递归简介
- 递归的两个特点:调用自身和结束条件
如:
def func(x):
if x>0:
print(x)
func(x-1)
func(3)
执行结果如下:
3
2
1
这里需要注意一下,如将打印语句放到下面,如下代码,结果将是完全不一样的
def func(x):
if x>0:
func(x-1)
print(x)
func(3)
执行结果如下:
1
2
3
2、汉诺塔问题
-
汉诺塔问题:

-
当n=2时操作步骤:
原始状况如下,目标是将A上的两个都移动到C上
步骤一:将A上的小盘从A移动到B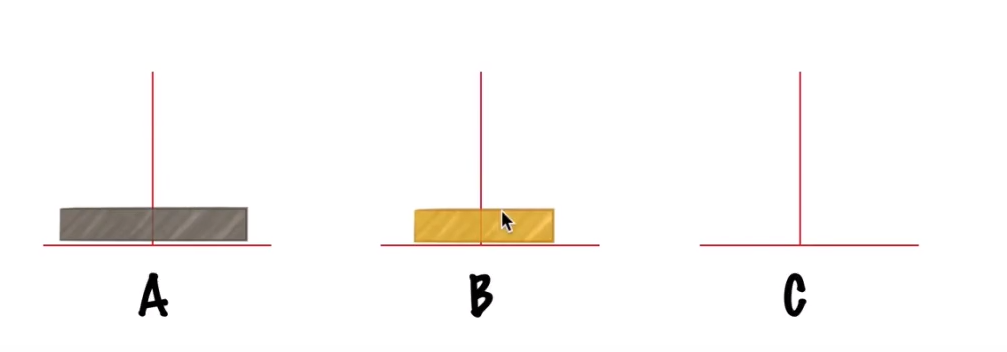
步骤二:将A盘上的大盘移动到C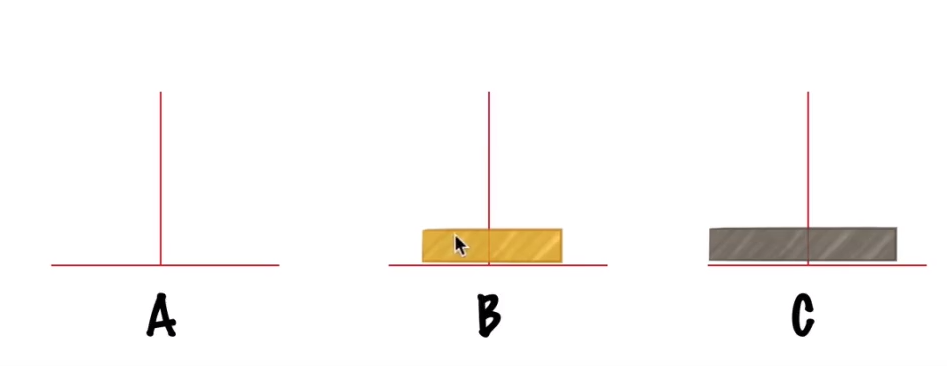
步骤三:将B上的小盘移动到C,结束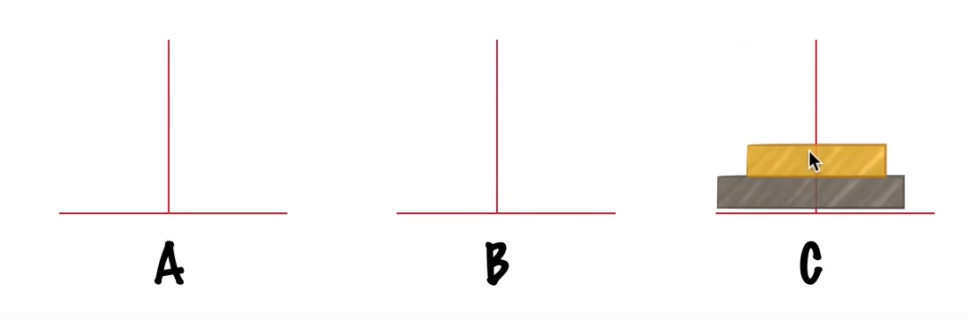
-
当n个盘时,思路是将A上的n-1个盘看做是一个小盘,将A最下面的大盘看做是一个大盘,此时即和n=2时的思路一致了
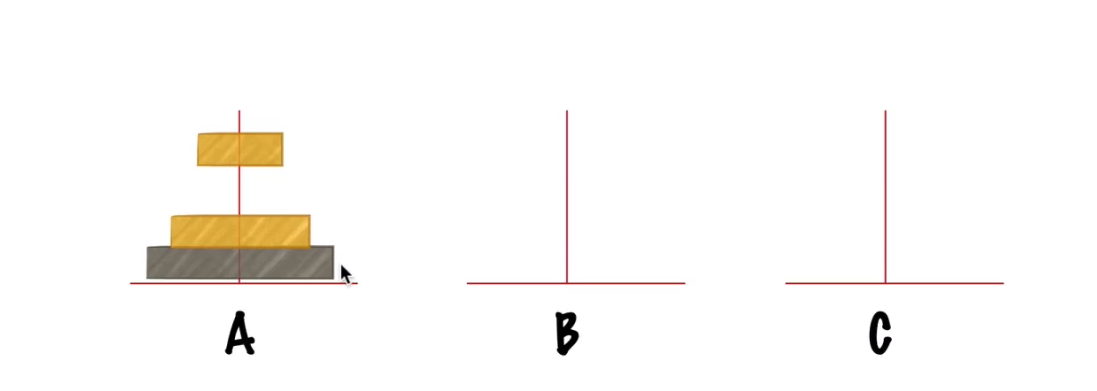
步骤一:将A上n-1个盘移动到B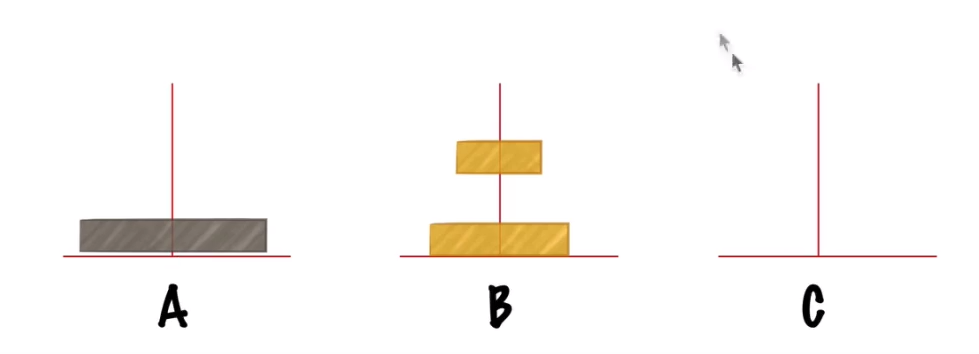
步骤二:将A上最下面的大盘移动到C盘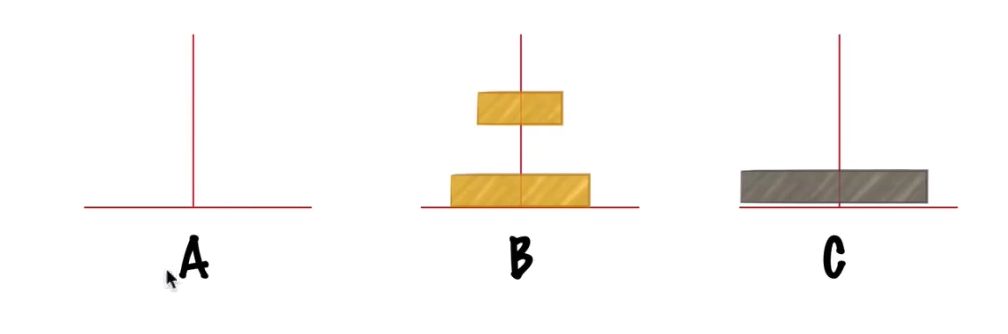
步骤三:将B上的n-1个盘移动到C盘上 -
算法实现如下:
def hanoi(n,a,b,c):
"""
将n个盘从a经过b移动到c
:param n:
:param a:
:param b:
:param c:
:return:
"""
if n>0:
hanoi(n-1,a,c,b)
print(f"moving {n} from {a} to {c}")
hanoi(n-1,b,a,c)
if __name__=="__main__":
print("---------------- n=2 -----------------------------")
hanoi(2,"A","B","C")
print("---------------- n=3 -----------------------------")
hanoi(3, "A", "B", "C")
print("---------------- n=4 -----------------------------")
hanoi(4, "A", "B", "C")
执行结果如下:
---------------- n=2 -----------------------------
moving 1 from A to B
moving 2 from A to C
moving 1 from B to C
---------------- n=3 -----------------------------
moving 1 from A to C
moving 2 from A to B
moving 1 from C to B
moving 3 from A to C
moving 1 from B to A
moving 2 from B to C
moving 1 from A to C
---------------- n=4 -----------------------------
moving 1 from A to B
moving 2 from A to C
moving 1 from B to C
moving 3 from A to B
moving 1 from C to A
moving 2 from C to B
moving 1 from A to B
moving 4 from A to C
moving 1 from B to C
moving 2 from B to A
moving 1 from C to A
moving 3 from B to C
moving 1 from A to B
moving 2 from A to C
moving 1 from B to C

