一、OpenFeign 参数传递和响应处理
1.1、feign 客户端参数传递
1.1.1、零散类型参数传递
OpenFeign 对零散类型参数传递有以下限制
- querystring 方式传递参数(例如 "/user?name=cyk" ):在 openfeign 接口声明中必须要给参数加入 @RequestParam 注解/
- restful 路径传参(例如 "/user/{id}/{name}" ):在 openfeign 接口声明中必须要给参数加入注解 @PathVariable 注解.
为什么 openfeign 要这样区分呢?
因为 openfeign 是 伪HttpClient 对象,我们在远程调用他的客户端提供的接口时,并不知道你到底是路径传参还是问号传参,因此需要通过注解的方式来指明传参方式(就像 Spring Web 一样,只不过 Spring Web 中如果没指明传参类型,底层会按默认方式走,而 openfeign 则没有).
1. 例如 querystring 方式传参
a)远程调用方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
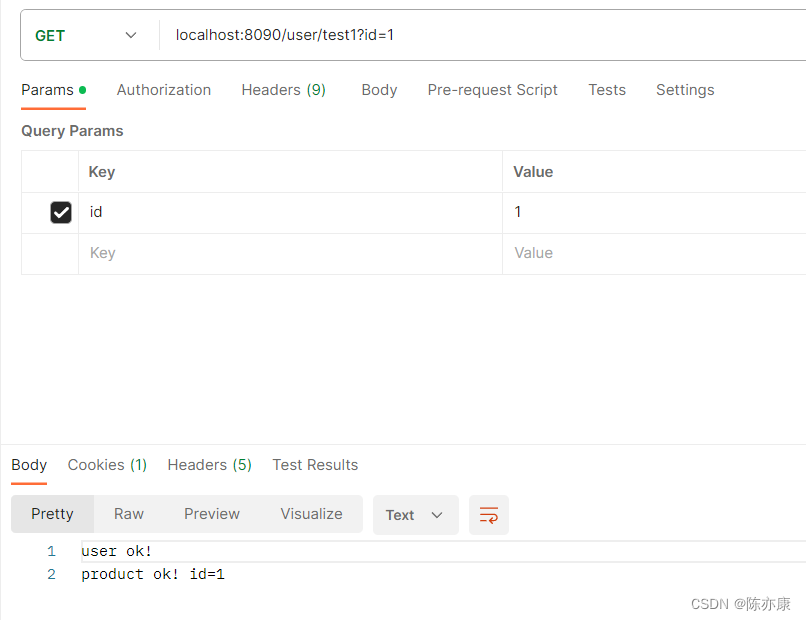
@GetMapping("/test1")
public String test1(Long id) {
String info = productClient.getInfo(id);
System.out.println(info);
return "user ok! \n" + info;
}
}
b)服务提供方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@GetMapping("/get_info")
public String getInfo(Long id) {
return "product ok! id=" + id;
}
}c)feign 客户端
@FeignClient(value = "product", configuration = LoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class)
public interface ProductClient {
@GetMapping("/product/get_info")
String getInfo(@RequestParam("id") Long id);
}d)测试结果:
2. 例如路径方式传参
a)远程调用方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
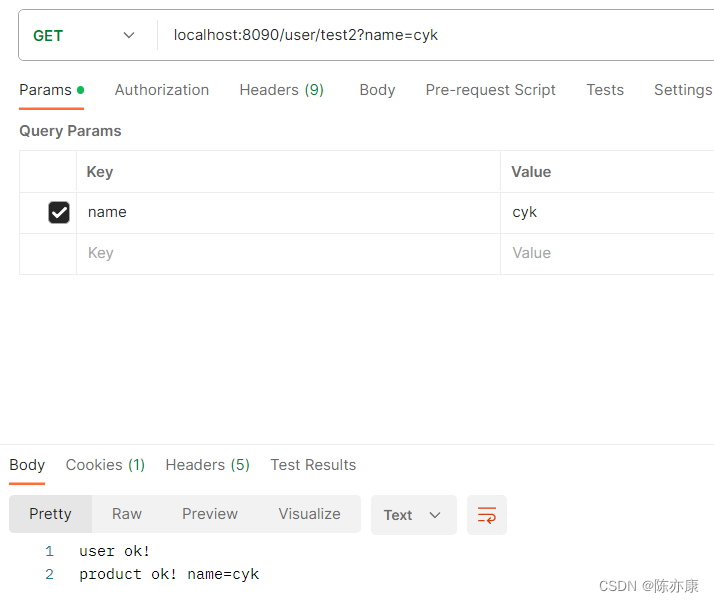
@GetMapping("/test2")
public String test2(String name) {
String info = productClient.getName(name);
System.out.println(info);
return "user ok! \n" + info;
}
}
