 学技术并发网始终建议同学们阅读原版官方文档,所以并发网每月都会组织大家翻译各种官方技术文档。3月份并发网组织大家翻译《Linkerd官方文档》,欢迎有兴趣的同学参与。
学技术并发网始终建议同学们阅读原版官方文档,所以并发网每月都会组织大家翻译各种官方技术文档。3月份并发网组织大家翻译《Linkerd官方文档》,欢迎有兴趣的同学参与。
如何领取
通过评论领取想要翻译的文章,每次领取一章或一节(根据内容长短),翻译完后再领取其他章节。领取完成之后,译文最好在一个星期内翻译完成,不要超过两周,如果不能完成翻译,也欢迎你邀请其他同学和你一起完成翻译。请谨慎领取,很多文章领取了没有翻译,导致文章很长时间没人翻译。
如何提交?
翻译完成之后请登录到并发网提交成待审核状态,会有专门的编辑校对后进行发布。如果多篇文章翻译被评为A级会升级您为译者,并加入译者沟通微信群。如果在本站翻译超过十篇文章,将有礼品赠送,比如签名版的《Java并发编程的艺术》或者其他图书。如果译文发布到并发网公众号,赞赏归译者所有。如果你喜欢使用markdown编写文章,可以将markdown生成后的HTML复制到网站上进行提交。mac下推荐MacDown软件。
- Linkerd介绍
- Linkerd是什么?
Get started
Get Linkerd up and running in just a few minutes. This section addresses running Linkerd in common environments.
Select an environment to get started:
- 《Linkerd官方文档》在本地运行Linkerd
- 《Linkerd官方文档》使用Docker运行Linkerd
- 《Linkerd官方文档》在Kubernetes中运行Linkerd
- 《Linkerd官方文档》在DC / OS中运行Linkerd
- 《Linkerd官方文档》与Istio一起运行Linkerd
- 《Linkerd官方文档》在ECS中运行Linkerd
Administration Overview
This section describes some of the major features included in Linkerd’s admin interface. For a complete list of available endpoints, refer to the config documentation.
- Dashboard: Admin UI showing graphs of requests, success rate, latency and more.
- Telemetry: Describes how to handle metrics exported by Linkerd.
- Dtab playground: A web UI that you can use to help debug Dtab rules.
- Shutdown: Gracefully shut down Linkerd.
Features
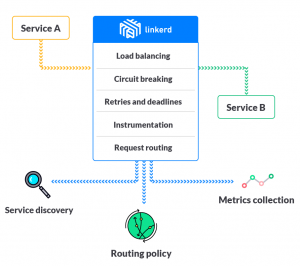
- Beyond adding reliability through circuit breaking and latency-aware load balancing, Linkerd automatically instruments top-line service metrics such as request volume, success rates, and latency distributions. Linkerd also provides request-level routing and multi-service discovery integration with a powerful language called dtabs.In this section you’ll find a rundown of Linkerd’s major features.
- Load balancing: Linkerd provides multiple load-balancing algorithms that use real-time performance metrics to distribute load and reduce tail latencies across your application.
- Circuit breaking: Linkerd includes automatic circuit breaking that will stop sending traffic to instances that are deemed to be unhealthy, giving them a chance to recover and avoiding cascading failures.
- Service discovery: Linkerd integrates with various service discovery backends, helping you to reduce the complexity of your code by removing ad-hoc service discovery implementations.
- Dynamic request routing: Linkerd enables dynamic request routing and rerouting, allowing you to set up staging services, canaries, blue-green deploys, cross-DC failover, and dark traffic with a minimal amount of configuration.
- Retries and deadlines : Linkerd can automatically retry requests on certain failures and can timeout requests after a specified period.
- TLS: Linkerd can be configured to send and receive requests with TLS, which you can use to encrypt communication across host boundaries without modification to your existing application code.
- HTTP proxy integration: Linkerd can act as an HTTP proxy, which is widely supported by almost all modern HTTP clients, making it easy to integrate into existing applications.
- Transparent Proxying: you can use iptables rules on your host to set up transparent proxying via Linkerd
- gRPC: Linkerd supports both HTTP/2 and TLS, allowing it to route gRPC requests, enabling advanced RPC mechanisms such as bidirectional streaming, flow control, and structured data payloads.
- Distributed tracing: Linkerd supports both distributed tracing and metrics instrumentation, providing uniform observability across all services.
- Instrumentation: Linkerd supports both distributed tracing and metrics instrumentation, providing uniform observability across all services.
Configuration Overview
Both Linkerd and namerd’s configuration is controlled via a configuration file, which must be provided as a command-line argument when the processes are started. Both YAML and JSON config file formats are supported. For the complete, up-to-date configuration reference guides, see:
- linkerd-1.3.6 config
- namerd-1.3.6 config
Advanced Overview
This section of the documentation contains in-depth information about advanced topics pertaining to both Linkerd and namerd. It is divided into the following subsections:
- Routing: Provides a comprehensive look at how Linkerd routes requests that it receives.
- namerd: Introduces namerd as a service that helps route Linkerd requests and centralizes routing decisions to provide global Linkerd control.
- Dtabs: Explains delegation tables and delegation rules, the primary mechanism by which Linkerd dynamically routes requests.
- Deployment: Addresses typical deployment models for running Linkerd in your architecture.
- Plugins: Sheds light on Linkerd’s modular plugin system, and provides a detailed walkthrough for writing your own plugins.
Our wiki also documents:
- Network Performance: Common approaches to diagnosing network performance issues that can negatively impact Linkerd.
- Debugging a Linkerd setup: Common approaches to finding and fixing Linkerd configuration issues that may prevent it from working properly in your setup.

