社区Istio提供的熔断功能,Envoy通过连接池实现对上游集群的限流熔断,通过周期性的动态异常检测来确定上游集群中的某些主机是否异常。如果发现异常,则将该主机从连接池中隔离出去。这本质上是针对上游主机整体的熔断。有以下两个缺点:
仅支持服务级别熔断,不支持某个API进行限流熔断。
在路由规则后起作用,无法做到流量分发之前进行限流熔断。
本文介绍一种通过wasm插件实现路由级熔断的技术方案
改链方式
首先比较明确的一点,这个熔断点应该在route前,因此,改链的方式大概率是要跟在route前。
关于envoy的filter链,可以参考Envoy 架构与配置结构 – Envoy 中文指南 (icloudnative.io)
目前改链的方法有三种
-
通过直接改envoy源码,即侵入envoy代码,相当于实现一个内置的熔断逻辑。
-
通过envoyfilter扩展wasm,代码编进istio镜像中。
-
通过wasmplugin扩展wasm,代码是单独的镜像地址,可以按需拉取。
以上方式灵活度从1-3递增
-
需要编译envoy源码,一旦有问题需要所有sidecar更新重启
-
需要修改istio,把wasm插件编到istio中,后续依然要所有sidecar更新重启。
-
只需要修改镜像地址和标签,更新代价小一点。
以上方式代码权限从1-3递减
-
有几乎所有的envoy上下文,自由决定在什么范围生效。
-
仅能获取有限的沙箱上下文,可以配置生效范围,粒度细到vhost和route级别。
-
仅能获取有限的沙箱上下文,生效范围只能配置到workload级别。
比对2,3方案:
2:相对性能稍好一点,可以少改一些链。但是要编译和维护多版本的istio源码。
如果用这套方案,envoyfilter的applyTo基本可以照抄,插件的逻辑可以少写一点匹配vhost之类的逻辑,仅关注熔断算法即可。
3:代码很好维护,但是下发的配置给到workload级别之后,还需要通过wasm的上下文attributes来做简单的过滤。
如果用这套方案,需要根据attributes来对route做一些过滤,以达到“生效范围”的效果
wasmplugin实现可行性
参考envoyfilter的一些字段:Istio / Envoy Filter
1. vhost(name,port)
2. route的名字(对应在vs中)
3. header(vs也能配,但是只有prefix,exact,regex选择较少),能力不够丰富,自己继续扩充了,多了invert_match,presenct_match,suffix_match。
沿着这个思路,其实vhost和route也只是方便用户关联而已,最后如果要做更精细的熔断策略,应该还是要结合url,path,query参数等自由配置,最后还是得继续扩展,这也是方案3也可以接受的原因。
仅就目前支持vhost和route_name的场景,我们看下wasm能否支持:
wasm能力
attributes的列表:
Attributes — envoy 1.30.0-dev-da6cea documentation (envoyproxy.io)
我们特别需要关注的attribute如下:
request相关
|
request.path |
string |
The path portion of the URL |
|
request.url_path |
string |
The path portion of the URL without the query string |
|
request.host |
string |
The host portion of the URL |
|
request.scheme |
string |
The scheme portion of the URL e.g. “http” |
|
request.method |
string |
Request method e.g. “GET” |
|
request.headers |
map<string, string> |
All request headers indexed by the lower-cased header name |
Additional attributes are available once the request completes:
|
Attribute |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
request.duration |
duration |
Total duration of the request |
|
request.size |
int |
Size of the request body. Content length header is used if available. |
|
request.total_size |
int |
Total size of the request including the approximate uncompressed size of the headers |
-
这里大概率需要结合host和scheme,决定port,如果参考envoyfilter的定义,是可以指定在某些vhost下生效的,由于wasm没有暴露vhost上下文,所以我们大概需要通过这两个字段来组合出vhost,正常来说就是domain:port
-
需要关注duration,这个是熔断算法的核心指标
response相关
response.* attributes are only available in http filters.
|
Attribute |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
response.code |
int |
Response HTTP status code |
|
response.code_details |
string |
Internal response code details (subject to change) |
|
response.flags |
int |
Additional details about the response beyond the standard response code encoded as a bit-vector |
|
response.grpc_status |
int |
Response gRPC status code |
|
response.headers |
map<string, string> |
All response headers indexed by the lower-cased header name |
|
response.trailers |
map<string, string> |
All response trailers indexed by the lower-cased trailer name |
|
response.size |
int |
Size of the response body |
|
response.total_size |
int |
Total size of the response including the approximate uncompressed size of the headers and the trailers |
这里code和grpc_status应该是主要关注的重点,请求是否失败应该需要用这个判断。
route上下文
|
Attribute |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
xds.node |
Node |
Local node description |
|
xds.cluster_name |
string |
Upstream cluster name |
|
xds.cluster_metadata |
Metadata |
Upstream cluster metadata |
|
xds.listener_direction |
int |
Enumeration value of the listener traffic direction |
|
xds.listener_metadata |
Metadata |
Listener metadata |
|
xds.route_name |
string |
Route name |
|
xds.route_metadata |
Metadata |
Route metadata |
|
xds.upstream_host_metadata |
Metadata |
Upstream host metadata |
|
xds.filter_chain_name |
string |
Listener filter chain name |
listener_direction可以区分是否outbound
route_name本地验证过就是vs里面的route名
route_metadata是结构体定义url,可以扩展加字段,看以后有没有必要,目前仅一个字段。
改链位置
从以下代码可以看出,right before the Router,在route之前是没问题的,问题是要有多前?
