1. 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出:[0,1]
解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
输出:[1,2]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6
输出:[0,1]
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 104
-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
-109 <= target <= 109
只会存在一个有效答案
思路
为了不使用暴力遍历,减少多一次遍历的机会,可以使用map集合进行存储,通过target的减法操作
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
//Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer,Integer>map =new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i< nums.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[] {map.get(target-nums[i]),i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}
20. 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
示例 1:
输入:s = “()”
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = “()[]{}”
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:s = “(]”
输出:false
示例 4:
输入:s = “([)]”
输出:false
示例 5:
输入:s = “{[]}”
输出:true
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104
s 仅由括号 ‘()[]{}’ 组成
思路
通过哈希和栈的判断,具体一个字符串,取出一个个字符s.charAt(i);进行哈希存储,以及栈的配对key
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int n = s.length();
if (n % 2 == 1) {
return false;
}
Map<Character, Character> pairs = new HashMap<Character, Character>() {{
put(')', '(');
put(']', '[');
put('}', '{');
}};
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (pairs.containsKey(ch)) {
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != pairs.get(ch)) {
return false;
}
stack.pop();
} else {
stack.push(ch);
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
或者单独通过栈,而不要哈希的话
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();
for (char ch : charArray) {
//如果是左括号则直接入栈
if (ch == '(' || ch == '{' || ch == '[') {
stack.push(ch);
} else {
//如果是右括号,并且此时栈不为空
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
if (ch == ')') {
if (stack.pop() != '(')
return false;
} else if (ch == '}') {
if (stack.pop() != '{')
return false;
} else {
if (stack.pop() != '[')
return false;
}
}
else{ //此时栈为空,但却来了个右括号,也直接返回false
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
21. 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1: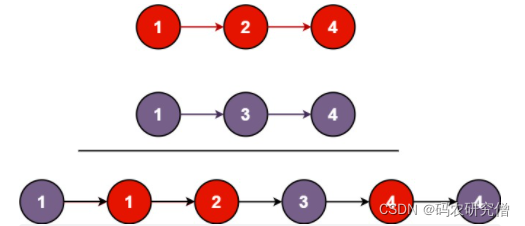
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
两个链表的节点数目范围是 [0, 50]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
l1 和 l2 均按 非递减顺序 排列
思路
通过递归遍历合并两个有序链表
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
} else if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
} else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
或者通过创建头节点进行遍历
遍历的同时,头节点 和l1 l2 的下一个位置移动
以及最后谁先结束 prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
最后返回的值是头结点的下一个next
通过创建一个头节点,以及头指针遍历
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = prehead;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
}
}
53. 最大子数组和
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
子数组 是数组中的一个连续部分。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
输出:6
解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1]
输出:1
示例 3:
输入:nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]
输出:23
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
进阶:如果你已经实现复杂度为 O(n) 的解法,尝试使用更为精妙的 分治法 求解
思路
通过动态规划的数组 存储大小值 进行判断
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int pre=0;
int max=nums[0];
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
pre=Math.max(pre+nums[i],nums[i]);
max=Math.max(pre,max);
}
return max;
}
}
70. 爬楼梯
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
