先简单介绍Liquibase
Liquibase是一个用于跟踪、管理和应用数据库变化的开源的数据库重构工具。它将所有数据库的变化(包括结构和数据)都保存在 changelog 文件中,便于版本控制,它的目标是提供一种数据库类型无关的解决方案,通过执行 schema 类型的文件来达到迁移。
Liquibase 特性
- 支持几乎所有主流的数据库,如 MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Sql Server, DB2 等;
- 支持多开发者的协作维护;
- 日志文件支持多种格式,如 XML, YAML, JSON, SQL等;
- 支持上下文相关逻辑
- 生成数据库变更文档
- 支持多种运行方式,如命令行、Spring 集成、Maven 插件、Gradle 插件等。
基本概念
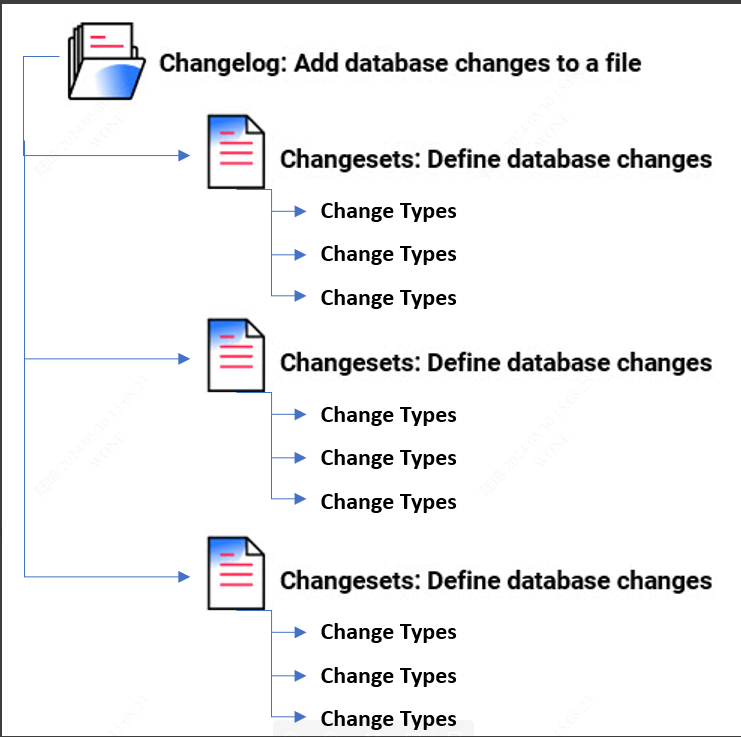
- Changelog & Changeset
Changeset 是 liquibase 对数据库执行变更的基本单元, 可以将数据库的各种 liquibase 变更类型组织到一起.
一个 Changelog 会记录一系列的 changesets 以及其中包含的各种变更.
- ChangeType
Change Type是一个数据库无关的定义,你可以用XML,YAML,JSON格式来指明对数据库更新操作。
操作包括实体操作,约束操作,数据操作等。
使用中遇到痛点
Liquibase相对flyway提供了更灵活的目标数据库适配,也为开发者提供了更多的扩展空间。在Liquibase中,如果我们需要上传初始化数据,会使用loadData或者loadUpdateData的ChangeType命令。
loadData适用批量插入新数据,loadUpdateData适用更新数据并支持失败回滚操作。但是由于插入的初始化数据跟随代码放在resources文件夹中,代码中根据安全要求是不能直接存放敏感数据(如密钥等)。
查询官网后,这个功能可以通过自定义ChangeType的方式实现。
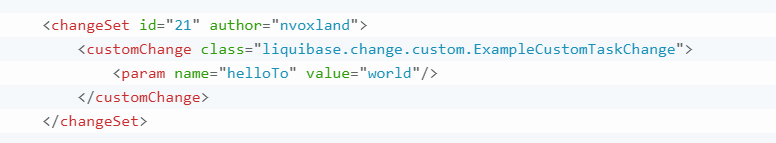
我们可以实现CustomSqlChange或CustomTaskChange接口获得自定义能力。
CustomTaskChange 和 CustomSqlChange 之间的区别如下:
- 在 CustomTaskChange 中,需要在execute() 实现自定义修改逻辑。
- 在 CustomSqlChange 中,有一个 generateStatements(Database database) 方法,它不执行修改逻辑,而是返回应该运行的 SQL。这使得自定义更改可以更好地与 update-sql 命令配合使用,该命令显示正在运行的 SQL。
