一、项目初始化
二、路由配置规则
path:配置路由访问的路径
name:给路由起名字(命名路由)
component:访问路由时,渲染的组件
{
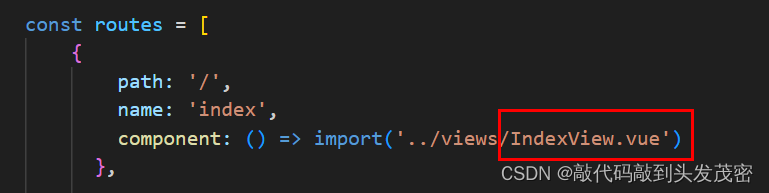
path: '/',
name: 'index',
component: () => import('../views/IndexView.vue')
},
App.vue
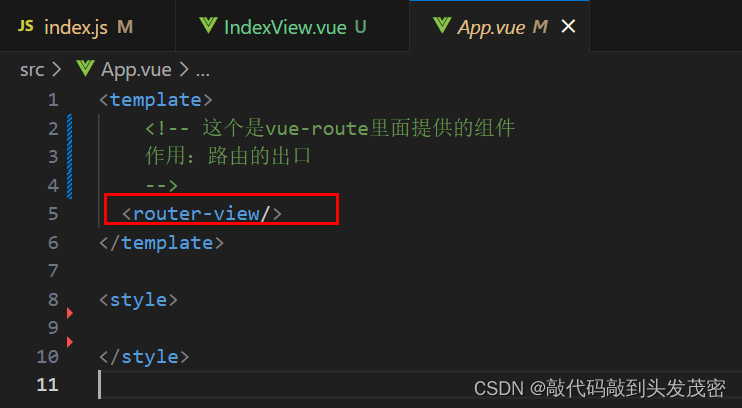
vue-route标签作用:路由匹配到的组件将渲染到这里
这个是vue-route里面提供的组件
作用:路由的出口
<template>
<router-view/>
</template>
举例:当我访问根路由时会渲染IndexView.vue组件
IndexView.vue中的内容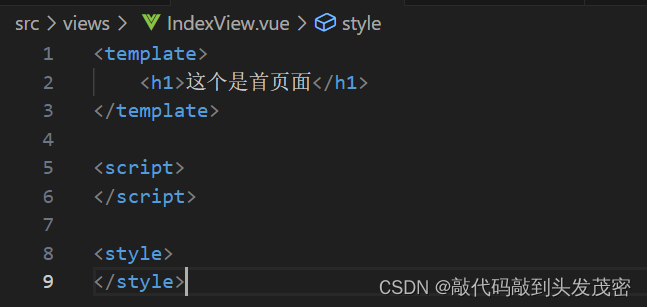
而IndexView.vue中的内容会在根组件下的<router-view/>中展示
router-link标签作用:路由导航(路由跳转的链接)
三、声明式导航和编程式导航
