any()源码解析:
def any(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Return True if bool(x) is True for any x in the iterable.
If the iterable is empty, return False.
"""
passany() 函数将一个可迭代对象作为参数,只要该可迭代对象中至少有一项为 True,就返回 True。如果列表中所有元素都为False,则返回False;否则有一个为Ture,就返回True
语法结构:
any(iterable)- 对于迭代中的任何 x,如果 bool(x) 是 True,返回 True
- 如果迭代是空,返回 False
示例代码:
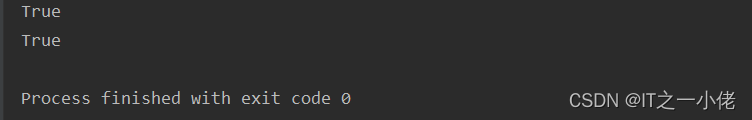
list_1 = [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]
# any(a list with at least one non-zero entry) returns True
print(any(list_1))
# Output True
list_2 = [0j, 0, 0, 0.0, 0, 0, 0.0, 0]
# any(a list of zeros) returns False
print(any(list_2))
# Output False
list_3 = [True, False, False]
# any(a list with at least one True value) returns True
print(any(list_3))
# Output True
list_4 = ["", "", "code more"]
# any(a list with at least one non-empty string) returns True
print(any(list_4))
# Output True
list_5 = ["", "", ""]
# any(a list of empty strings) returns False
print(any(list_5))
# Output False
运行结果:
使用any() 函数检查字符串中的数字
示例代码:
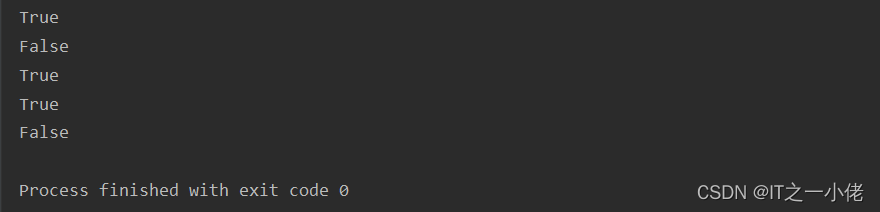
my_string = "coding**is**cool**345"
# 列表推导
are_there_digits = [char.isdigit() for char in my_string]
print(are_there_digits)
# 调用any函数
print(any(are_there_digits))
运行结果:

使用any()函数将多个条件与逻辑 OR 组合在一起
示例代码:
a, b, c, d = False, False, True, False
if a or b or c or d:
print(True)
else:
print(False)
# 将a, b, c, d放到一个可迭代对象中,如列表list
lst = [a, b, c, d]
# 使用any()
if any(lst):
print(True)
else:
print(False)
运行结果: