ACL介绍
redis 6.0之前只有一个默认用户default,没有用户权限管理,权限比较大,6.0开始有ACL(Access Control List)机制了,即可以给每个用户设置权限,通过给用户设置密码和能访问哪些命令以及key来控制该用户的访问权限,最小粒度的控制该用户的操作内容,提高安全性
具体来说主要有下面几种控制方式:
- 按能否执行某个命令或者某类命令来控制权限,可以细粒度到控制某命令下子命令的权限
- 按能否操作某个key或者某些key(字符串pattern表示一类key)来控制权限
- 用户密码认证
- 启用/禁用用户
- 读写权限控制
- 对订阅或者发布的频道进行权限控制
权限相关数据是保存在acl文件中,该文件保存了所有用户信息,包括该用户的权限信息,或者在没有启用acl控制时,则default用户信息保存在redis.conf中
acl list查看acl规则
gai> ACL LIST --显示用户信息
1) "user default on #ba7816bf8f01cfea414140de5dae2223b00361a396177a9cb410ff61f20015ad ~* +@all"acl list命令是读取users.acl文件中的内容,针对每一行说明如下:
|
参 数 |
说明 |
|
user |
代表是一个用户 |
|
default |
表示默认用户名,或则自己定义的用户名 |
|
on |
表示是否启用该用户,默认为off(禁用) |
|
#... |
表示用户密码,nopass表示不需要密码,#后面的密码是sha256生成的(echo -n passowrd | sha256sum),执行acl save时会将内存中的密码(sha256加密的)写入到该文件中,如果不是以#开头,以>开头的话表示明文密码,启动读取时acl文件时会进行sha256加密,保存到内存中 |
|
~* |
表示可以访问的Key(正则匹配) |
|
+@ |
表示用户的权限,+/-表示授权还是销权; @为权限类。+@all 表示可以执行所有命令,acl cat命令看所有的分类,acl cat category看分类下有哪些命令,如+@set |
|
&* |
表示该用户有权限对所有channel进行订阅或者发布,如针对channel名为test,该用户能否订阅test频道或者往该test频道发布消息 |
|
&test |
表示可以pub/sub test频道,在ACLCheckAllPerm函数中会进行权限校验 |
|
nopass |
表示没有密码认证 |
|
其他 |
看ACLSetUser函数即可,该函数会处理然后保存到User对象中,代表了该User有哪些权限 |
配置用户权限的字段
执行命令:ACL SETUSER myuser +set,表示给该用户添加set命令的权限,其他权限字段如下:
|
权限字段 |
含义 |
|
+<command> |
将命令添加到用户可以调用的命令列表中,如+set、+hset |
|
-<command> |
将命令从用户可以调用的命令列表中移除 |
|
+@<category> |
添加一类命令,如:@admin, @set,@hash ... 可以`ACL CAT` 查看具体的操作指令。特殊类别@all表示所有命令,包括当前在服务器中存在的命令,以及将来将通过模块加载的命令 |
|
-@<category> |
类似+@<category>,从客户端可以调用的命令列表中删除命令 |
|
allcommands |
+@all的别名,允许所有命令操作执行。注意,这意味着可以执行将来通过模块系统加载的所有命令。 |
|
nocommands |
-@all的别名,不允许所有命令操作执行。 |
|
+<command>|subcommand |
允许特定子命令。只能以"+"开头,没有以"-"开头的命令 |
- 允许特定子命令说明
通常来说提供将命令整体加入ACL可执行命令列表或者从列表中删除是不够的,很多Redis命令通过子命令做很多不同的事。例如CLIENT命令可以被用于执行危险或不危险的操作。很多项目部署不会将CLIENT KILL交给非管理员用户执行,但是却允许它们使用CLIENT SETNAME来设置连接用户属性。如:acl setuser myuser -client +client|getname +client|setname, 此时只能执行client getname和client setname命令,其他命令包括client list等命令没有权限执行(默认会加上-@all)
命令和子命令区别

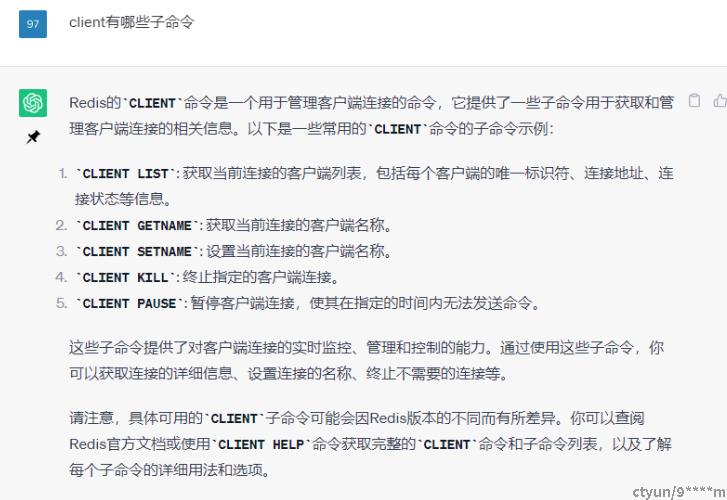
ACL SETUSER myuser -client +client|getname +client|setname,表示myuser用户只有client getname和client setname权限,而没有client其他子命令权限
acl配置的两种方式
- redis.conf中进行配置,如:user default nopass ~* +@all

- aclfile进行配置,即将账号密码保存至users.acl文件中,并把users.acl 路径写入redis.conf
,内容跟上面一样
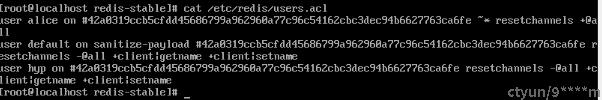
两种方式互斥,不能同时启用,更推荐aclfile方式。因为redis.conf方式加载配置需要重启Redis,而aclfile方式执行acl load即可。
|
对比项 |
redis.conf方式 |
aclfile方式 |
|
加载方式 |
重启redis |
acl load |
|
持久化 |
config rewrite |
acl save |
aclfile配置方式启动redis
- redis.conf启用aclfile,aclfile中配置内容,aclfile和redis.conf中定义的ACL DSL(Domain specific language) 命令不能同时存在,所以为了使用aclfile,需要将redis.conf中末尾的dsl规则(user default xxx)去掉,顺便开启logfile配置,默认不会开启日志
- redis-server ./redis.conf启动即可,此时可以添加用户等操作了,执行acl save可以保存用户到aclfile
权限认证流程
总体流程大概就是,redis启动时,如果redis.conf中配置了aclfile,则启动时读取acl文件,读取每个用户的权限信息,保存到全局Users中,一个User对象保存了该用户支持的权限,密码是什么(sha256加密的),支持的命令和子命令等权限信息,详见User对象数据结构,密码auth认证和命令权限校验认证就会用这个user对象中的权限信息,此外启动时也会创建一个default用户(密码从redis.conf中的requirepass字段来),该用户也会保存在Users对象中,如果acl文件中有default用户,则会优先使用acl文件中的default用户,如果acl文件中没有default用户,则会使用一个nopass的default用户,而不会使用启动时创建的default用户,但如果没有启用aclfile,则会使用redis.conf中的requirepass字段配置的default用户
