一、Spring Data Redis
1.1、缓存功能
1.1.1、分析
使用 redis 作为缓存, MySQL 作为数据库组成的架构
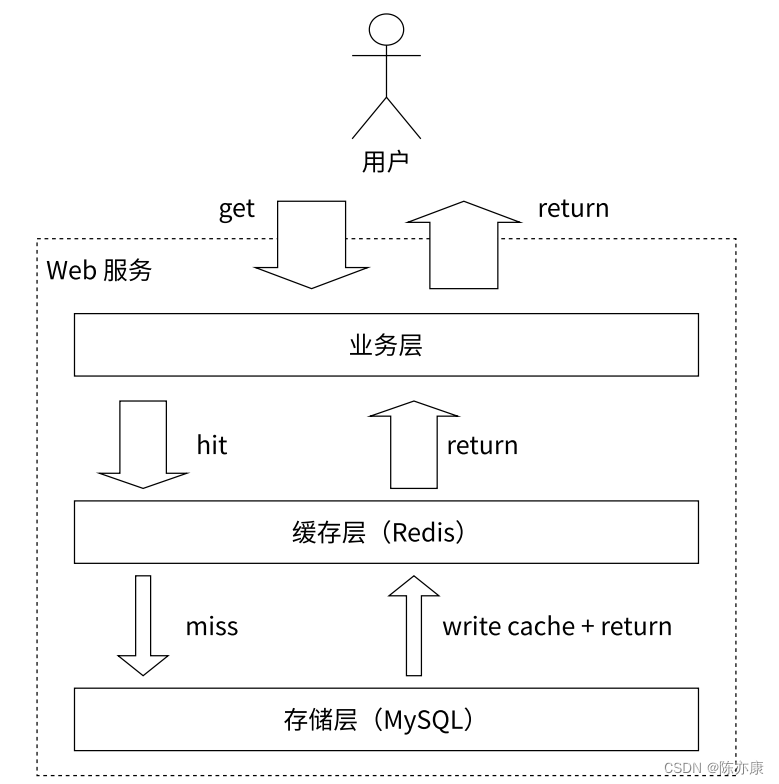
整体思路:
应用服务器访问数据的时候,先查询 Redis,如果 Redis 上存在该数据,就从 Redis 中取数据直接交给应用服务器,不用继续访问数据库了;如果 Redis 上不存在该数据,就会去 MySQL 中把读到的结构返回给应用服务器,同时,把这个数据也写入到 Redis 中.
由于 Redis 这样的缓存经常用来存储 “热点数据”,也就是高频使用的数据,那什么样的数据算高频呢?这里暗含了一层假设,某个数据一旦被用到了,那么可能在最近这段时间就可能被反复用到.
随着时间推移,越来越多的 key 在 redis 上访问不到,那 redis 的数据不是越来越多么?
- 把数据写给 redis 的同时,会给这个 key 设置一个过期时间.
- Redis 也有内存不足的时候,因此提供了 淘汰策略(之前的文章展开讲过).
1.1.2、案例实现
例如论坛网站,有些帖子的访问评论很高,就需要设置成热点文章,缓存起来(比起去 MySQL 数据库中查询文章要快的多).
实现思路:
根据上面理论,暗含假设当前使用的文章就是热点文章,也就是说,如果在缓存中有该文章,就直接返回,如果没有,就去数据库中查,然后再缓存起来,同时设置 30min(不同场景合理分配) 的过期时间.
帖子实体类.
@Data
public class Article {
private String title;
private String content;
}
文章 mapper.
@Mapper
public interface ArticleMapper {
/**
* 根据 id 查询文章
* @param id
* @return
*/
Article selectArticleById(@Param("id") Integer id);
}
<select id="selectArticleById" resultType="com.example.cyk.cache.Article">
select * from article where id = #{id};
</select>
帖子 controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/article")
public class ArticleController {
@Autowired
private IArticleService articleService;
@GetMapping("/get")
public HashMap<String, Object> get(@NonNull Integer id) {
//1.获取文章服务
Article article = articleService.getArticleInfo(id);
//2.返回响应
return HandlerResponse(1000, "操作成功", article);
}
/**
* 处理返回格式
* @param code
* @param msg
* @param data
* @return
*/
private HashMap<String, Object> HandlerResponse(Integer code, String msg, Object data) {
HashMap<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", code);
result.put("msg", msg);
result.put("data", data);
return result;
}
}
帖子 service .