b)服务提供方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@GetMapping("/{name}")
public String getName(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return "product ok! name=" + name;
}
}c)feign 客户端
@FeignClient(value = "product", configuration = LoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class)
public interface ProductClient {
@GetMapping("/product/{name}")
String getName(@PathVariable("name") String name);
}
d)测试结果:
扩展:restful 和 问号传参的区别
RESTful 风格是一种基于 HTTP 协议的 API 设计风格,它通过使用不同的 HTTP 方法(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等)和不同的 URL 来表示不同的操作和资源。RESTful 风格的优点包括:
- 清晰、简洁的 URL 设计:RESTful 风格的 URL 通常比较简洁,易于理解和记忆,能够清晰地表达出资源的结构和操作。
- 良好的可扩展性:RESTful 风格的设计允许你在原有的 API 上添加新的资源和方法,而不会对原有的 API 造成影响。
- 支持缓存:RESTful 风格的 API 可以利用 HTTP 缓存机制,提高 API 的响应速度和性能。
- 跨平台、跨语言:RESTful 风格的 API 可以被不同的平台和语言调用,具有很好的兼容性和可集成性。
问号传参风格是一种通过在 URL 中使用问号传参的方式来传递参数的 API 设计风格。它的优点包括:
- 动态参数传递:问号传参风格允许你在 URL 中直接传递参数,可以方便地实现动态参数的传递。
- 支持复杂参数类型:问号传参风格可以支持复杂的数据类型,例如对象、数组等,能够更好地满足复杂参数传递的需求。
- 易于开发和实现:问号传参风格的 API 开发起来相对简单,容易实现和调试。
总的来说,如果你需要设计一个简单的 API,并且对性能和扩展性要求不高,问号传参风格可能是一个不错的选择。而如果你需要设计一个复杂的 API,需要支持缓存、扩展性、跨平台和跨语言等要求,那么 RESTful 风格可能更适合你的需求。
1.1.2、对象参数传递
对象参数传递方式有两种,一种是 form 表单提交,另一种是 application/json 方式(推荐),这里主要讲第二种方式(实际开发中用的).
openfeign 接口要求对象传参必须要使用 @RequestBody 注解指明类型.
原因:这就像是我们给后端传递一个 json 格式数据类型,然后后端使用 一个对象接收参数,并通过 @RequestBody 指明他是 json 格式.
注意:openfeign 中对象传参只能使用 POST,并且也符合使用习惯,最主要是因为 GET 请求传对象会报错 Method Not Allowed.