示例 1:
输入:n = 2
输出:2
解释:有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
- 1 阶 + 1 阶
- 2 阶
示例 2:
输入:n = 3
输出:3
解释:有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
- 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
- 1 阶 + 2 阶
- 2 阶 + 1 阶
提示:
1 <= n <= 45
思路
通过动态归化,制定前面两个数初始值
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n==0)return 0;
if(n==1)return 1;
int []a=new int [n+1];
a[1]=1;
a[2]=2;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i-2];
}
return a[n];
}
}
或者通过滑动数组进行动态规划
class Solution {
public:
int climbStairs(int n) {
int p = 0, q = 0, r = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
p = q;
q = r;
r = p + q;
}
return r;
}
};
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
示例 1:
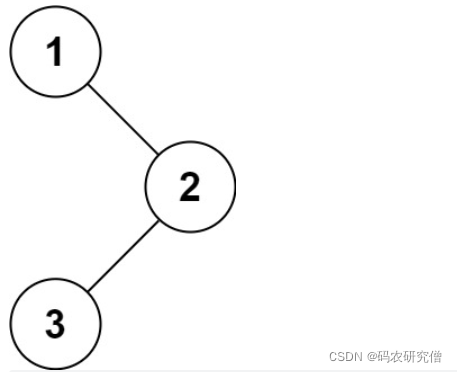
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
示例 4:
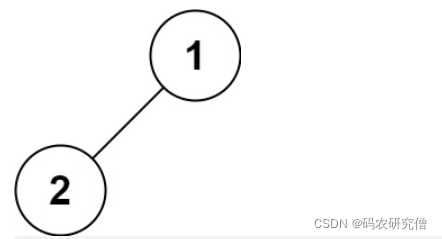
输入:root = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 5:
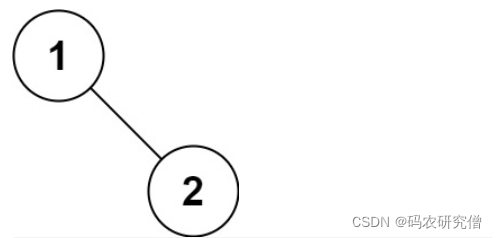
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:[1,2]
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
思路
通过递归的方式进行遍历
此处有一个注意事项,就是不能直接递归,要通过一个函数(传入集合),不然集合会重复创建
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, res);
}
}
或者通过构造栈的方式进行存储
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while (root != null || !stk.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
}
101. 对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
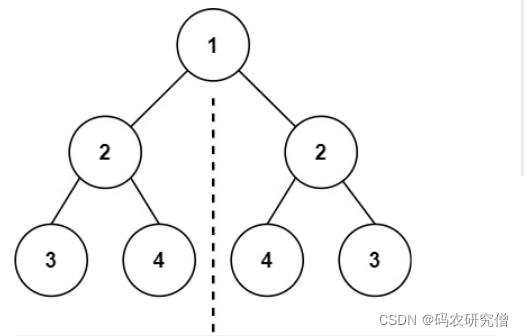
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2: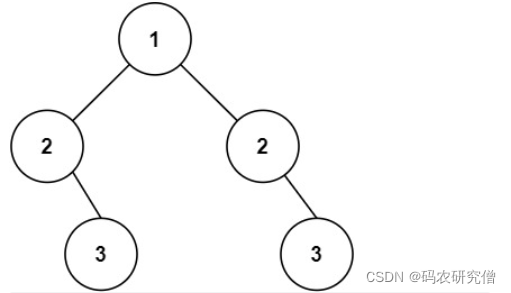
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [1, 1000] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶:你可以运用递归和迭代两种方法解决这个问题吗?
思路:
通过递归遍历的方式进行求解,左指针 右指针的递归遍历相同
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return ss(root,root);
}
public boolean ss(TreeNode L1,TreeNode L2){
if(L1==null&&L2==null) return true;
if(L1 ==null ||L2==null) return false;
return L1.val==L2.val && ss(L1.left,L2.right) && ss(L1.right,L2.left);
}
}
或者通过迭代的方式进行,主要通过队列的方式配对
队列Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
通过offer或者poll进行进出
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root, root);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode u, TreeNode v) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q.offer(u);
q.offer(v);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
u = q.poll();
v = q.poll();
if (u == null && v == null) {
continue;
}
if ((u == null || v == null) || (u.val != v.val)) {
return false;
}
q.offer(u.left);
q.offer(v.right);
q.offer(u.right);
q.offer(v.left);
}
return true;
}
}
104. 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],

返回它的最大深度 3 。
思路
通过深度优先遍历进行递归,判断左右的数字那个比较大,记得加上1即可
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}
通过队列的方法进行执行
队列调用一层,数量加1.
具体通过判断队列是否为空,内部判断队列尺寸是否为空(方便之后一层层移除)
这个递归比较难记忆,相对博主来说
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
int ans = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
size--;
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
}
121. 买卖股票的最佳时机
给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出:5
解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
示例 2:
输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
输出:0
解释:在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。
提示:
1 <= prices.length <= 105
0 <= prices[i] <= 104
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
说明:
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗?
136. 只出现一次的数字
示例 1:
输入: [2,2,1]
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: [4,1,2,1,2]
输出: 4
思路
思路一:
使用异或位运算
1.a⊕a=0
2.a⊕0=a
3.a⊕b⊕a=b⊕a⊕a=b⊕(a⊕a)=b⊕0=b
假设数组为1,1,2,2,3,4,4,5,5
1与0分别进行异或,即0与1异或为1,1与1异或为0
2与0分别进行异或,即0与2异或为2,2与2异或为0
3与0进行异或,即0与3进行异或为3
…
或者是1与1,2与2等分别进行异或均为0,0与3异或为3
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int temp=0;
for(int num:nums){
temp^=num;
}
return temp;
}
}
不使用for each结构,用for循环,需要标出数组下标
使用for each的耗时为1ms,使用for循环的耗时为2ms
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
nums[0]^=nums[i];
}
return nums[0];
}
}
思路二:
如果使用额外的空间实现而不是线性
可以先排序在暴力遍历
此处需要从下标1开始,单独在for内部循环讨论为0的特殊情况
耗时8ms
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i=1; i<nums.length; i++) {
if(i == 0 && nums[i] != nums[i+1]
|| i == (nums.length-1) && nums[i] != nums[i-1]
|| nums[i-1] != nums[i] && nums[i] != nums[i+1])
return nums[i];
}
return nums[0];
或者使用另一种暴力遍历的条件
耗时9ms
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i=0; i<nums.length-1; ) {
if( nums[i] != nums[i+1])
return nums[i];
else i=i+2;
}
return nums[nums.length-1];
}
}
思路三:
使用哈希表
本身遍历nums的数组,其 value为nums 的值而不是下标
get(value)因为还是哈希表,还未添加,所以获取其下标元素的时候都是null
即判断是否为null,如果为null则赋值为1,如果不为null,也就是get(value)已经添加一些值上去,所以count++
最后一一添加进入map
之后通过KeySet进行遍历map的key值
最后判断key值中value是否为1就可以
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer value : nums) {
Integer count = map.get(value);
count = count == null ? 1 : ++count;
map.put(value, count);
}
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
Integer count = map.get(key);
if (count == 1) {
return key;
}
}
return -1; // can't find it.
}
}
或者是这种写法
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer i=0;i<nums.length;i++) {
Integer value=map.get(nums[i]);
if(value!=null)value++;
else value=1;
map.put(nums[i],value);
}
for (Integer key : map.keySet()) {
if (map.get(key) == 1) {
return key;
}
}
return -1; // can't find it.
}
}
或者是这种写法(区分集合遍历,map转换set怎么遍历)
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer i=0;i<nums.length;i++) {
Integer value=map.get(nums[i]);
if(value!=null)value++;
else value=1;
map.put(nums[i],value);
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() == 1) {
return entry.getKey();
}
}
return -1; // can't find it.
}
}
141. 环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1: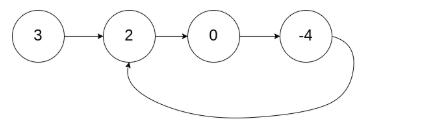
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
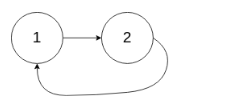
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 104]
