
题目
剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。
你可以以任意顺序返回这个字符串数组,但里面不能有重复元素。
示例:
输入:s = “abc”
输出:[“abc”,“acb”,“bac”,“bca”,“cab”,“cba”]
限制:
1 <= s 的长度 <= 8
思路
既然不能有重复的字符串,那么我们可以将原始字符串(长度为n)分解为一个个的字符(会有k个不同字符,k<=n),然后我们设想给每个字符有一个箱子装着备用(将原始字符串拆成一个个字符放到对应字符的箱子里),而组装新的字符串的过程可以看为现在有我从箱子里拿字符放到新字符串的一个个空位上(总共n个空位),比如放第一个字符空位的时候,我可以从每种不同箱子里拿一个字符放进第一个字符空位,而放了这个之后我剩下的字符继续按这个步骤往里面放即可。
我们需要注意在每一个空位,遍历放每种可用字符时,我们用的是数组保存这些信息,字符剩余个数和当前正在组装的字符数组是会变化的,因此每次继续下一个空位的时候在后续回溯要恢复状态。
至于为什么有个评估结果个数的函数,熟悉源码的同学应该知道,ArrayList默认容量是10,每次扩容需要移动元素,而这里做这种排列结果会非常多,因此会有不必要的对数组扩容,扩容时又需要拷贝已经存在数组的所有元素,做了不必要的拷贝,因此直接预估出一个近似的容量值来避免掉不断的扩容。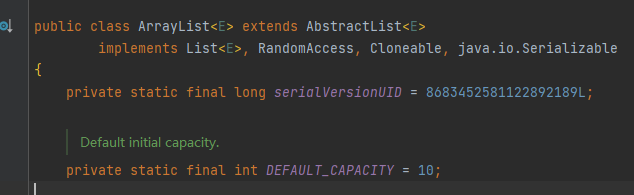
容量增长函数我们可以看到java源码里是增长1.5倍
oldCapacity>>1是相当于除以2,位运算更快。

代码
提交的代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public String[] permutation(String s) {
//提取字符和个数
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(s.length());
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
Integer count = map.get(c);
if (count == null) {
count = 1;
} else {
count += 1;
}
map.put(c, count);
}
Character[] key = map.keySet().toArray(new Character[0]);
Integer[] value = map.values().toArray(new Integer[0]);
char[] chars = new char[key.length];
for (int i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
chars[i] = key[i];
}
int[] counts = new int[value.length];
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
counts[i] = value[i];
}
//预估量避免arraylist因为扩容做太多不必要扩容操作
int initialSize = estimateSize(s.length(), counts);
//创建容器
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(initialSize);
//深搜遍历可能的组合
dfs(chars, counts, list, new char[s.length()], 0);
return list.toArray(new String[0]);
}
/**
* @param chars 字符数组
* @param counts 可用个数数组
* @param list 最后的list
* @param ret 生成的字符顺序数组
* @param size 已生成了多少个了
*/
public void dfs(char[] chars, int[] counts, List<String> list, char[] ret, int size) {
if (size == ret.length) {
//出口
String s = new String(ret);
list.add(s);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (counts[i] > 0) {
//有字符可用
ret[size] = chars[i];
counts[i] = counts[i] - 1;
dfs(chars, counts, list, ret, size + 1);
counts[i] = counts[i] + 1;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 粗略评估个数,以减少数组扩容
*
* @param len
* @param counts
* @return
*/
public int estimateSize(int len, int[] counts) {
int ret = 1;
int[] newCounts = new int[counts.length];
System.arraycopy(counts, 0, newCounts, 0, newCounts.length);
int distinctCharCount = newCounts.length;
//不乘以第一次的
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int index = -1, lastCharCount = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < distinctCharCount; j++) {
int t = newCounts[j];
if (t > 0) {
lastCharCount++;
if (index == -1) {
index = j;
}
}
}
newCounts[index] = newCounts[index] - 1;
ret *= lastCharCount;
}
ret = Math.max(ret, 16);
return ret;
}
}
解题时调试的代码
需要junit支持,maven项目,idea编辑器
将log成员变量设置为true即可打印遍历和组装新字符串过程。
package leetcode.offer.q38;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。
* <p>
*
* <p>
* 你可以以任意顺序返回这个字符串数组,但里面不能有重复元素。
* <p>
*
* <p>
* 示例:
* <p>
* 输入:s = "abc"
* 输出:["abc","acb","bac","bca","cab","cba"]
*
* <p>
* 限制:
* <p>
* 1 <= s 的长度 <= 8
* <p>
* 来源:力扣(LeetCode)
* 链接:https:///problems/zi-fu-chuan-de-pai-lie-lcof
* 著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