1. 对象参数传递案例
a)远程调用方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@GetMapping("/test3")
public String test3(@RequestBody User user) {
user.setUsername(user.getUsername());
user.setPassword(user.getPassword());
String userinfo = productClient.getUser(user);
return "user ok! \n" + userinfo;
}
}b)服务提供方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@PostMapping("/get_user")
public String getUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return "product ok! " + user.toString();
}
}
c)feign 客户端
@FeignClient(value = "product", configuration = LoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class)
public interface ProductClient {
//注意:openfeign 中对象传参只能使用 POST,并且也符合使用习惯
//GET 请求传对象会报错: Method Not Allowed
@PostMapping("/product/get_user")
String getUser(@RequestBody User user);
}
d)测试结果:
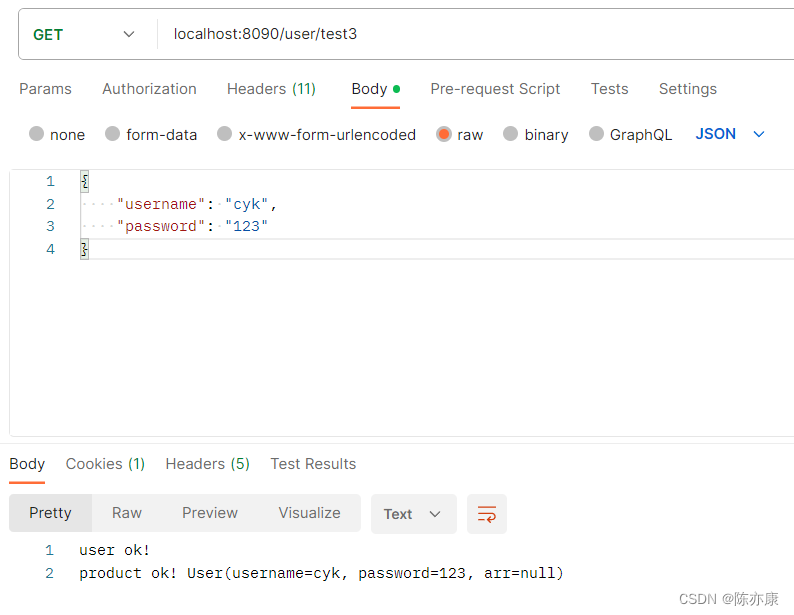
1.1.3、数组参数传递
数组参数传递要求在 feign 客户端接口使用 @RequestParam 注解指明参数类型.
原因:数组参数传递,实际上就是 querystring 方式传参,例如 " /user/?name=123&name=456&name=789 ",其中 name 就是数组.
1. 数组传参案例
a)远程调用方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@GetMapping("/test4")
public String test4(String[] arr) {
String result = productClient.getArr(arr);
return "user ok! \n" + result;
}
}
b)服务提供方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@GetMapping("/get_arr")
public String getArr(@RequestParam("arr") String[] arr) {
return "product ok!" + Arrays.toString(arr);
}
}
c)feign 客户端
@FeignClient(value = "product", configuration = LoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class)
public interface ProductClient {
@GetMapping("/product/get_arr")
String getArr(@RequestParam("arr") String[] arr);
}
d)测试结果
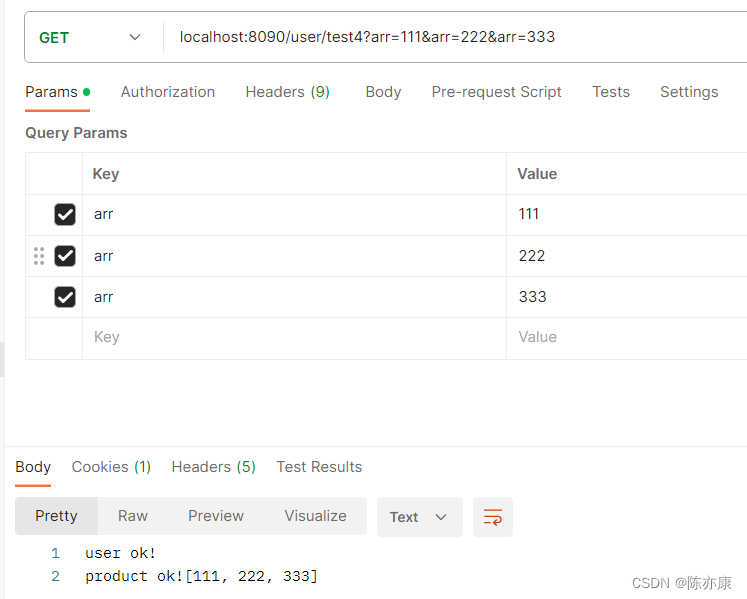
1.1.4、集合类型的参数传递(了解)
spring mvc 不能直接接收集合类型参数(例如 List)!如果一定要接收,需要将集合类型参数放入对象中,然后使用对象的方式传递.
