python中对数据的排序主要使用sort()和sorted()方法。
1、sort()方法
语法结构:
列表序列.sort( key=None, reverse=False)注意: reverse 表示排序规则, reverse = True 降序, reverse = False 升序(默认)
示例代码1:
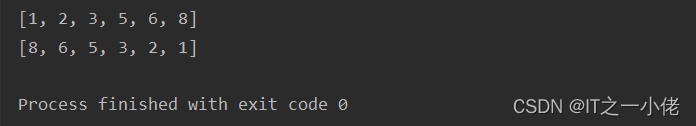
num_list1 = [1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8]
num_list1.sort()
# 结果:[1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8]
print(num_list1)
num_list2 = [1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8]
num_list2.sort(reverse=True)
# 结果:[8, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1]
print(num_list2)运行结果:
示例代码2:
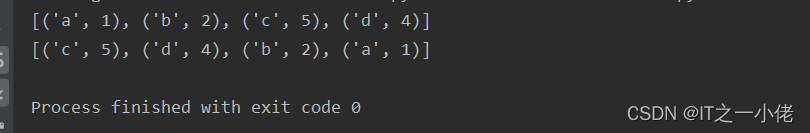
num_list1 = [("b", 2), ("a", 1), ("c", 5), ("d", 4)]
num_list1.sort()
print(num_list1)
num_list2 = [("b", 2), ("a", 1), ("c", 5), ("d", 4)]
num_list2.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
print(num_list2)
运行结果:
示例代码3:
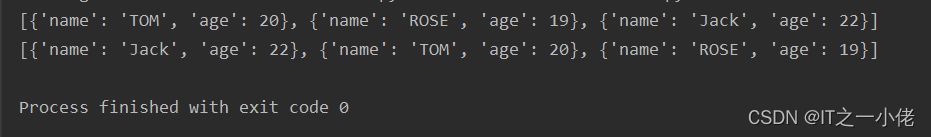
students = [
{'name': 'TOM', 'age': 20},
{'name': 'ROSE', 'age': 19},
{'name': 'Jack', 'age': 22}
]
students.sort(key=lambda x: x['name'], reverse=True)
print(students)
students.sort(key=lambda x: x['age'], reverse=True)
print(students)
运行结果:
2、sorted()方法
语法结构:
sorted(*args, **kwargs)示例代码1:
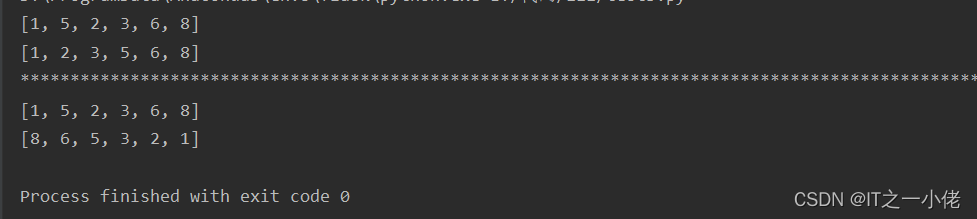
num_list1 = [1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8]
ret = sorted(num_list1)
print(num_list1)
print(ret)
print("*" * 100)
num_list2 = [1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8]
ret2 = sorted(num_list2, reverse=True)
print(num_list2)
print(ret2)
运行结果:
示例代码2:
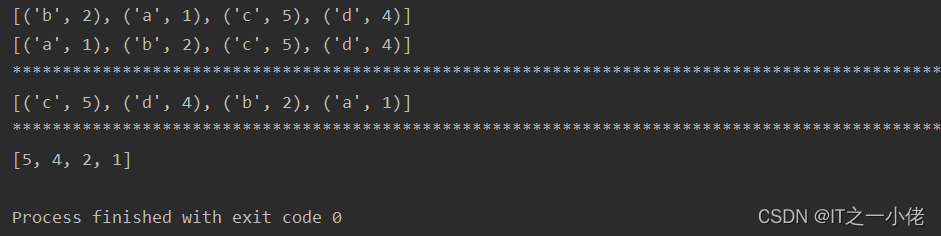
num_list1 = [("b", 2), ("a", 1), ("c", 5), ("d", 4)]
ret = sorted(num_list1)
print(num_list1)
print(ret)
print("*" * 100)
num_list2 = [("b", 2), ("a", 1), ("c", 5), ("d", 4)]
ret2 = sorted(num_list2, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
print(ret2)
print("*" * 100)
num_list3 = [("b", 2), ("a", 1), ("c", 5), ("d", 4)]
ret3 = sorted(map(lambda x: x[1], num_list3), reverse=True)
print(ret3)
运行结果:
示例代码3:
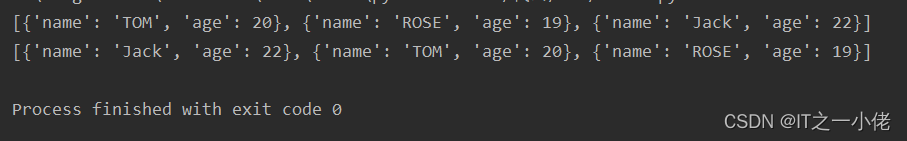
students = [
{'name': 'TOM', 'age': 20},
{'name': 'ROSE', 'age': 19},
{'name': 'Jack', 'age': 22}
]
ret = sorted(students, key=lambda x: x['name'], reverse=True)
print(ret)
ret2 = sorted(students, key=lambda x: x['age'], reverse=True)
print(ret2)
运行结果;
3、sort()和sorted()区别
- sort 是应用在 list 上的方法,而sorted 可以对所有可迭代的对象进行排序操作,是python内置的全局方法;
- sort是对原有列表进行操作,而sorted返回的是一个新的可迭代对象,不会改变原来的对象;
- sort使用方法为list.sort(), 而sorted的使用方法为sorted(list)