显然相对CustomTaskChange,CustomSqlChange能提供更好的框架适配性,并且CustomSqlChange和LoadDataChange核心方法都是SqlStatement[] generateStatements(Database database)。 我们优先选择实现CustomSqlChange子类的方案。
源码分析
由于我们是对loadData和loadUpdateData进行功能扩展,先在源码中找到这个两个类进行分析。
具体代码在liquibase.change.core.LoadDataChange和liquibase.change.core.LoadUpdateDataChange
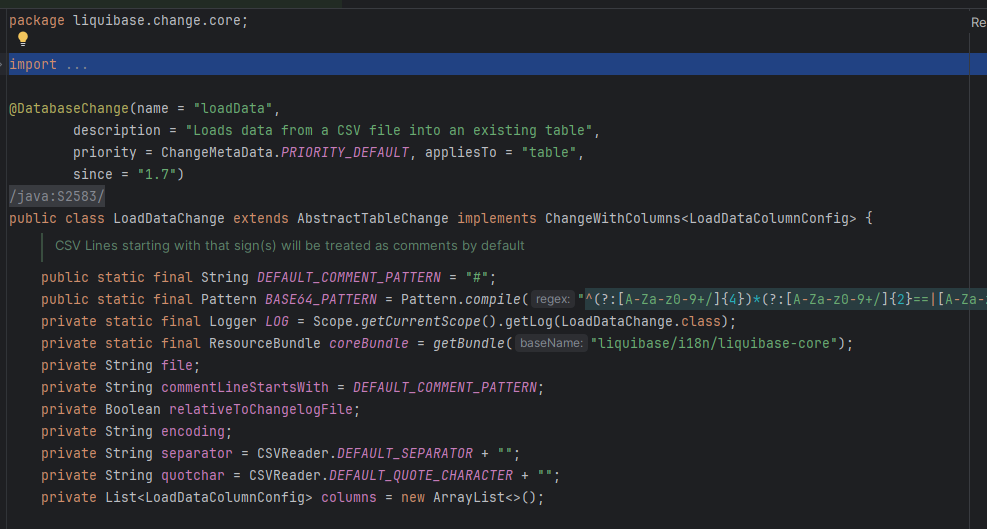
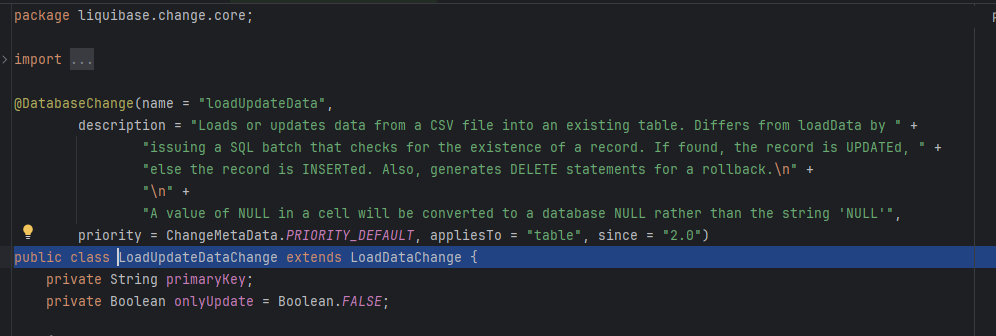
LoadUpdateDataChange代码不多,只是对LoadDataChange部分方法的重载。我们主要关注LoadDataChange。
这个类的主流程聚焦在接口的实现方法public SqlStatement[] generateStatements(Database database)
在代码上我加了注释代码
@Override
public SqlStatement[] generateStatements(Database database) {
// 是否支持批量更新操作
supportsBatchUpdates(database);
try (CSVReader reader = getCSVReader()) { // 根据参数创建CSV读对象
if (reader == null) {
throw new UnexpectedLiquibaseException("Unable to read file " + this.getFile());
}
// 从第一行数据获取csv文件的表头
String[] headers = reader.readNext();
if (headers == null) {
throw new UnexpectedLiquibaseException("Data file " + getFile() + " was empty");
}
// 根据读到的表头信息初始化列对象信息
// Make sure all take the column list we interpolated from the CSV headers
addColumnsFromHeaders(headers);
// 如果数据库适用JDBC,从数据库中获得列对象更具体的数据类型
// If we have an real JDBC connection to the database, ask the database for any missing column types.
try {
retrieveMissingColumnLoadTypes(columns, database);
} catch (DatabaseException e) {
throw new UnexpectedLiquibaseException(e);
}
// 开始按行读取数据
String[] line;
// Start at '1' to take into account the header (already processed):
int lineNumber = 1;
boolean isCommentingEnabled = StringUtil.isNotEmpty(commentLineStartsWith);
List<LoadDataRowConfig> rows = new ArrayList<>();
while ((line = reader.readNext()) != null) {
lineNumber++;
if
((line.length == 0) || ((line.length == 1) && (StringUtil.trimToNull(line[0]) == null)) ||
(isCommentingEnabled && isLineCommented(line))
) {
//nothing interesting on this line
continue;
}
// 检查当前行的列是否跟表头的个数一致
// Ensure each line has the same number of columns defined as does the header.
// (Failure could indicate unquoted strings with commas, for example).
if (line.length != headers.length) {
throw new UnexpectedLiquibaseException(
"CSV file " + getFile() + " Line " + lineNumber + " has " + line.length +
" values defined, Header has " + headers.length +
". Numbers MUST be equal (check for unquoted string with embedded commas)"
);
}
boolean needsPreparedStatement = false;
// 遍历当前csv行的数据,根据之前建立的列信息生成拥有具体值的数据列信息
List<LoadDataColumnConfig> columnsFromCsv = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < headers.length; i++) {
String value = line[i];
String columnName = headers[i].trim();
LoadDataColumnConfig valueConfig = new LoadDataColumnConfig();
LoadDataColumnConfig columnConfig = getColumnConfig(i, columnName);
// 根据配置,设置当前列的具体值
if (columnConfig != null) {
if ("skip".equalsIgnoreCase(columnConfig.getType())) {
continue;
}
// don't overwrite header name unless there is actually a value to override it with
if (columnConfig.getName() != null) {
columnName = columnConfig.getName();
}
//
// Always set the type for the valueConfig if the value is NULL
//
if ("NULL".equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
valueConfig.setType(columnConfig.getType());
}
valueConfig.setName(columnName);
valueConfig.setAllowUpdate(columnConfig.getAllowUpdate());
if (value.isEmpty()) {
value = columnConfig.getDefaultValue();
}
if (StringUtil.equalsWordNull(value)) {
valueConfig.setValue(null);
} else if (columnConfig.getType() == null) {
// columnConfig did not specify a type
valueConfig.setValue(value);
} else if (columnConfig.getTypeEnum() == LOAD_DATA_TYPE.BOOLEAN) {
if (value == null) { // TODO getDefaultValueBoolean should use BooleanUtil.parseBoolean also for consistent behaviour
valueConfig.setValueBoolean(columnConfig.getDefaultValueBoolean());
} else {
valueConfig.setValueBoolean(BooleanUtil.parseBoolean(value));
}
} else if (columnConfig.getTypeEnum() == LOAD_DATA_TYPE.NUMERIC) {
if (value != null) {
valueConfig.setValueNumeric(value);
} else {
valueConfig.setValueNumeric(columnConfig.getDefaultValueNumeric());
}
} else if (columnConfig.getType().equalsIgnoreCase("date")
|| columnConfig.getType().equalsIgnoreCase("datetime")
|| columnConfig.getType().equalsIgnoreCase("time")) {
if ("NULL".equalsIgnoreCase(value) || "".equals(value)) {
valueConfig.setValue(null);
} else {
try {
// Need the column type for handling 'NOW' or 'TODAY' type column value
valueConfig.setType(columnConfig.getType());
if (value != null) {
valueConfig.setValueDate(value);
} else {
