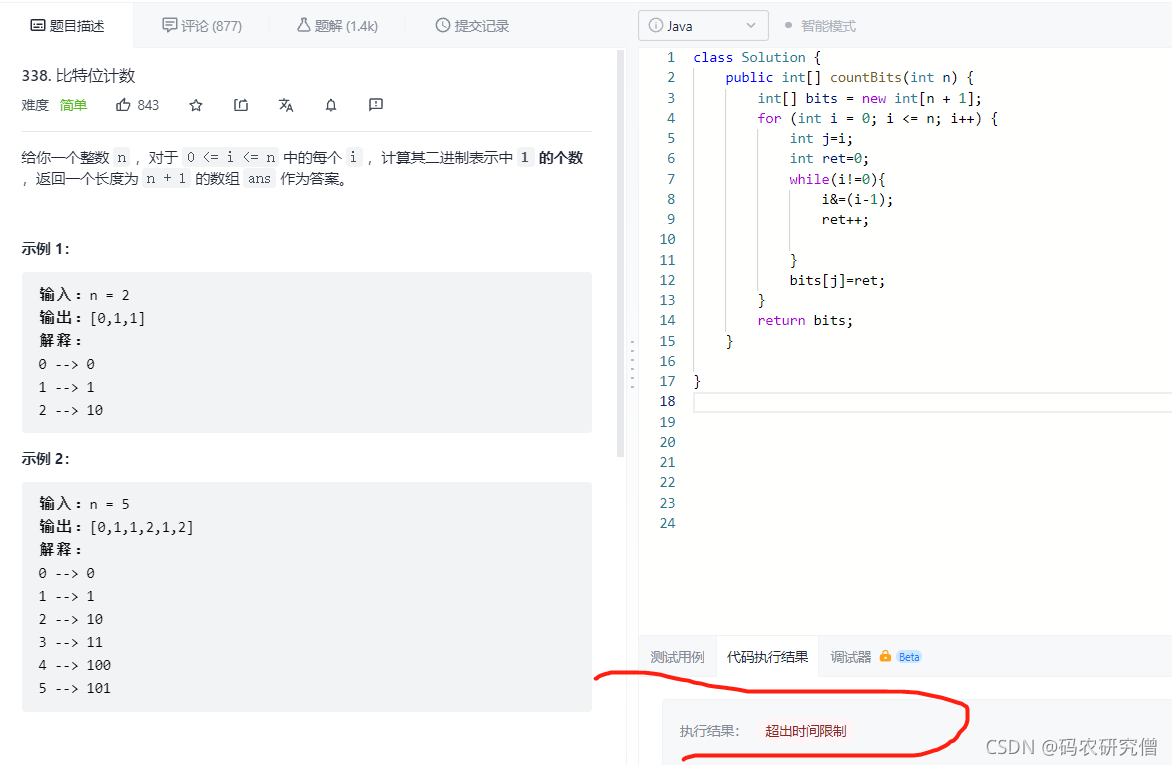
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
int j=i;
int ret=0;
while(i!=0){
i&=(i-1);
ret++;
}
bits[j]=ret;
}
return bits;
}
}
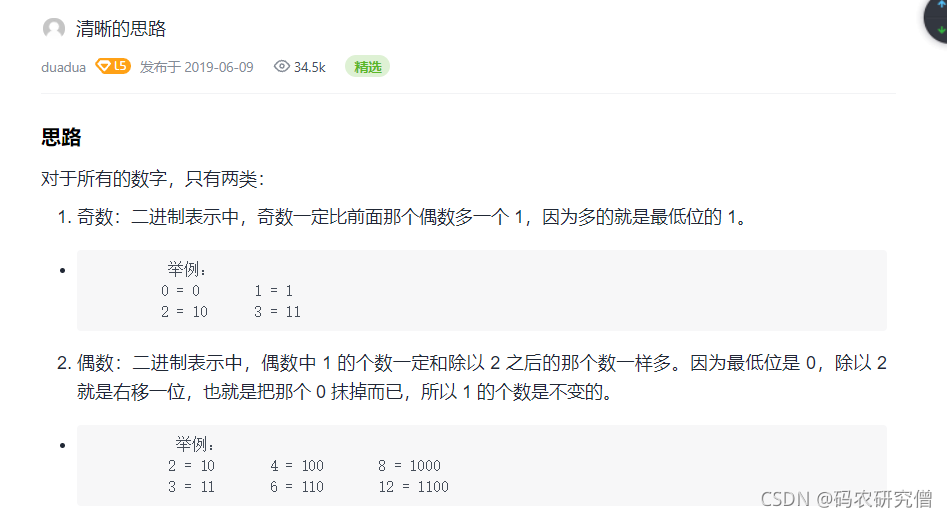
思路三:
运用奇偶数的判断
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] result = new int[n + 1];
result[0]=0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(i % 2 == 1)
{
result[i] = result[i-1] + 1;
}
else
{
result[i] = result[i/2];
}
}
return result;
}
}