声明式导航
<router-link to="/login"></router-link>
<router-link :to="{path:'/login'}"></router-link>
编程式导航
推荐使用路由的名字进行跳转,不推荐直接写路径
<!-- 编程式导航 -->
<button @click='$router.push("/login")'>登录按钮</button>
<br>
<button @click='$router.push({"path":"/login"})'>登录按钮</button>
<br>
<button @click='$router.push({"name":"login"})'>登录按钮</button>
<br>
<button @click='$router.push({"name":"login"})'>登录按钮</button>
<br>
<button @click="loginBtn">登录按钮1</button>
</template>
<script>
export default{
methods:{
loginBtn(){
this.$router.push('/login');
}
}
}
</script>
通过调用app.use(router),我们可以在任意组件中以this.$router的形式访问它,并且以this.$router的形式访问当前路由
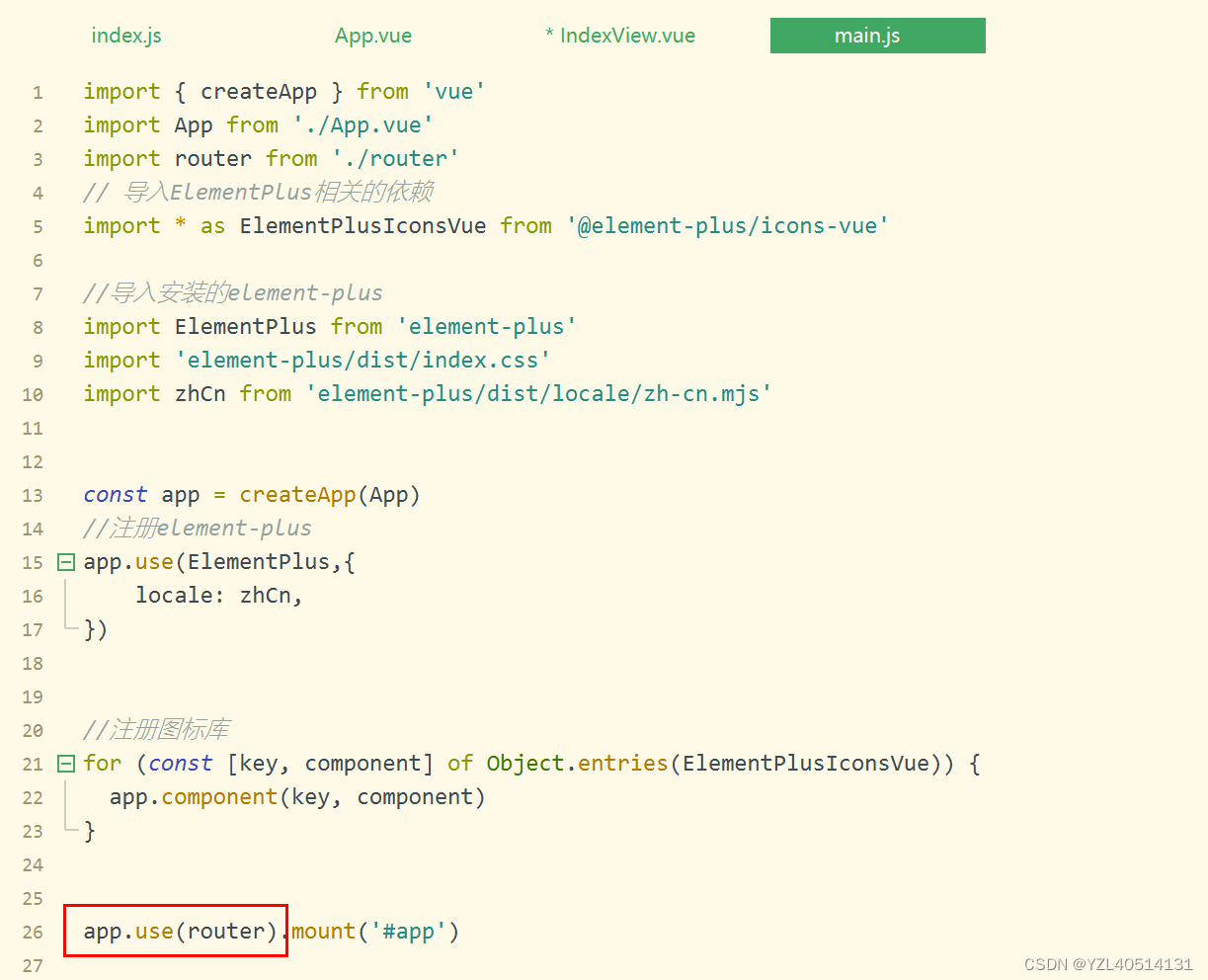
路由命名:推荐使用路由的名字进行跳转,不推荐直接写路径,主要是为了好维护、好管理。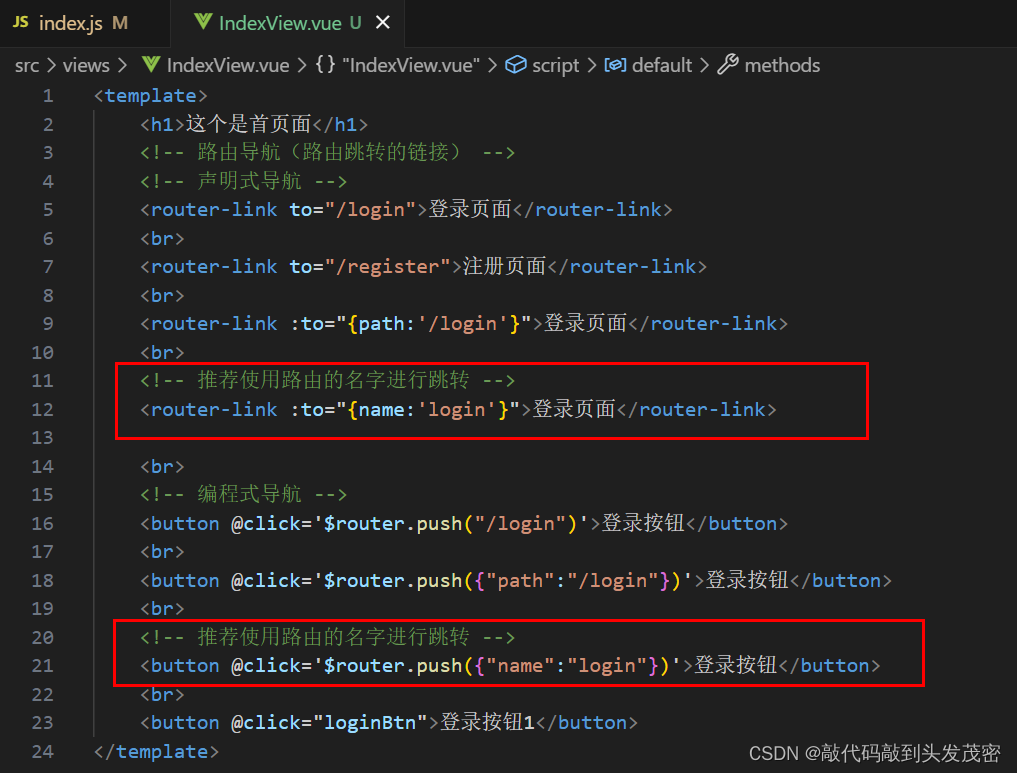
四、路由重定向
当访问http://localhost:8080/#/project这个路由
会跳转到http://localhost:8080/#/login这个路由
{
path: '/project',
name:'project',
// 路由重定向配置
redirect:{
name:'login',
}
},
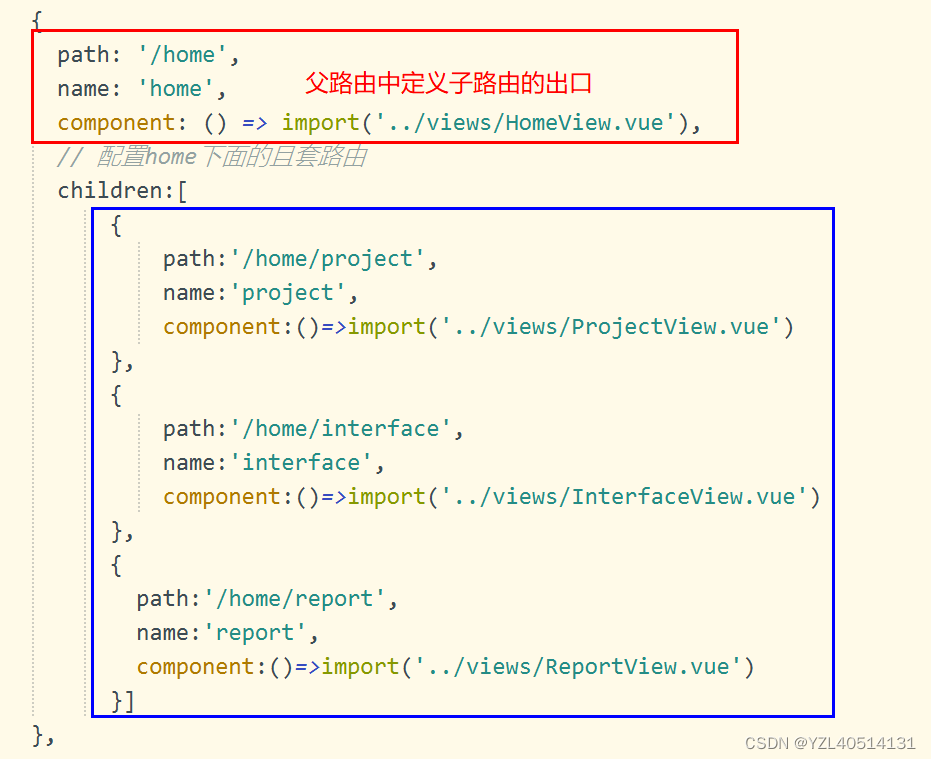
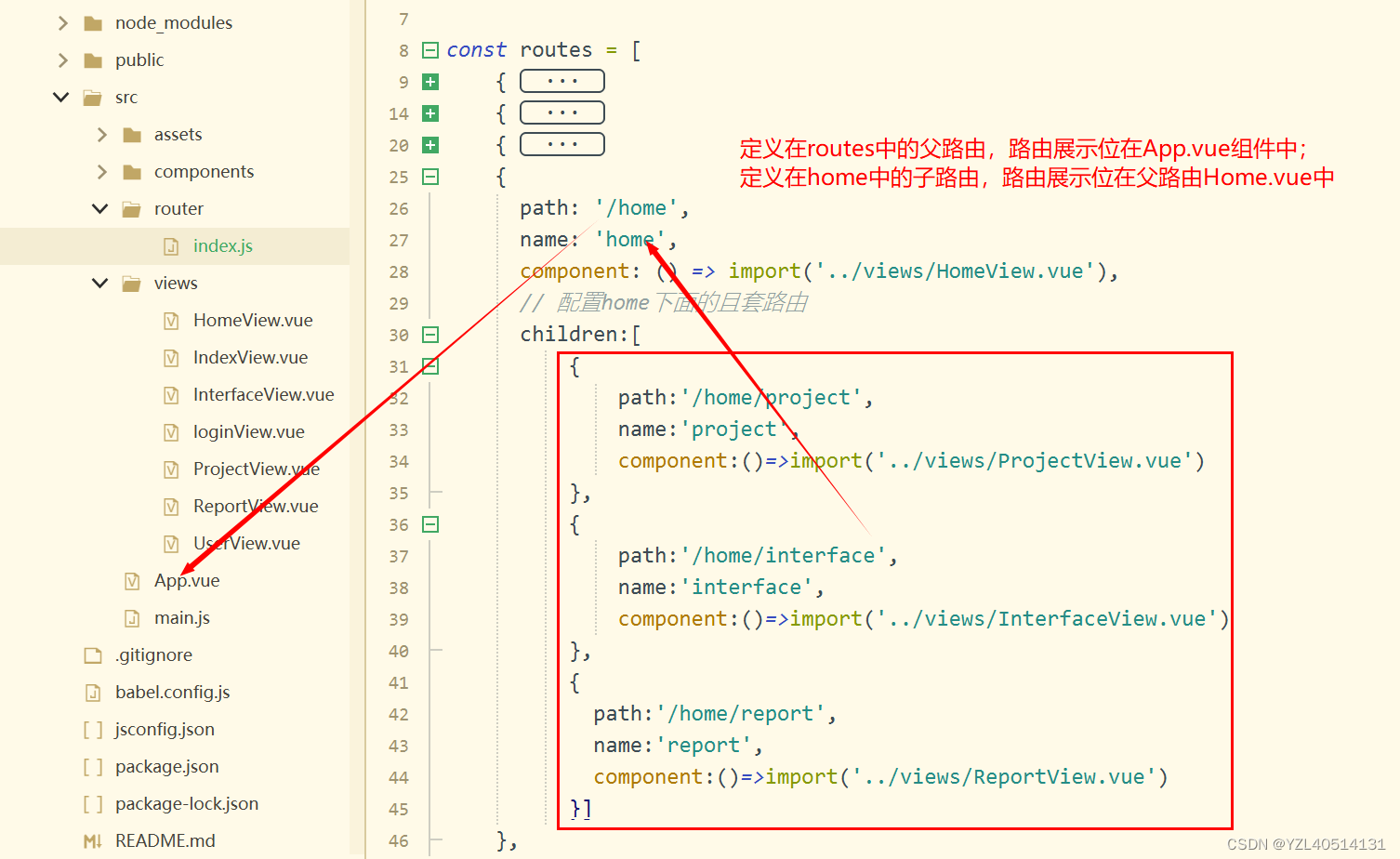
五、嵌套路由
index.js:路由配置
{
path: '/home',