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos 为 -1 或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
思路一:
使用哈希表进行遍历
用add或者是contains的结合
链表中的大维度,整体条件还是head!=null
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (!set.add(head)) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
或者
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (set.contains(head)) {
return true;
}else set.add(head);
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}
链表与数组查重很相似
可查看我上一篇写过的文章
【leetcode】数组-寻找重复数
思路二:
快慢指针的遍历
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}
思路三:
快慢指针
同一起点但是不一样速度
最后如果能碰面说明有环
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
160. 相交链表
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
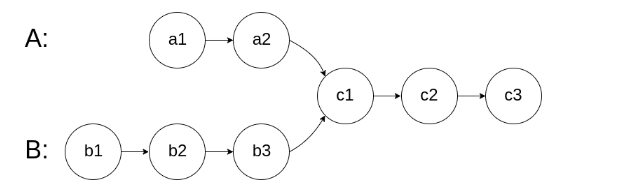
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
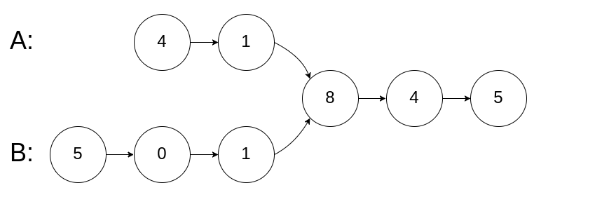
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2: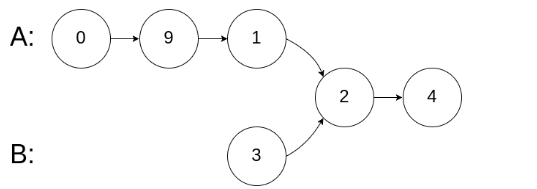
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3: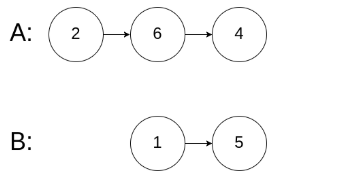
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
1.思路一:
暴力解法,逐一进行遍历,也就是O(mn)
遍历链表注意 while循环的条件,以及初始条件
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode A1=headA;
while(A1!=null){
ListNode A2=headB;
while(A2!=null){
if(A1==A2){
return A1;
}else{
A2=A2.next;
}
}
A1=A1.next;
}
return null;
}
}
这个ListNode A2=headB;必须卸载中间嵌套的循环里,初始化原来的位置,要么if前,要么if/else后,记得不要落下
2.思路二:
用两个双指针进行判断,不是则next
长度不同时,将短的一条链并入到另一条链的开头
因为a+c+b=b+c+a
因为要保证上面的公式,所以某一端为空的时候,指针要续上。
而且即使不相交 链也不想等,这样子相等为空的时候也是直接为null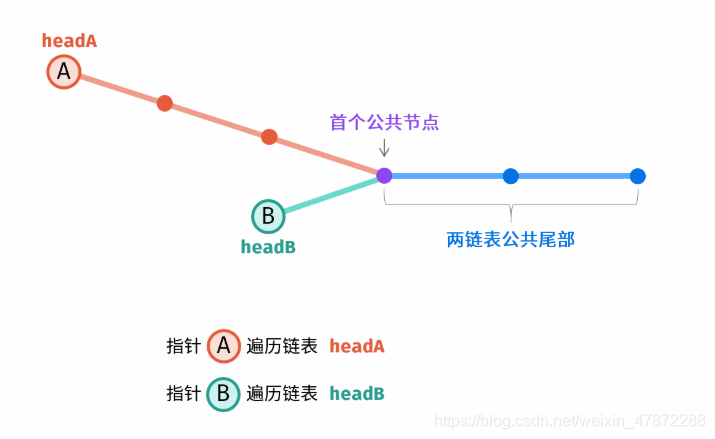
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode A1=headA;
ListNode A2=headB;
while(A1!=A2){
if(A1!=null){
A1=A1.next;
}else{
A1=headB;
}
if(A2!=null){
A2=A2.next;
}else{
A2=headA;
}
}
return A1;
}
}
思路三:
通过哈希表的判断
使用HashSet
注意大小写
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> set =new HashSet<>();
while(headA!=null){
set.add(headA);
headA=headA.next;
}
while(headB!=null){
if(set.contains(headB)){
return headB;
}else{
headB=headB.next;
}
}
return null;
}
}
3.总结:
判断两个指针是否相等而不是判断两个链表中的值是否相等
做链表题的时候,区分头结点是否有无意义,以及在算法前,记得判断特殊状态
169. 多数元素
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数 大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。
示例 1:
输入:[3,2,3]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:[2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
输出:2
进阶:
尝试设计时间复杂度为 O(n)、空间复杂度为 O(1) 的算法解决此问题。
思路一:
利用排序,出现多数的元素一定在n/2.
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length / 2];
}
}
思路二:
利用哈希表的map进行查找遍历
刚开始的伪代码 主要如下:(但是不通过)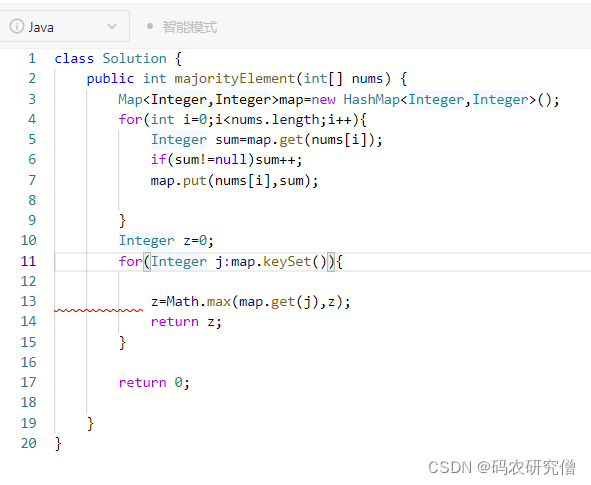
正确代码如下:
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counts = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (!counts.containsKey(num)) {
counts.put(num, 1);
} else {
counts.put(num, counts.get(num) + 1);
}
}
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> majorityEntry = null;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
if (majorityEntry == null || entry.getValue() > majorityEntry.getValue()) {
majorityEntry = entry;
}
}
return majorityEntry.getKey();
}
}
具体map函数用法可查看我上一篇文章
java之map函数详细分析(全)
206. 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1: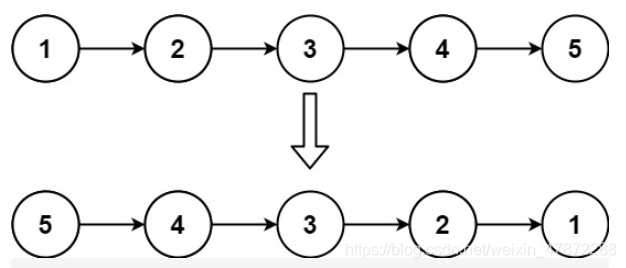
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
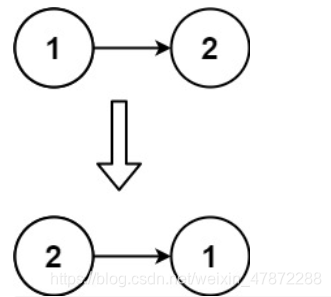
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 5000]
-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
1.思路一:
ListNode rear可以在任何时刻定义
也可直接使用ListNode rear=cur.next;
返回的是pre指针,而不是cur指针也不是head指针
具体的逻辑思路如下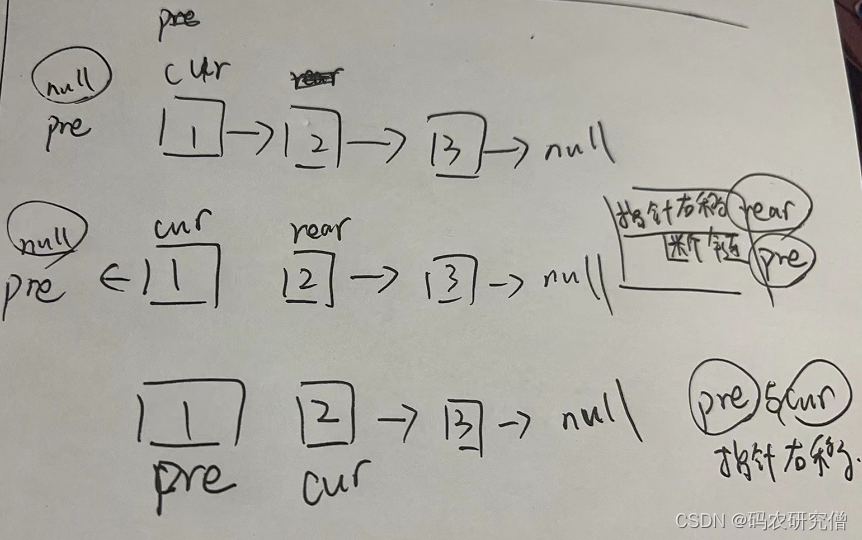
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur=head,pre=null;
ListNode rear;
while(cur!=null){
rear=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=rear;
}
return pre;
}
}
中途的错误做法:
只截取上面片段代码作为讲解:
将rear=cur.next;放在while里面最后定义,rear已经越界了
ListNode cur=head,pre=null;
ListNode rear;
while(cur!=null){
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=rear;
rear=cur.next;
}
2.思路二:
使用递归的条件进行反转
递这个用法用在了层层递进
归这个用法用在了每一层的特殊情节,也就是两个链表地址空间的反转
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 1. 递归终止条件
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newhead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newhead;
}
226. 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树
示例:
输入:

输出:
备注:
这个问题是受到 Max Howell 的 原问题 启发的 :
谷歌:我们90%的工程师使用您编写的软件(Homebrew),但是您却无法在面试时在白板上写出翻转二叉树这道题,这太糟糕了。
思路一:
java代码
使用递归思路
将其左右子树的next反转即可
终止条件是子树没有
这种递归是从下往上
代码为
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return null;
TreeNode l=invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode r=invertTree(root.right);
root.left=r;
root.right=l;
return root;
}
}
从上往下的递归为
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
//递归函数的终止条件,节点为空时返回
if(root==null) {
return null;
}
//下面三句是将当前节点的左右子树交换
TreeNode tmp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = tmp;
//递归交换当前节点的 左子树
invertTree(root.left);
//递归交换当前节点的 右子树
invertTree(root.right);
//函数返回时就表示当前这个节点,以及它的左右子树
return root;
}
}
此处讲解一下js代码的思路
js代码可以有特殊的结构(结构赋值)
var invertTree = function(root) {
if(root !== null){
[root.left, root.right] = [invertTree(root.right), invertTree(root.left)]
}
return root
};
234. 回文链表
----中等难度----
3. 无重复字符的最长子串
给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长子串 的长度。
示例 1:
输入: s = “abcabcbb”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “abc”,所以其长度为 3。
示例 2:
输入: s = “bbbbb”
输出: 1
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “b”,所以其长度为 1。
示例 3:
输入: s = “pwwkew”
输出: 3
解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 “wke”,所以其长度为 3。