例如如下:
@Data
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private List<String> arr;
}
这里就不演示了,因为 使用方式 以及 注意事项 和对象传递参数一样.
1.2、feign 客户端响应处理
1.2.1、天坑!
这里我们只需要知道一点就可以,Feign 客户端不能处理 Object 这种类型的返回格式!无论是对象中包含 Object 类型还是 Map 中存在 Object 类型....... 只要有他,就会出现各种格式问题.
例如,服务提供方传入的是一个 Long 类型,但是远程调用方接收到参数之后就变成了 Integer 类型(这里的处理,和 RabbitMQ 消息发送后的格式转化一个尿性),强转就会报以下错误:
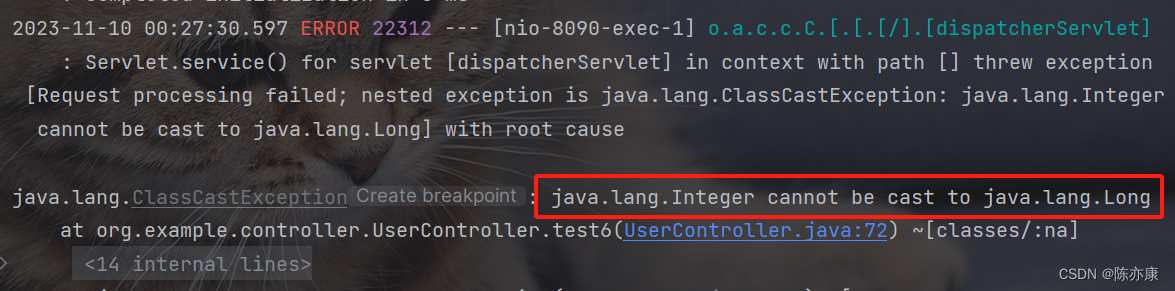
ChatGPT 给出了以下解释:
这是因为 OpenFeign 在默认情况下会自动将对象和 Map 对象转换成 JSON 格式。它使用了 Jackson 作为默认的序列化/反序列化库。当你在使用 OpenFeign 进行远程调用时,返回的对象会被自动转换成 JSON 格式。
然而,需要注意的是,OpenFeign 只能处理简单的 Java 对象和 Map 对象,对于复杂的 Java 对象或包含特殊类型的对象,可能无法自动进行正确的序列化和反序列化。在这种情况下,你可能需要自定义序列化/反序列化方式,或者使用其他序列化库来替代默认的 Jackson。
1.2.2、解决办法
只要服务提供方的返回值类型涉及到 Object 、对象、Map 这些复杂类型,都可以在 Feign 客户端使用 String 类型作为接口返回值类型(因为 openfeign 会自动转换为 json 格式),远程调用方接收到响应之后,就可以使用 ObjectMapper.readValue() 反序列化成我们所需要的对象即可.
