最短路径问题
问题描述:平面上有n个点(n<=100),每个点的坐标均在-10000~10000之间。其中的一些点之间有连线。若有连线,则表示可从一个点到达另一个点,即两点间有通路,通路的距离为两点间的直线距离。现在的任务是找出从一点到另一点之间的最短距离。
输入:
第1行为整数n,表示图中顶点的个数。
第2行到第n+1行(共n行),每行两个整数x和y,描述了一个点的坐标(以一个空格分隔)。
第n+2行为一个整数m,表示图中连线的个数。
此后的m行,每行描述一条连线,由两个整数i和j组成,表示第i个点和第j个点之间有连线。
最后一行:两个整数s和t,分别表示源点和目标点。
输出:
仅1行,一个实数(保留两位小数),表示从s到t的最短路径长度。
输入样例:
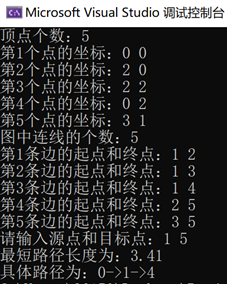
5
0 0
2 0
2 2
0 2
3 1
5
1 2
1 3
1 4
2 5
3 5
1 5
输出样例:
3.41
代码示例👇
//author:Mitchell_Donovan
//date:5.18
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<iomanip>//用于保留两位小数输出
using namespace std;
//边类
class Edge {
public:
int from, to;
double weight;
Edge() {
from = -1;
to = -1;
weight = 0;
}
Edge(int fromValue, int toValue, double weightValue) {
from = fromValue;
to = toValue;
weight = weightValue;
}
};
//图类
class Graph {
public:
int numVertex;
int numEdge;
int* Mark;//标记图中顶点是否被访问过
int* Indegree;//存放图中顶点的入度
Graph(int num) {
numVertex = num;
numEdge = 0;
Indegree = new int[numVertex];
Mark = new int[numVertex];
for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++) {
Mark[i] = 0;//0表示未访问过
Indegree[i] = 0;//入度设为0
}
}
~Graph() {
delete[]Mark;
delete[]Indegree;
}
//判断是否为边
bool isEdge(Edge oneEdge) {
if (oneEdge.weight > 0 && oneEdge.weight < INFINITY && oneEdge.to >= 0) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
//访问
void Visit(Graph& G, int v) {
cout << v + 1 << " ";
//cout << G.data[v];
}
};
//用相邻矩阵表示图
class Graphm :public Graph {//类继承
private:
double** matrix;//指向相邻矩阵的指针
public:
Graphm(int num) :Graph(num) {
matrix = (double**)new double* [numVertex];//申请二维数组空间
for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++) {
matrix[i] = new double[numVertex];
}
for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++) {//相邻矩阵初始化
for (int j = 0; j < numVertex; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
~Graphm() {
for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++) {
delete[]matrix[i];
}
delete[] matrix;
}
//返回顶点的第一条边
Edge firstEdge(int oneVertex) {
Edge myEdge;
myEdge.from = oneVertex;
for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++) {
if (matrix[oneVertex][i] != 0) {
myEdge.to = i;
myEdge.weight = matrix[oneVertex][i];
break;
}
}
return myEdge;
}
//返回与已知边相同顶点的下一条边
Edge nextEdge(Edge preEdge) {
Edge myEdge;
myEdge.from = preEdge.from;
if (preEdge.to >= numVertex) {//不存在下一条边
return myEdge;
}
for (int i = preEdge.to + 1; i < numVertex; i++) {
if (matrix[preEdge.from][i] != 0) {
myEdge.to = i;
myEdge.weight = matrix[preEdge.from][i];
break;
}
}
return myEdge;
}
//为图设置一条边
void setEdge(int from, int to, double weight) {
if (matrix[from][to] <= 0) {//如果原边不存在
numEdge++;
Indegree[to]++;
}
matrix[from][to] = weight;
}
//删除图的一条边
void delEdge(int from, int to) {
if (matrix[from][to] > 0) {//如果原边存在
numEdge--;
Indegree[to]--;
}
matrix[from][to] = 0;
}
};
//结构体Dist用于保存最短路径信息
struct Dist {
int index;//顶点的索引项
double length;//当前最短路径长度
int pre;//路径最后经过的顶点
};
//递归函数print用于输出具体路径
void print(int from, int to, Dist*& D) {
if (D[to].pre == from) {
cout << from << "->" << to;
}
else {
print(from, D[to].pre, D);
cout << "->" << to;
}
}
//Dijkstra算法求源点s到其他各点的最短路径
void Dijkstra(Graphm& G, int s, int to) {
Dist* D = new Dist[G.numVertex];
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertex; i++) {//初始化Mark数组和D数组
G.Mark[i] = 0;
D[i].index = i;
D[i].length = INFINITY;
D[i].pre = s;
}
D[s].length = 0;//源点到自身长度设置为0
//定义D.length小的优先级高的运算符
struct cmp {
bool operator ()(const Dist& a, const Dist& b) {
return a.length > b.length;
}
};
priority_queue<Dist, vector<Dist>, cmp> minHeap;//最小堆(优先队列)用于找出最短路径
minHeap.push(D[s]);
for (int i = 0; i < G.numVertex; i++) {
bool FOUND = false;
Dist d;
while (!minHeap.empty()) {
d = ();//获得到s路径长度最小的顶点
minHeap.pop();
if (G.Mark[d.index] == 0) {//如果该标记点未访问过
FOUND = true;
break;
}
}
if (!FOUND) {//如果没有符合条件的最短路径则跳出本次循环
break;
}
int v = d.index;
G.Mark[v] = 1;
//加入v以后要刷新D中v的邻接点的最短路径长度
for (Edge e = G.firstEdge(v); G.isEdge(e); e = G.nextEdge(e)) {
if (D[e.to].length > (D[v].length + e.weight)) {
D[e.to].length = D[v].length + e.weight;
D[e.to].pre = v;
minHeap.push(D[e.to]);
}
}
}
//打印出结果
cout << "最短路径长度为:" << fixed << setprecision(2) << D[to].length << endl;//保留两位小数输出
cout << "具体路径为:";
print(s, to, D);
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cout << "顶点个数:";
cin >> n;
Graphm test(n);
struct position {
int x;
int y;
};
position* pos = new position[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << "第" << i + 1 << "个点的坐标:";
cin >> pos[i].x;
cin >> pos[i].y;
}
cout << "图中连线的个数:";
cin >> m;
int from, to;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cout << "第" << i + 1 << "条边的起点和终点:";
cin >> from;
cin >> to;
double length = sqrt(pow(pos[to - 1].x - pos[from - 1].x, 2) + pow(pos[to - 1].y - pos[from - 1].y, 2));
test.setEdge(from - 1, to - 1, length);
test.setEdge(to - 1, from - 1, length);
}
cout << "请输入源点和目标点:";
cin >> from;
cin >> to;
Dijkstra(test, from - 1, to - 1);
}
输出示例👇
补充参考
C++优先队列自定义排序总结
C / C++ 保留两位小数(setprecision(n)的一些用法总结)