const (
// Control plane decides where to insert the plugin. This will generally
// be at the end of the filter chain, right before the Router.
// Do not specify `PluginPhase` if the plugin is independent of others.
PluginPhase_UNSPECIFIED_PHASE PluginPhase = 0
// Insert plugin before Istio authentication filters.
PluginPhase_AUTHN PluginPhase = 1
// Insert plugin before Istio authorization filters and after Istio authentication filters.
PluginPhase_AUTHZ PluginPhase = 2
// Insert plugin before Istio stats filters and after Istio authorization filters.
PluginPhase_STATS PluginPhase = 3
)
作为一个熔断器,走一次auth感觉也是有在消耗后端资源,个人倾向于在AUTHN前,尽早做熔断。这样的话链的顺序基本是
break -> authn -> authz -> stats
结论
使用wasm插件可以基本实现相应的效果,性能有一点损耗,因为wasmplugin是指定到route链前,但是apply的是整个httpFilter,不再做精细的vhost指定,需要在插件中劫持所有的流量,在根据上下文在内存中过滤。
熔断算法
目前主要参考hystrix。从参数来看,是比较明显的滑动窗口算法,hystrix的官方流程图如下:
其他细节可以参考How it Works · Netflix/Hystrix Wiki · GitHub
| 如果wasm来实现,hystrix底层的内存管理,数据共享,事件触发,线程池管理之类的肯定要重写的,因为以前调研过wasm的内存机制,锁竞争是很剧烈的,性能比较低下,所以在高压场景下,熔断器可能会有统计失败/统计不灵敏的情况,熔断器失常时应该放行流量。 |
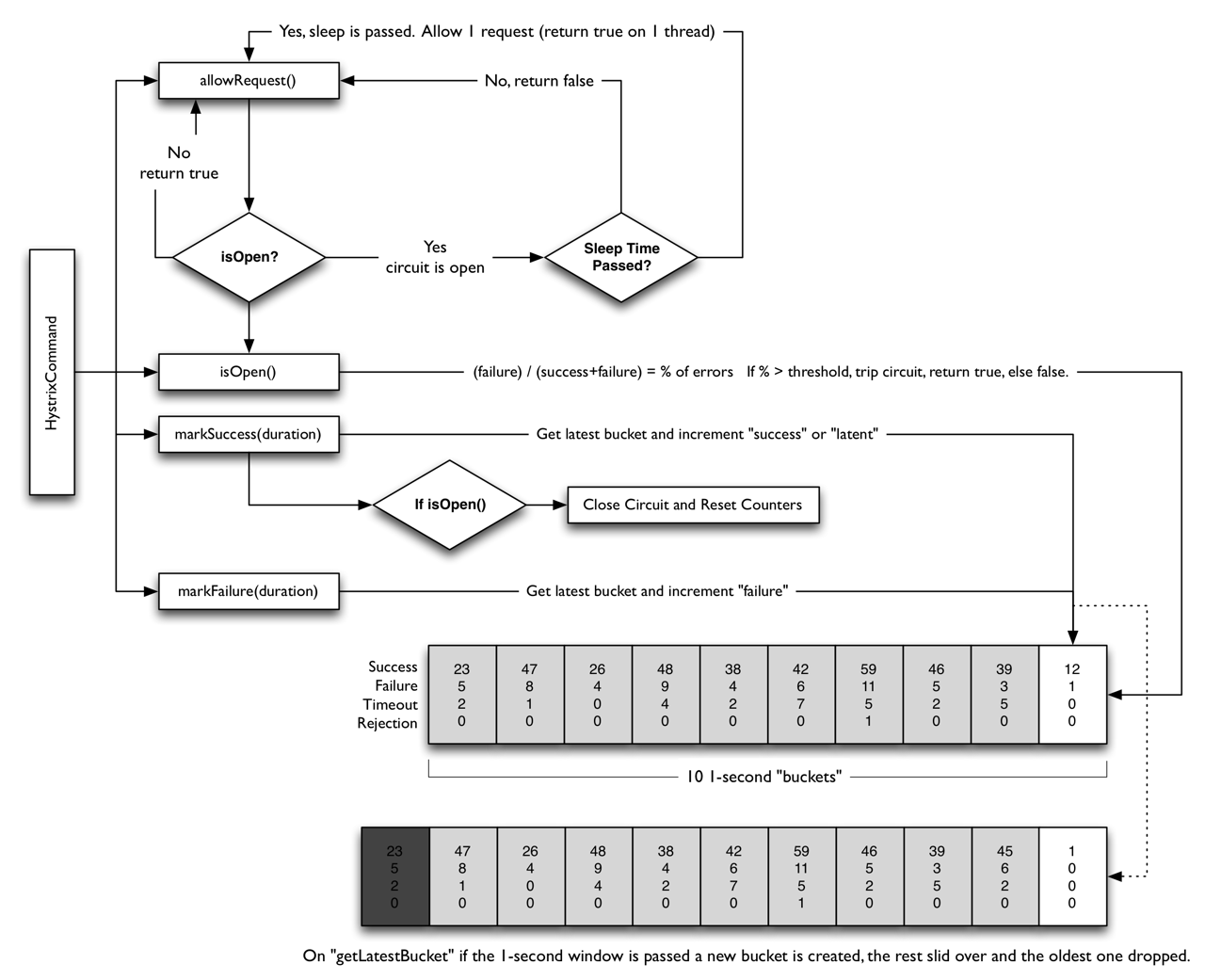
逻辑设计
滑动窗口的抽象,统计bucket的抽象目测可以复用。线程管理、信号量、锁等等逻辑在wasm环境下皆不可用,需要重写。
进一步分析代码
部分类是可以复用的,主要是rolling和metric*, 指标可以先用默认指标里面的一部分,然后http和线程池逻辑抽掉,http请求可以跳过了,直接用wasm的上下文中的耗时,请求次数,请求大小之类的填充。
// DefaultMetricCollector holds information about the circuit state.
// This implementation of MetricCollector is the canonical source of information about the circuit.
// It is used for for all internal hystrix operations
// including circuit health checks and metrics sent to the hystrix dashboard.
//
// Metric Collectors do not need Mutexes as they are updated by circuits within a locked context.
type DefaultMetricCollector struct {
mutex *sync.RWMutex
numRequests *rolling.Number