案例一
a)远程调用方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@SneakyThrows
@GetMapping("/test6")
public String test6() {
String data = productClient.getData();
Long finalData = objectMapper.readValue(data, Long.class);
return "user ok!" + finalData;
}
}
b)服务提供方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@GetMapping("/get_data")
public Object getData() {
return 100L;
}
}
c)feign 客户端
@FeignClient(value = "product", configuration = LoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class)
public interface ProductClient {
@GetMapping("/product/get_data")
String getData();
}
测试结果:
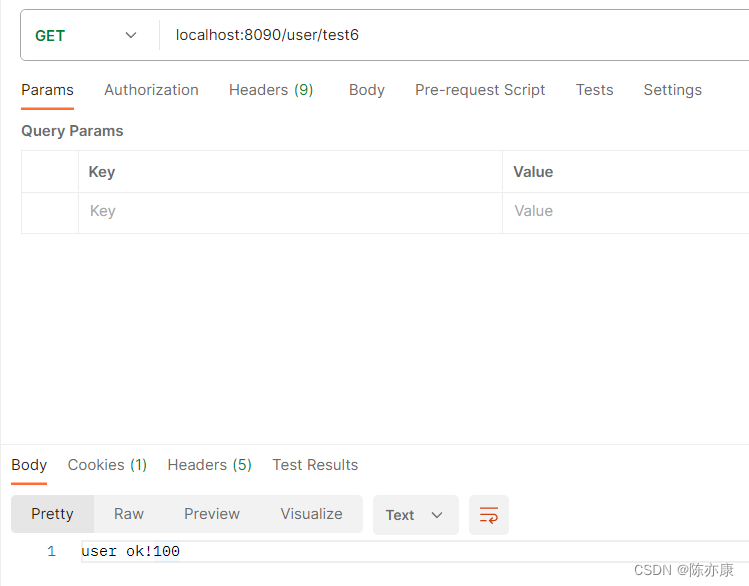
案例二(复杂数据类型)
a)Feign 客户端接口响应类型
@Data
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private List<String> arr;
}
b)远程调用方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
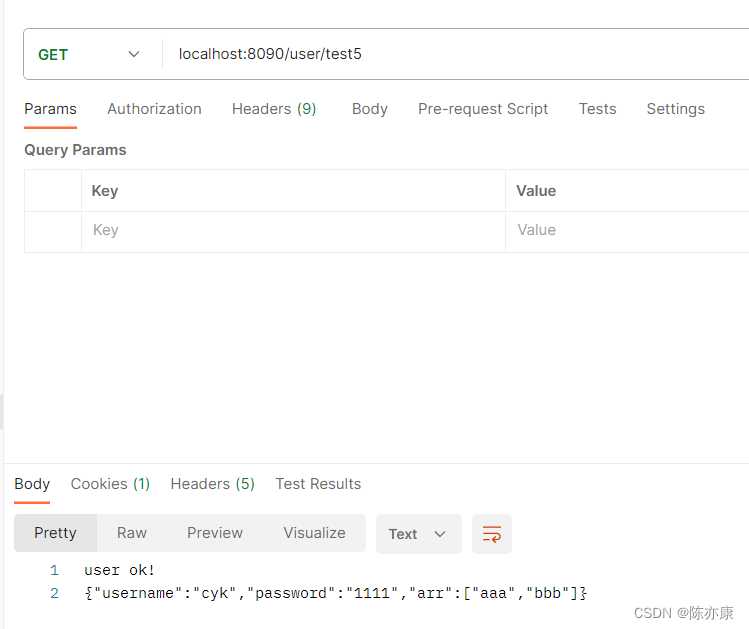
@GetMapping("/test5")
public String test5() throws JsonProcessingException {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("cyk");
user.setPassword("1111");
List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("aaa");
arrayList.add("bbb");
user.setArr(arrayList);
String userList = productClient.getUserList(user);
User user2 = objectMapper.readValue(userList, User.class);
System.out.println(user2);
return "user ok! \n" + userList;
}
}
c)服务提供方
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@PostMapping("/get_user_list")
public User getUserList(@RequestBody User user) {
return user;
}
}d)feign 客户端
@FeignClient(value = "product", configuration = LoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class)
public interface ProductClient {
@PostMapping("/product/get_user_list")
String getUserList(@RequestBody User user);
}
测试结果: