有时候数据读写不一定是文件,也可以在内存中读写。StringIO顾名思义就是在内存中读写str。
Python在内存中读写数据,用到的模块是StringIO和BytesIO。
getvalue()方法用于获得写入后的str。
StringIO操作的只能是str,如果要操作二进制数据,就需要使用BytesIO。
StringIO用法:
源码解释:
class StringIO(_TextIOBase):
"""
Text I/O implementation using an in-memory buffer.
The initial_value argument sets the value of object. The newline
argument is like the one of TextIOWrapper's constructor.
"""示例代码1:
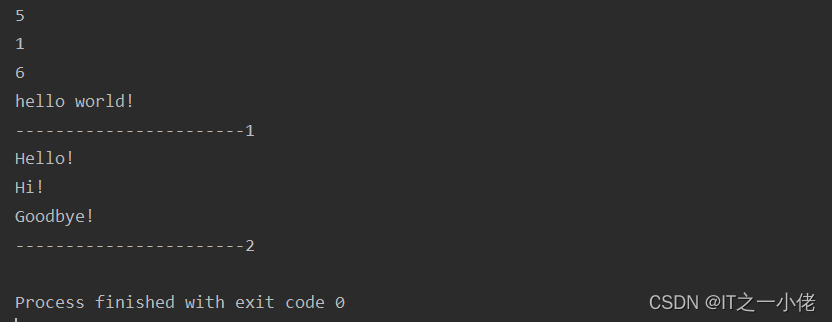
# StringIO:在内存中读写str
from io import StringIO
f = StringIO()
print(f.write('hello'))
print(f.write(' '))
print(f.write('world!'))
# getValue()方法用于获取写入的str
print(f.getvalue())
print('-----------------------1')
# 要读取StringIO,可以用一个str初始化StringIO,然后,像读文件一样读取:
f = StringIO('Hello!\nHi!\nGoodbye!')
while True:
s = f.readline()
if s == '':
break
print(s.strip())
print('-----------------------2')
运行结果:
BytesIO用法:
# 源码解释:
class BytesIO(_BufferedIOBase):
""" Buffered I/O implementation using an in-memory bytes buffer. """示例代码2:
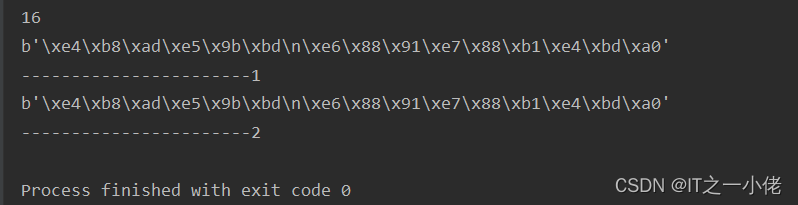
# StringIO操作的只能是str,如果要操作二进制数据,就需要使用BytesIO
from io import BytesIO
f = BytesIO()
print(f.write('中国\n我爱你'.encode('utf-8')))
print(f.getvalue())
print('-----------------------1')
# 和StringIO类似,可以用一个bytes初始化BytesIO,然后,像读文件一样读取
f = BytesIO(b'\xe4\xb8\xad\xe5\x9b\xbd\n\xe6\x88\x91\xe7\x88\xb1\xe4\xbd\xa0')
print(f.read())
while True:
s = f.readline()
if s == b'':
break
print(s.strip())
print('-----------------------2')
运行结果: