有时候可以通过批量操作来减少网络请求。如:批量查询、批量插入数据。
批量查询_mget
# 当查询的数据都存在时
POST /test/user/_mget
# 请求数据
{
"ids": [
"1002",
"1003"
]
}
# 响应结果
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1002",
"_version": 5,
"_seq_no": 10,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 23,
"sex": "女"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1003",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 11,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1003,
"name": "王五",
"age": 27,
"sex": "男"
}
}
]
}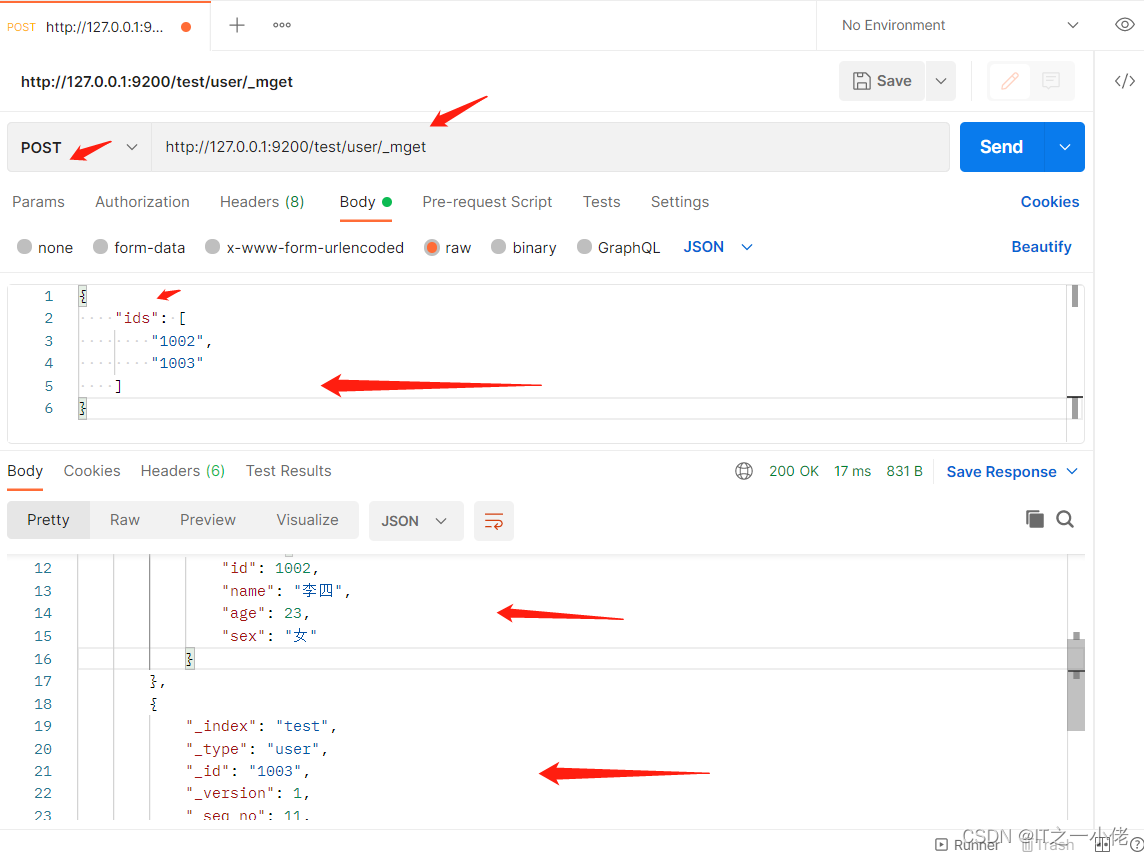
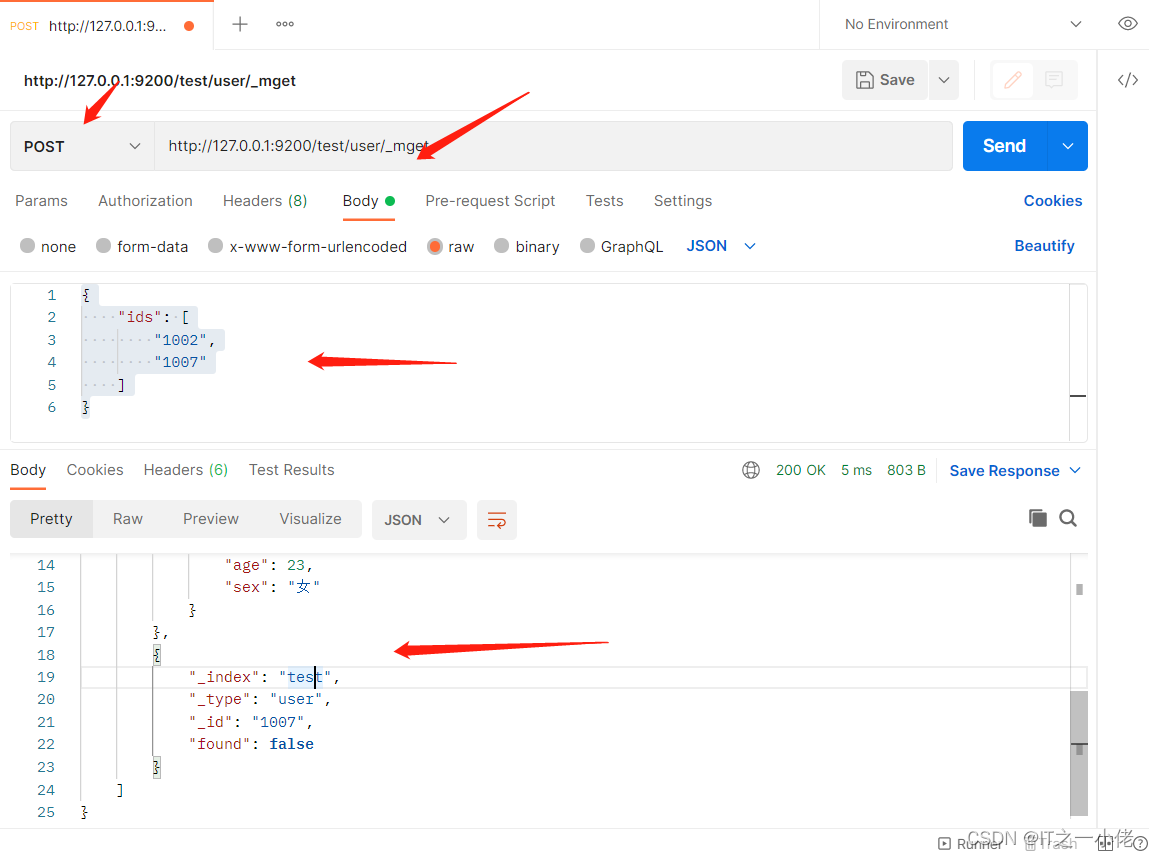
当某一条数据不存在,不影响整体响应,需要通过found的值进行判断是否查询到数据。
# 当查询的数据有不存在的时候
POST /test/user/_mget
# 请求数据
{
"ids": [
"1002",
"1007"
]
}
# 响应结果
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1002",
"_version": 5,
"_seq_no": 10,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 23,
"sex": "女"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1007",
"found": false
}
]
} _bulk操作
_bulk操作
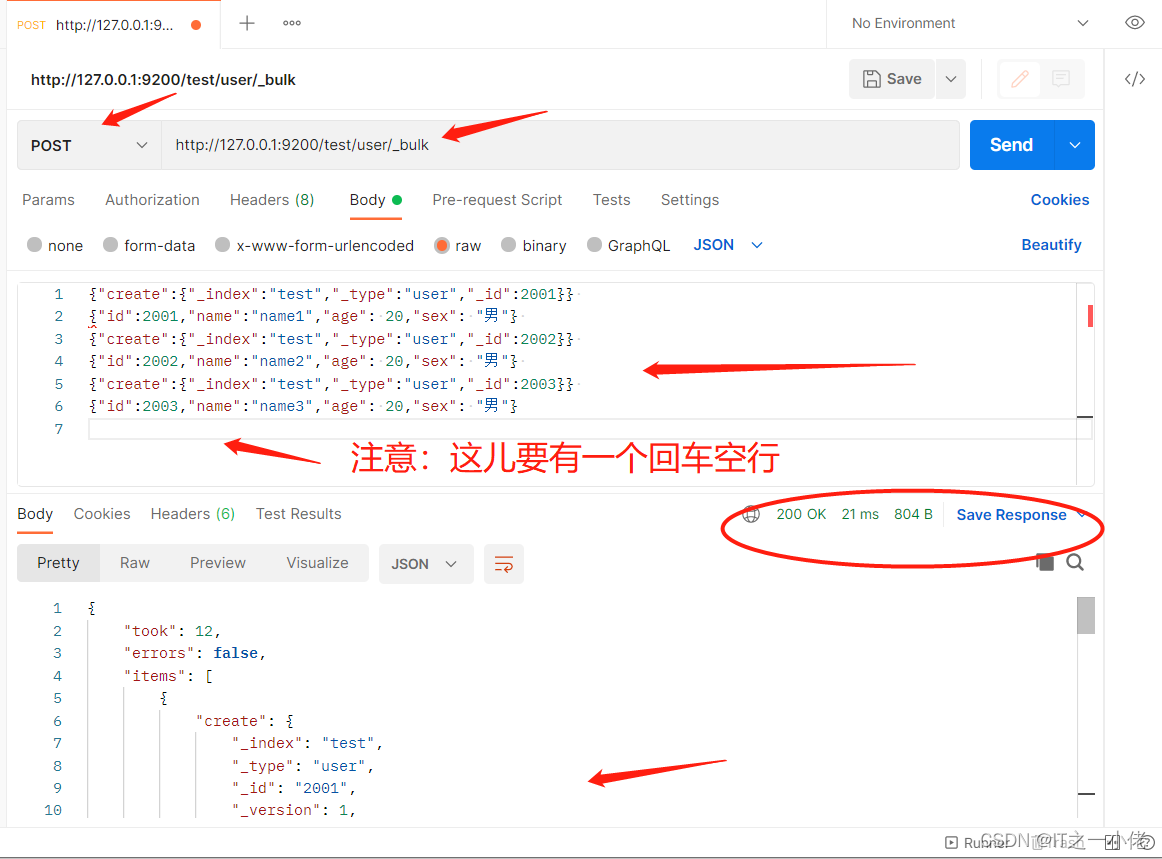
在Elasticsearch中,支持批量的插入、修改、删除操作,都是通过_bulk的api完成的。 请求格式如下:(请求格式不同寻常)
{ action: { metadata }}\n
{ request body }\n
{ action: { metadata }}\n
{ request body }\n
...批量插入数据:
{"create":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"id":2001,"name":"name1","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"id":2002,"name":"name2","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
{"id":2003,"name":"name3","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
注意:最后一行要有一个回车。
POST /test/user/_bulk
#请求数据
{"create":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"id":2001,"name":"name1","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"id":2002,"name":"name2","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
{"id":2003,"name":"name3","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
# 响应结果
{
"took": 12,
"errors": false,
"items": [
{
"create": {
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2001",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 13,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
},
{
"create": {
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2002",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 14,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
},
{
"create": {
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2003",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 15,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
}
]
}

批量删除
{"delete":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"delete":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"delete":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
POST /test/user/_bulk
# 请求数据
{"delete":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"delete":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"delete":{"_index":"test","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
# 响应数据
{
"took": 11,
"errors": false,
"items": [
{
"delete": {
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2001",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 16,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
},
{
"delete": {
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2002",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 17,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
},
{
"delete": {
"_index": "test",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "2003",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 18,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
}
]
}


ElasticSearch一次请求多少性能最高?
- 整个批量请求需要被加载到接受我们请求节点的内存里,所以请求越大,给其它请求可用的内存就越小。有一 个最佳的bulk请求大小。超过这个大小,性能不再提升而且可能降低。
- 最佳大小,当然并不是一个固定的数字。它完全取决于你的硬件、你文档的大小和复杂度以及索引和搜索的负 载。
- 幸运的是,这个最佳点(sweetspot)还是容易找到的:试着批量索引标准的文档,随着大小的增长,当性能开始 降低,说明你每个批次的大小太大了。开始的数量可以在1000~5000个文档之间,如果你的文档非常大,可以使用较小的批次。
- 通常着眼于你请求批次的物理大小是非常有用的。一千个1kB的文档和一千个1MB的文档大不相同。一个好的 批次最好保持在5-15MB大小间。