*
* @author humorchen
* @date 2022/2/9 15:16
*/
public class Solution {
private boolean log = false;
@Test
public void testDfs() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c'}, new int[]{1, 1, 1}, list, new char[3], 0);
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
@Test
public void testPermutation() {
String[] ret = permutation("abc");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ret));
System.out.println("实际个数:" + ret.length);
}
public String[] permutation(String s) {
//提取字符和个数
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(s.length());
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
Integer count = map.get(c);
if (count == null) {
count = 1;
} else {
count += 1;
}
map.put(c, count);
}
Character[] key = map.keySet().toArray(new Character[0]);
Integer[] value = map.values().toArray(new Integer[0]);
char[] chars = new char[key.length];
for (int i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
chars[i] = key[i];
}
int[] counts = new int[value.length];
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
counts[i] = value[i];
}
//预估量避免arraylist因为扩容做太多不必要扩容操作
int initialSize = estimateSize(s.length(), counts);
//创建容器
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(initialSize);
//深搜遍历可能的组合
dfs(chars, counts, list, new char[s.length()], 0);
return list.toArray(new String[0]);
}
/**
* @param chars 字符数组
* @param counts 可用个数数组
* @param list 最后的list
* @param ret 生成的字符顺序数组
* @param size 已生成了多少个了
*/
public void dfs(char[] chars, int[] counts, List<String> list, char[] ret, int size) {
if (size == ret.length) {
//出口
String s = new String(ret);
if (log) {
System.out.printf("生成了字符串:");
System.out.println(s);
}
list.add(s);
} else {
if (log) {
System.out.println("\n\n传入的参数:");
for (char c : chars) {
System.out.printf(c + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int i : counts) {
System.out.printf(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("已经生成的:" + Arrays.toString(ret) + " (" + size + ")");
}
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (counts[i] > 0) {
//有字符可用
ret[size] = chars[i];
counts[i] = counts[i] - 1;
if (log) {
System.out.println("第" + (size + 1) + "位使用了字符 " + chars[i] + "使用后生成的:" + Arrays.toString(ret) + " (" + (size + 1) + ")");
}
dfs(chars, counts, list, ret, size + 1);
counts[i] = counts[i] + 1;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 粗略评估个数,以减少数组扩容
*
* @param len
* @param counts
* @return
*/
public int estimateSize(int len, int[] counts) {
int ret = 1;
int[] newCounts = new int[counts.length];
System.arraycopy(counts, 0, newCounts, 0, newCounts.length);
int distinctCharCount = newCounts.length;
//不乘以第一次的
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// max 哪个字符还有最多多少个,maxIndex 字符下标,lastCharCount 还有多少个没有被使用的字符
int index = -1, lastCharCount = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < distinctCharCount; j++) {
int t = newCounts[j];
if (t > 0) {
lastCharCount++;
if (index == -1) {
index = j;
}
}
}
newCounts[index] = newCounts[index] - 1;
System.out.print("乘以:" + lastCharCount + " ");
System.out.println();
ret *= lastCharCount;
}
System.out.println("评估可能性个数:" + ret);
ret = Math.max(ret, 16);
System.out.println("最终评估结果:" + ret);
return ret;
}
}
结果