请注意,你的答案必须是 子串 的长度,“pwke” 是一个子序列,不是子串。
示例 4:
输入: s = “”
输出: 0
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
s 由英文字母、数字、符号和空格组成
思路一:
无重复 可以使用哈希表
最长子串,还需要使用Math.max进行筛查比对
注意事项
-
字符串是1-n,而数组是0到n-1
字符串变成数组的时候,下标应该是0到n-1
因为运用到了charAt这个函数 -
使用两边循环,出内层循环,就删除一个字母,从下一个开始,可以使用set.remove(特定字母)
而且删除的时候应该是删除上一次的字母,所以是i-1 -
返回最大值的时候,右指针减左指针还要加1,比如12345,5-1=4,其实是有5个数字,所以还要加上自已,也就是多加一个1
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Set <Character> set =new HashSet<>();
int n=s.length();
int sum=0,right=-1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i!=0){
set.remove(s.charAt(i-1));
}
while(right+1<n&&!set.contains(s.charAt(right+1))){
set.add(s.charAt(right+1));
right++;
}
sum=Math.max(sum,right-i+1);
}
return sum;
}
}
或者通过如下,rk加1之后发现不满足,也就是(0,n-1),rk为(0,n-1)。最后发现
abcabcbb为 下标0123457,也就是rk为下标3了(下标3为a不满足)i为0,所以最大值为3-0
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Set <Character>set=new HashSet<>();
int n=s.length();
int rk=0,ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i!=0){
set.remove(s.charAt(i-1));
}
while(rk<n && !set.contains(s.charAt(rk))){
set.add(s.charAt(rk));
rk++;
}
ans=Math.max(ans,rk-i);
}
return ans;
}
}
上面的思路是通过set集合
下面代码通过hashmap集合
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if (s.length()==0) return 0;
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
int max = 0;
int left = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i ++){
if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))){
left = Math.max(left,map.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1);
}
map.put(s.charAt(i),i);
max = Math.max(max,i-left+1);
}
return max;
}
}
11. 盛最多水的容器
题目:
给定一个长度为 n 的整数数组 height 。有 n 条垂线,第 i 条线的两个端点是 (i, 0) 和 (i, height[i]) 。
找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
返回容器可以储存的最大水量。
说明:你不能倾斜容器。
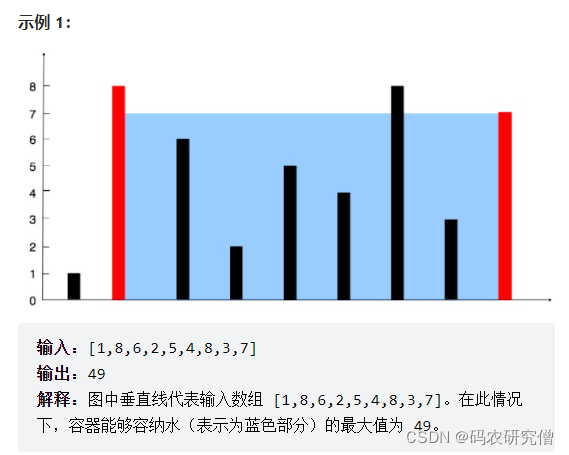
示例 2:
输入:height = [1,1]
输出:1
提示:
n == height.length
2 <= n <= 105
0 <= height[i] <= 104
思路就是利用双指针
通过判定左右指针哪个比较小,存取其最大值。
具体移动可以通过左右指针的长度进行判定
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int l=0;
int r=height.length-1;
int res=0,ans=0;
while(l<r){
res=Math.min(height[l],height[r])*(r-l);
ans=Math.max(res,ans);
if(height[l]<=height[r]){
l++;
}
else{
r--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
题目:
整数数组 nums 按升序排列,数组中的值 互不相同 。
在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 <= k < nums.length)上进行了 旋转,使数组变为 [nums[k], nums[k+1], …, nums[n-1], nums[0], nums[1], …, nums[k-1]](下标 从 0 开始 计数)。例如, [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 在下标 3 处经旋转后可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] 。
给你 旋转后 的数组 nums 和一个整数 target ,如果 nums 中存在这个目标值 target ,则返回它的下标,否则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
输出:4
示例 2:
输入:nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
输出:-1
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1], target = 0
输出:-1
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 5000
-104<= nums[i] <= 104
nums 中的每个值都 独一无二
题目数据保证 nums 在预先未知的某个下标上进行了旋转
-104 <= target <= 104
进阶:你可以设计一个时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的解决方案吗?
思路:
具体思路可以通过二分查找
具体的逻辑思路可以参照官方的解释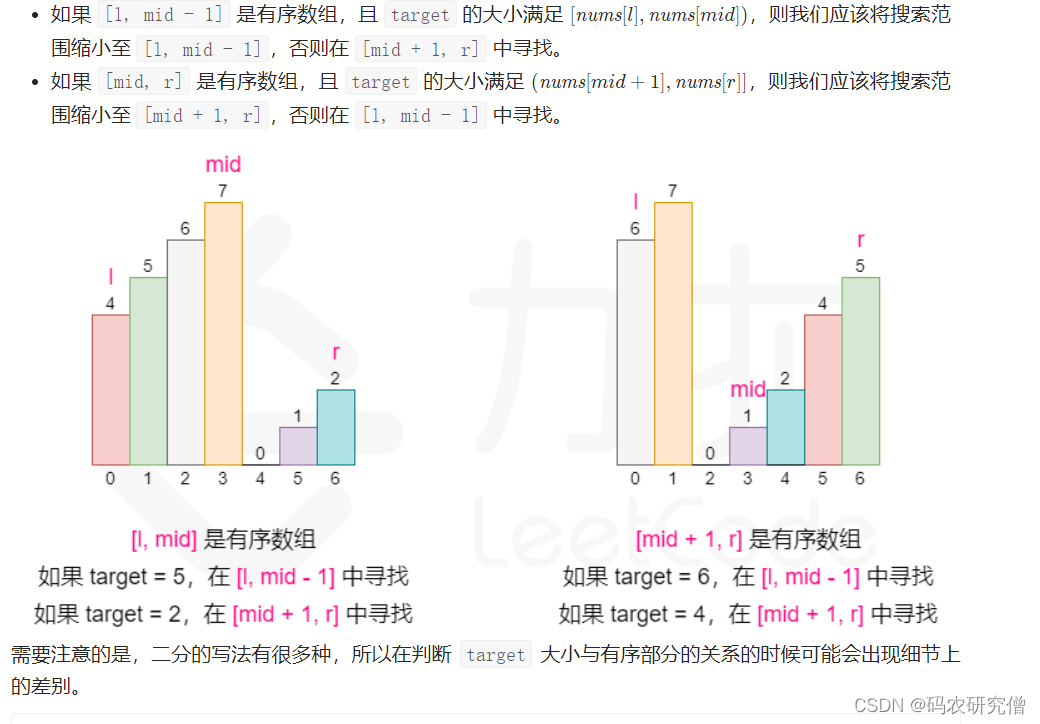
以下代码注意两个事项:
一个是左右边界的值,等于号要注意
一个是刚开始的临界条件,要先行判断
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int n=nums.length;
if (n == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (n == 1) {
return nums[0] == target ? 0 : -1;
}
int l=0;
int r=n-1;
while(l<=r){
int mid=(l+r)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target)return mid;
if(nums[0]<=nums[mid]){
if(nums[0]<=target&&target<nums[mid]){
r=mid-1;
}else l=mid+1;
}else {
if(nums[mid]<target&&target<=nums[n-1]){
l=mid+1;
}else r=mid-1;
}
}
return -1;
}
}