@Slf4j
@Service
public class ArticleService implements IArticleService {
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
public Article getArticleInfo(Integer id) {
//1.非空校验
if(id == null) {
log.warn("文章 id 为空");
throw new RuntimeException("文章 id 为空");
}
//2.先去 redis 上看有没有文章对应的这个id
//我这里约定 redis 上存储格式:
//key: art:id
//value: $title$content ($ 是分隔符)
//例如 key: art:1 value: $决定$今天要好好学习
String articleInfo = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("art:" + id);
if(articleInfo != null) {
//存在直接返回
("从 redis 中获取到文章数据");
//1) 解析格式
Article article = analysisArticle(articleInfo);
//2) 返回数据
return article;
}
//3.redis 上没有数据,因此需要从 mysql 中取
Article article = articleMapper.selectArticleById(id);
if(article == null) {
log.warn("文章不存在");
throw new RuntimeException("文章不存在!");
}
//4.将文章存到 redis 中
//1) 合成 redis 所需格式的文章
articleInfo = synthesisArticle(article);
//2) 设置 5 分钟过期时间(为了演示效果)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("art:" + id, articleInfo, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
("从 mysql 中获取到文章数据");
return article;
}
/**
* 合成 redis 需要的格式(提前约定好的)
* @param article
* @return
*/
private String synthesisArticle(Article article) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("$");
stringBuilder.append(article.getTitle());
stringBuilder.append("$");
stringBuilder.append(article.getContent());
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
/**
* 解析文章格式
* @param articleInfo
* @return
*/
private Article analysisArticle(String articleInfo) {
Article article = new Article();
String title = articleInfo.split("\\$")[1];
String content = articleInfo.split("\\$")[2];
article.setTitle(title);
article.setContent(content);
return article;
}
}
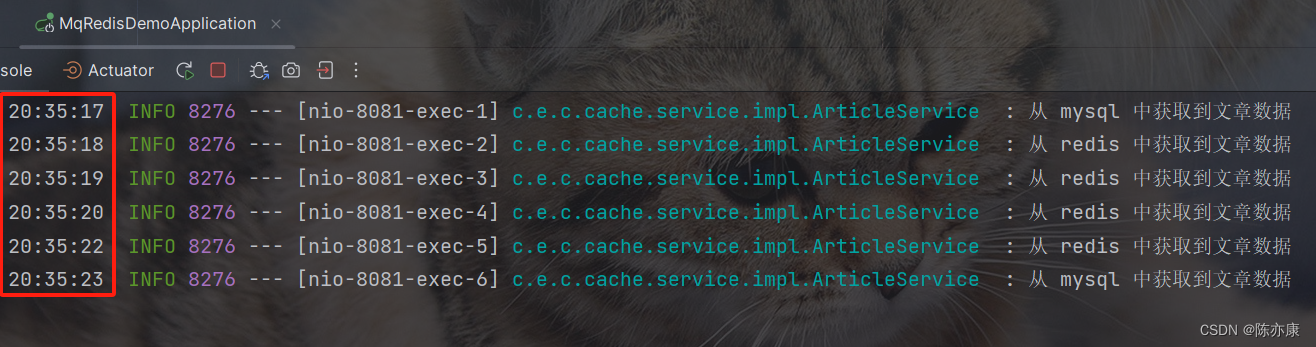
1.1.3、效果演示
1.2、计数功能(Redis + RabbitMQ)
1.2.1、分析
许多都会使应用用 Redis 作为计数的基础⼯具,它可以实现快速计数、查询缓存的功能,例如网站视频的播放量,点赞数量......