name: 'home',
component: () => import('../views/HomeView.vue'),
// 配置home下面的且套路由
children:[
{
path:'/home/project',
name:'project',
component:()=>import('../views/ProjectView.vue')
},
{
path:'/home/interface',
name:'interface',
component:()=>import('../views/InterfaceView.vue')
},
{
path:'/home/report',
name:'report',
component:()=>import('../views/ReportView.vue')
}]
},
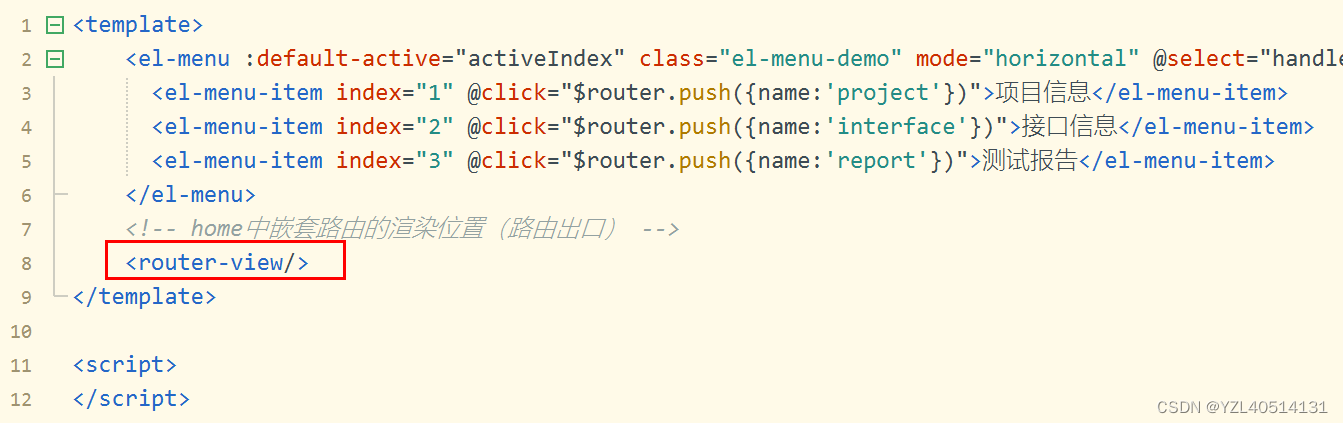
HomeView.vue组件
<template>
<el-menu :default-active="activeIndex" class="el-menu-demo" mode="horizontal" @select="handleSelect">