errors *rolling.Number
successes *rolling.Number
failures *rolling.Number
rejects *rolling.Number
shortCircuits *rolling.Number
timeouts *rolling.Number
contextCanceled *rolling.Number
contextDeadlineExceeded *rolling.Number
fallbackSuccesses *rolling.Number
fallbackFailures *rolling.Number
totalDuration *rolling.Timing
runDuration *rolling.Timing
}
这里锁应该是没用的,wasm的shareData都是一个隔离的副本,而且读写之前envoy已经加了粗粒度的锁。可以考虑干掉。
默认指标大部分可以用,大部分也都可以在wasm上下文中取到。核心的通过率计算,熔断时间长度等,可以参考,但是估计也得重写,因为里面大量用了event和chan来互通,这些在wasm语境下肯定都是不可用的。
// IsOpen is called before any Command execution to check whether or
// not it should be attempted. An "open" circuit means it is disabled.
func (circuit *CircuitBreaker) IsOpen() bool {
circuit.mutex.RLock()
o := circuit.forceOpen || circuit.open
circuit.mutex.RUnlock()
if o {
return true
}
if uint64(circuit.metrics.Requests().Sum(time.Now())) < getSettings(circuit.Name).RequestVolumeThreshold {
return false
}
if !circuit.metrics.IsHealthy(time.Now()) {
// too many failures, open the circuit
circuit.setOpen()
return true
}
return false
}
内存布局
wasm没有给出shareData的delete方法,所以要自行设计内存的布局。这里可能无限多的key,需要分哈希桶。
最终实现方式是:
circuit-breaker的name/namespace做桶。因为一个breaker就对应一个route_name,就是一个路由(header_match直接把不匹配的请求丢弃就行了)。
- 每个route还能再指定host,port和header过滤
- 一个breaker可以设置多个route,也可以不设置(不设置就是整个workload的所有流量都统计)
- 综上,不是简单的取名字就行了,应该还要增加matcher的md5,如果matcher有修改,数据应该另开一个桶统计。可以先用breakername+##+matcher后缀做key。
- 对应到sharedata的哈希桶key,应该还是再算一个哈希值取模1000。
- 超时时间应大于等于break_duration,理论上也不能无限大,不如要求最多熔断180s。
- 超时时间超过1s的请求,落桶按结束秒数来落
- 每个桶再按时间窗口分slot,0-11(最多12个,即12s)个slot。每个slot里面仅有duration,requestNum之类的数值,应该占用很小。
按指标数估算,每个指标假定都是float64,即8字节,10个指标(或许可以预留多一点后续可以扩展)即80字节,12个slot即960字节,约算他1k。
大约1k个breaker占用就1M。前期感觉可以约定每个workload最多设定一万个熔断器,内存占用大约10M左右,属于可控水平。