Ps:这些都是相比较 MySQL 数据库而言的,Redis 可以通过简单的键值对操作完成计数任务并且实在内存中完成的,而 MySQL 就需要先查询数据库,然后 +1,然后再存入数据库,是在需要进行硬盘存储的
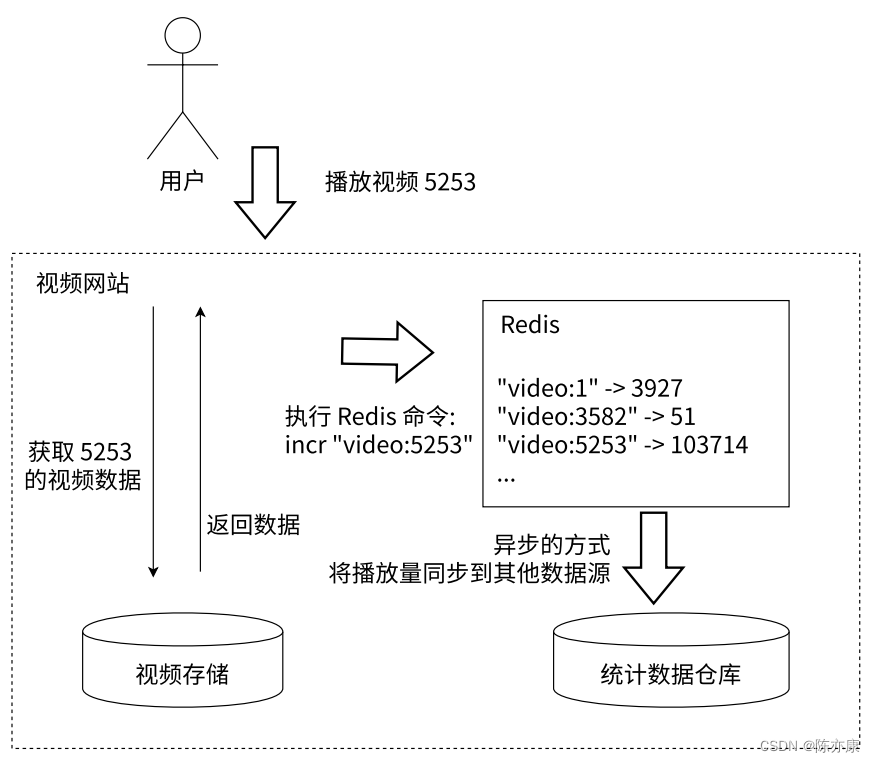
1.2.2、案例实现
实现思路:
假设,用户点击某个帖子,此时需要进行访问量 + 1 的操作,这时候应用服务器就会直接去操作 Redis ,执行 incr 命令,然后将返回的数据反馈给用户,最后 Redis 会以异步的方式(RabbitMQ 实现异步)将播放量同步到 MySQL 数据库中(异步就表示:这里并不是每一个播放请求,都需要立即写入数据~ 至于什么时候写入,需要根据实际的业务需求场景而定),将数据持久化.
Ps:实际中要开发⼀个成熟、稳定的真实计数系统,要⾯临的挑战远不⽌如此简单:防作弊、按 照不同维度计数、避免单点问题、数据持久化到底层数据源等。
文章实体类
@Data
public class Article implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String content;
private Long visits; //访问量
}
rabbit 交换机、队列、绑定配置.
public class MqFinal {
//处理文章的直接交换机
public static final String UPDATE_DIRECT = "article.update.direct";
//用于修改文章数据的队列
public static final String UPDATE_QUEUE = "article.update.queue";
//bindingKey
public static final String UPDATE_KEY = "article.update.key";
}
@Configuration
public class MqConfig {
/**
* 消息转化器
* @return
*/
@Bean
public MessageConverter jsonMessageConverter() {
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
@Bean
public DirectExchange ArticleDirectExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(MqFinal.UPDATE_DIRECT, true, false);
}
@Bean
public Queue ArticleUpdateQueue() {
return new Queue(MqFinal.UPDATE_QUEUE, true);
}
@Bean
public Binding ArticleUpdateBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(ArticleUpdateQueue()).to(ArticleDirectExchange()).with(MqFinal.UPDATE_KEY);
}
}
mq 监听配置
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListenerArticle {
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
/**
* 同步数据库
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = MqFinal.UPDATE_QUEUE)
public void syncVisits(HashMap<String, Object> data) {
Integer id = (Integer) data.get("id");
// Rabbitmq 这里有一个问题,Map<String, Object> 中 Object 传入为 Long 类型,需要用 Integer 来接受,否则报错
// 因此发送消息之前,体现将 Long 类型转化为 String,接收到消息之后只需要将 String 转化为 Long 即可
String visits = (String) data.get("visits");
articleMapper.updateArticleVisits(id, Long.valueOf(visits));
("访问量数据同步完成!");
}
}
访问量增加服务(这里为了可读性,只展示了本业务的核心逻辑)
@Override
public Article getArticleInfo(Integer id) {
//1.非空校验
if(id == null) {
log.warn("文章 id 为空");
throw new RuntimeException("文章 id 为空");
}
//2.访问量 +1
//注意:incr 这个命令执行时,即使 key 不存在,也会自动生成 key,然后自增
Long visits = redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("v_art:" + id);
//3.rabbitmq 实现异步数据同步(发送一个消息即可)
HashMap<String, Object> visitsInfo = new HashMap<>();
visitsInfo.put("id", id);
visitsInfo.put("visits", visits.toString()); //转化原因前面解释过了
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(MqFinal.UPDATE_DIRECT, MqFinal.UPDATE_KEY, visitsInfo);
//4.获取文章数据
//业务逻辑(这里为了可读性,就先不展示这里了)......
//5.放入文章
Article article = new Article();
article.setVisits(visits);
article.setId(id);
return article;
}