valueConfig.setValueDate(columnConfig.getDefaultValueDate());
}
} catch (DateParseException e) {
throw new UnexpectedLiquibaseException(e);
}
}
} else if (columnConfig.getTypeEnum() == LOAD_DATA_TYPE.STRING) {
valueConfig.setType(columnConfig.getType());
valueConfig.setValue(value == null ? "" : value);
} else if (columnConfig.getTypeEnum() == LOAD_DATA_TYPE.COMPUTED) {
if (null != value) {
liquibase.statement.DatabaseFunction function =
new liquibase.statement.DatabaseFunction(value);
valueConfig.setValueComputed(function);
} else {
valueConfig.setValueComputed(columnConfig.getDefaultValueComputed());
}
} else if (columnConfig.getTypeEnum() == LOAD_DATA_TYPE.SEQUENCE) {
if (value == null) {
throw new UnexpectedLiquibaseException(
"Must set a sequence name in the loadData column defaultValue attribute"
);
}
liquibase.statement.SequenceNextValueFunction function =
new liquibase.statement.SequenceNextValueFunction(getSchemaName(), value);
valueConfig.setValueComputed(function);
} else if (columnConfig.getType().equalsIgnoreCase(LOAD_DATA_TYPE.BLOB.toString())) {
if ("NULL".equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
valueConfig.setValue(null);
} else if (BASE64_PATTERN.matcher(value).matches()) {
valueConfig.setType(columnConfig.getType());
valueConfig.setValue(value);
needsPreparedStatement = true;
} else {
valueConfig.setValueBlobFile(value);
needsPreparedStatement = true;
}
} else if (columnConfig.getTypeEnum() == LOAD_DATA_TYPE.CLOB) {
valueConfig.setValueClobFile(value);
needsPreparedStatement = true;
} else if (columnConfig.getTypeEnum() == LOAD_DATA_TYPE.UUID) {
valueConfig.setType(columnConfig.getType());
if ("NULL".equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
valueConfig.setValue(null);
} else {
valueConfig.setValue(value);
}
} else if (columnConfig.getType().equalsIgnoreCase(LOAD_DATA_TYPE.OTHER.toString())) {
valueConfig.setType(columnConfig.getType());
if ("NULL".equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
valueConfig.setValue(null);
} else {
valueConfig.setValue(value);
}
} else if (columnConfig.getTypeEnum() == LOAD_DATA_TYPE.UNKNOWN) {
// columnConfig did not match a specific type
valueConfig.setValue(value);
} else {
throw new UnexpectedLiquibaseException(
String.format(coreBundle.getString("loaddata.type.is.not.supported"),
columnConfig.getType()
)
);
}
} else {
// No columnConfig found. Assume header column name to be the table column name.
if (columnName.contains("(") || (columnName.contains(")") && (database instanceof
AbstractJdbcDatabase))) {
columnName = ((AbstractJdbcDatabase) database).quoteObject(columnName, Column.class);
}
valueConfig.setName(columnName);
valueConfig.setValue(getValueToWrite(value));
}
columnsFromCsv.add(valueConfig);
}
// end of: iterate through all the columns of a CSV line
// 检测是否可以使用prepared statements方式插入数据。
// Try to use prepared statements if any of the following conditions apply:
// 1. There is no other option than using a prepared statement (e.g. in cases of LOBs) regardless
// of whether the 'usePreparedStatement' is set to false
// 2. The database supports batched statements (for improved performance) AND we are not in an
// "SQL" mode (i.e. we generate an SQL file instead of actually modifying the database).