<el-menu-item index="1" @click="$router.push({name:'project'})">项目信息</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="2" @click="$router.push({name:'interface'})">接口信息</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="3" @click="$router.push({name:'report'})">测试报告</el-menu-item>
</el-menu>
<!-- home中嵌套路由的渲染位置(路由出口) -->
<router-view/>
</template>
<script>
</script>
<style>
</style>
特别注意
把不变的内容写到父路由中,并且父路由中预留路由展示位。将变化的内容写到子路由中
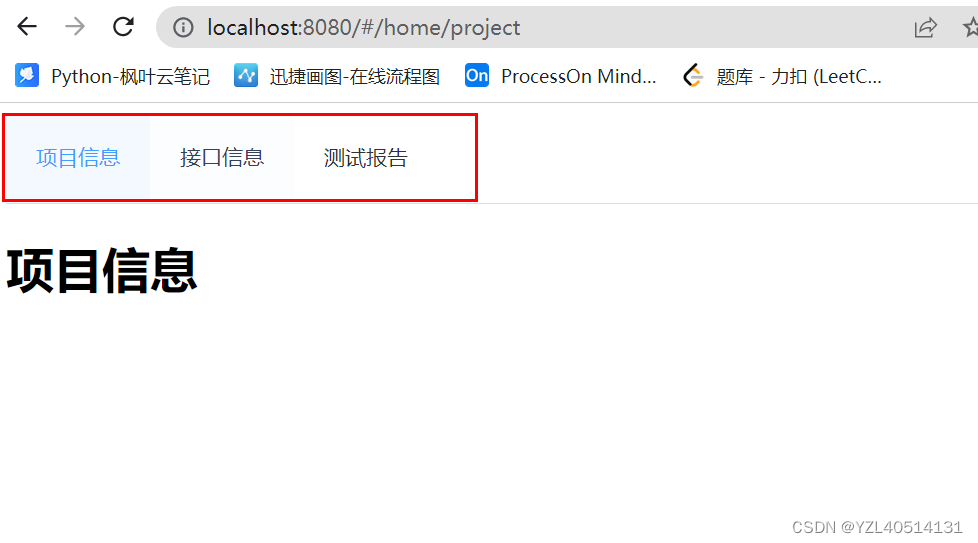
总结
定义在routes下的路由,路由出口在App.vue中
定义在home路由下的子路由,路由出口在HomeView.vue中
六、路由参数动态匹配
{
path:'/user/:id',
name:'user',
component: () => import('../views/UserView.vue')
},
访问路由:http://localhost:8080/#/user/666
UserView.vue组件
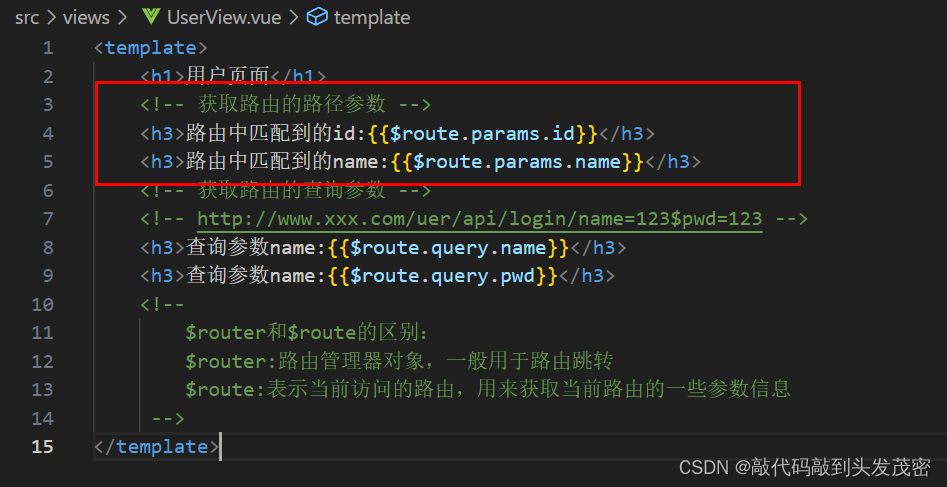
获取路由的路径参数
<template>
<h1>User页面</h1>
<!-- 获取路由的路径参数 -->
<h3>路由中匹配的id:{{$route.params.id}}</h3>
</template>
<script>
</script>
<style>
</style>
路由配置: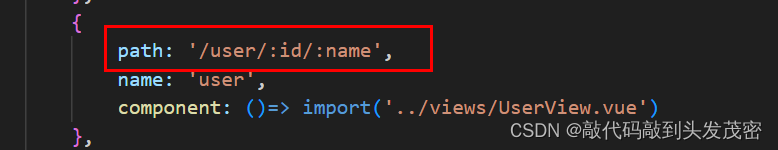
访问路由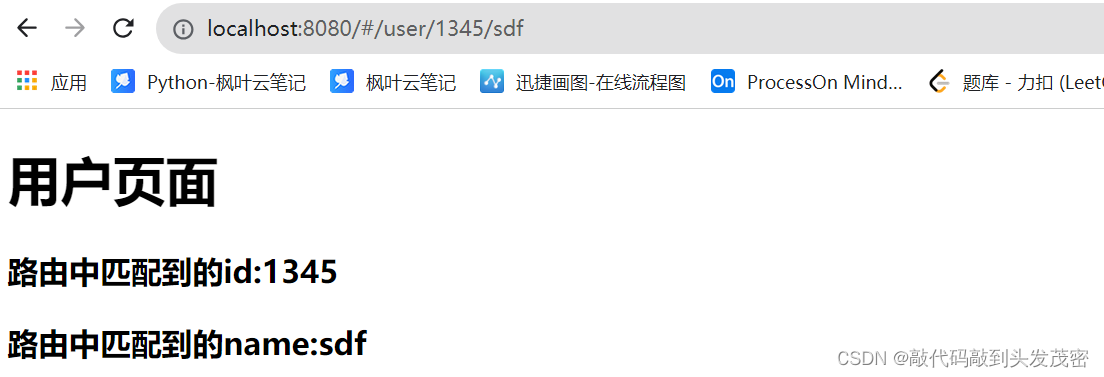
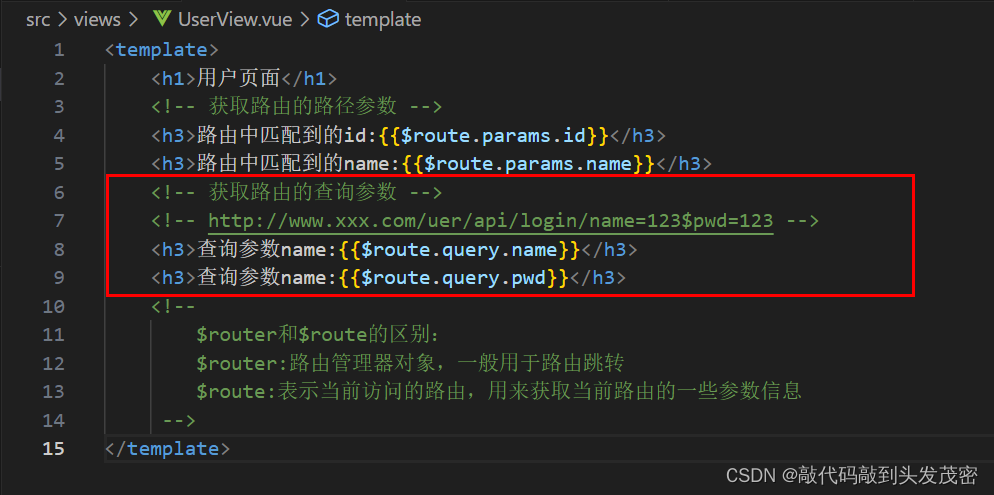
获取路由的查询参数
http://localhost:8080/#/user/666?name=kobe
<template>
<h1>User页面</h1>
<!-- 获取路由的查询参数 -->
<h4>查询参数name:{{$}}</h4>
</template>
<script>
</script>
<style>
</style>
访问路由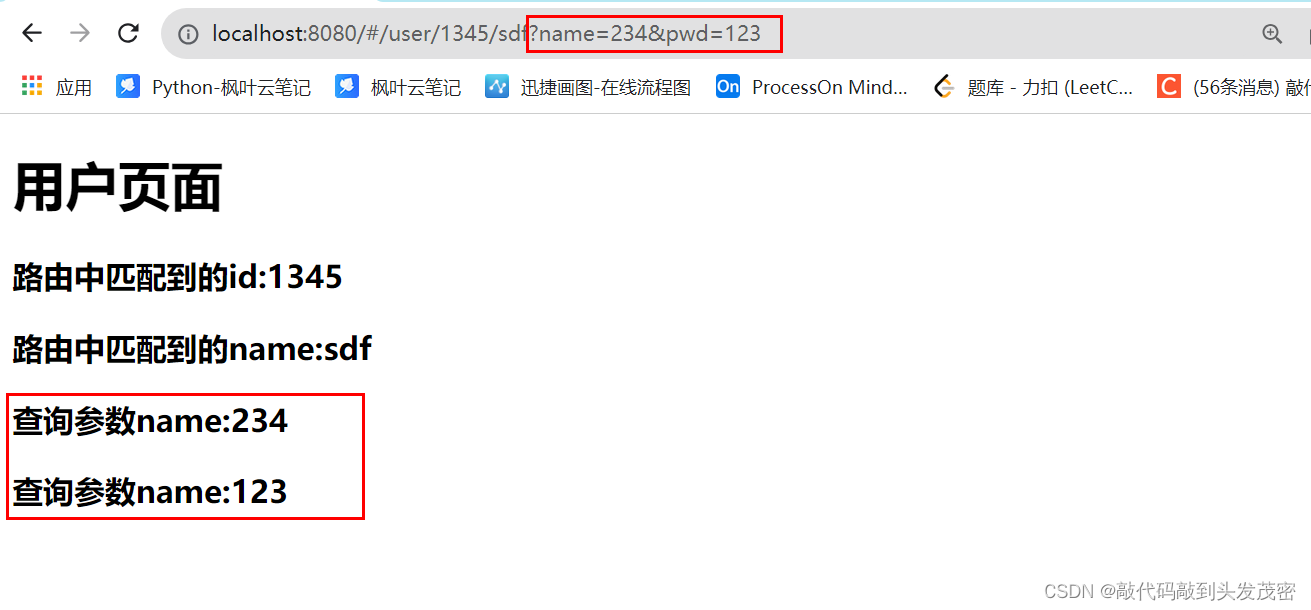
特别注意
$router和$route的区别:$router:路由管理器对象,一般用于路由跳转$route:表示当前访问的路由,用来获取当前路由参数的一些信息
七、导航跳转时传递路由参数
params:路径参数
query:查询参数
<router-link :to="{name:'user',params:{id:888},query:{name:111}}">user页面</router-link>
<button @click="$router.push({name:'user',params:{id:666},query:{name:222}})">user按钮</button>
路径参数:需要在路由中配置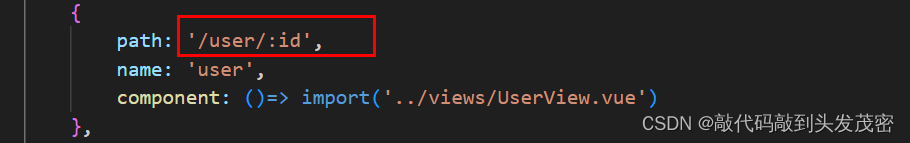
查询参数不需要配置
八、路由导航守卫
设置路由导航守卫(控制前端的路由访问权限)
router.beforeEach(async (to, from) => {
/*
1、判断用户是否登录
1.1从本地获取用户身份信息(存储在cookie或者localstroge中的token,session)
window.cookieStore.get('token')
window.localStorage.getItem('token')
window.sessionStore.getItem('token')
1.2验证token是否有效
*/
// const isAuthenticated=true
// if (
// // 检查用户是否已登录
// !isAuthenticated &&
// // ❗️ 避免无限重定向
// !== 'Login'
// ) {
// // 将用户重定向到登录页面
// return { name: 'Login' }
// }
// })
})