// BUT: if the user specifically requests usePreparedStatement=false, then respect that
boolean actuallyUsePreparedStatements = false;
if (hasPreparedStatementsImplemented()) {
if (usePreparedStatements != null) {
if (!usePreparedStatements && needsPreparedStatement) {
throw new UnexpectedLiquibaseException("loadData is requesting usePreparedStatements=false but prepared statements are required");
}
actuallyUsePreparedStatements = usePreparedStatements;
} else {
actuallyUsePreparedStatements = needsPreparedStatement || (!isLoggingExecutor(database) && preferPreparedStatements(database));
}
}
rows.add(new LoadDataRowConfig(actuallyUsePreparedStatements, columnsFromCsv));
}
// 根据每行数据对象生成具体的SqlStatement数组并返回
return generateStatementsFromRows(database, rows);
} catch (CsvMalformedLineException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error parsing " + getRelativeTo() + " on line " + e.getLineNumber() + ": " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException | LiquibaseException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (UnexpectedLiquibaseException ule) {
if ((getChangeSet() != null) && (getChangeSet().getFailOnError() != null) && !getChangeSet()
.getFailOnError()) {
LOG.info("Changeset " + getChangeSet().toString(false) +
" failed, but failOnError was false. Error: " + ule.getMessage());
return SqlStatement.EMPTY_SQL_STATEMENT;
} else {
throw ule;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// Do nothing
}流程简化后如下图所示
自定义实现
经过分析,我们可以从生成具体数据列数组的时候对输入的原始数据做处理。
customChange只能支持键值对传入定义信息。所以通过增加两个参数定义待解密字段和密钥相关信息。
- decryptColumns:用逗号分割待解密数据对应的表头
- decryptionKeyRef:指定环境变量(JVM属性或系统属性)中存储密钥信息的键。例如 DECRYPT_KEY=AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding,MTIzNDU2Nzg5MA==
根据DECRYPT_KEY,我们构建一个Decryption类对象,该类从DECRYPT_KEY获取加密的Transform信息,譬如AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding中可以获取加密算法、工作模、填充模式,后面用逗号分割的base64中获取到加密算法的key和iv向量(可选)的属性。
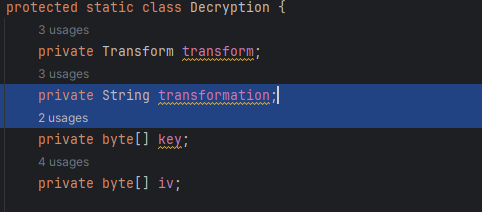
Decryption类的decrypt方法则读取加密文本返回解密数据。
public String decrypt(String text) {
if (isEmpty(text)) {
return null;
}
// convert encrypted text to byte array
byte[] textBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(text);
try {
// create cipher
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(transformation);
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, this.transform.getAlg());
if (null == this.iv || this.iv.length == 0) {
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKeySpec);
} else {
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKeySpec, new IvParameterSpec(iv));
}
// 解密字节数组
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(textBytes);
// 将明文转换为字符串
return new String(decryptedBytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
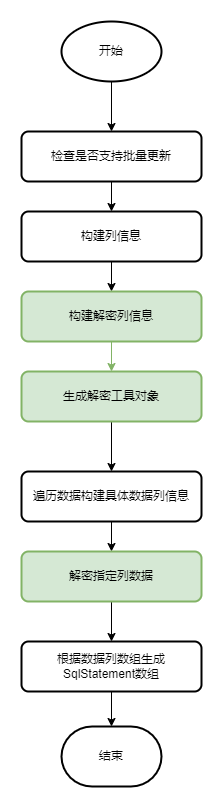
}解密工具准备好,我们可以开始修改主流程了。在构建列信息的时候,我们增加用户定义的解密列信息解析和解密工具类对象的创建。在生成数据列信息数组的时候,保存解密工具对象对加密数据解密后的值。简化流程改变成如如图。
实际演示
Liquibase定义changeset
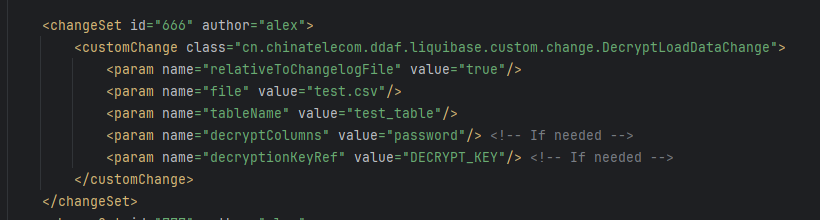
例子数据
"id","name","password"
1,aa,yHAuc7xtopx6haGbBO8CAg==
2,bb,FJUXeYNP6bYbZPDssIZFgw==环境变量
DECRYPT_KEY=AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding,MTIzNDU2Nzg5MDEyMzQ1Ng==
第二个是key(“1234567890123456”)的base64编码
程序启动后,插入解密后数据到数据库。
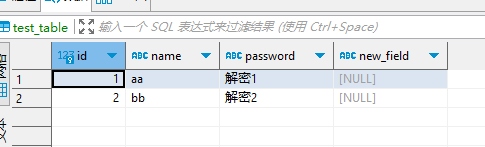
总结
本文基于LoadDataChange源码结合CustomSqlChange的特性,自定义解密工具类,在数据列信息生成过程中根据配置对加密数据解密并生成正确的sqlstatement。解决了liquibase在加载敏感数据的安全问题。
具体实现代码可以私下咨询作者。