源码简析
相关数据结构初始化
用户是通过rax前缀压缩树数据结构管理的,可以简单理解rax维护了key->value的映射,同时对前缀相同的字符串只保存一份前缀节省空间,另外可以根据key快速定位到value,该数据结构用于两个地方:
- commandId 全局对象,每个命令会有对应一个命令id,该对象用于根据命令名快速定位到命令id,key是命令名,value是命令id,每次使用时调用ACLGetCommandID函数生成,同时插入到commandId对象中,main -> initServerConfig -> populateCommandTable -> ACLGetCommandID
static rax *commandId = NULL; /* Command name to id mapping */
- Users全局对象,根据用户名快速的定位对应的用户对象(保存了用户权限配置),key是用户名,value是user对象,保存了该用户的权限配置信息
rax *Users; /* Table mapping usernames to user structures. */
typedef struct {
sds name; /* The username as an SDS string. */
uint64_t flags; /* See USER_FLAG_* */
/* The bit in allowed_commands is set if this user has the right to
* execute this command. In commands having subcommands, if this bit is
* set, then all the subcommands are also available.
*
* If the bit for a given command is NOT set and the command has
* subcommands, Redis will also check allowed_subcommands in order to
* understand if the command can be executed. */
// 命令id转换为word和idx,word作为下表,idx作为第几个bit,将该bit设置为1(如果可以执行该命令的话)
uint64_t allowed_commands[USER_COMMAND_BITS_COUNT/64];
/* This array points, for each command ID (corresponding to the command
* bit set in allowed_commands), to an array of SDS strings, terminated by
* a NULL pointer, with all the sub commands that can be executed for
* this command. When no subcommands matching is used, the field is just
* set to NULL to avoid allocating USER_COMMAND_BITS_COUNT pointers. */
sds **allowed_subcommands;
// u->allowed_subcommands[id][items-2] = sdsnew(sub);,指向了能执行的命令
// 密码保存到这里,是一个sha256的加密密码列表,acl文件中如果是明文则sha256生成后插入到该list中
list *passwords; /* A list of SDS valid passwords for this user. */
list *patterns; /* A list of allowed key patterns. If this field is NULL
the user cannot mention any key in a command, unless
the flag ALLKEYS is set in the user. */
// 可发布或者订阅的频道列表,保存的是频道名,表示该用户可以对这些频道进行发布或者订阅
// 在ACLCheckPubsubPerm函数中进行判断的,ACLCheckAllPerm -> ACLCheckPubsubPerm
list *channels; /* A list of allowed Pub/Sub channel patterns. If this
field is NULL the user cannot mention any channel in a
`PUBLISH` or [P][UNSUBSCRIBE] command, unless the flag
ALLCHANNELS is set in the user. */
} user;部分字段说明如下:
|
字段 |
含义 |
|
name |
用户名 |
|
flags |
保存该用户是否启用/禁用,是否nopass,是否可以访问所有命令/所有key等信息 |
|
allowed_commands |
保存该用户是否可以执行该命令,所有可执行的命令保存在redisCommandTable全局变量中,这里是一个位图,下标和值是通过命令id计算得到的,见下文ACLSetUserCommandBit函数 |
|
allowed_subcommands |
三维指针,可以执行的子命令,用于精细化控制,见上文"允许特定子命令说明"部分 |
|
passwords |
该用户的密码列表,可以多个密码 |
|
patterns |
允许访问的key pattern,其中~*是所有key |
ACLLoadFromFile -> ACLSetUser -> ACLSetUserCommandBit函数用于初始化allowed_commands,即保存了命令是否可以被执行,读取acl文件,得到授权的命令(如+@set),通过set查找CommandId得到命令id,然后调用ACLGetCommandBitCoordinates命令id得到word和bit,word作为allowed_commands下标,bit作为某个二进制位,有权限则该bit置1,否则置0
void ACLSetUserCommandBit(user *u, unsigned long id, int value) {
uint64_t word, bit;
if (ACLGetCommandBitCoordinates(id,&word,&bit) == C_ERR) return;
if (value) {
u->allowed_commands[word] |= bit;
} else {
u->allowed_commands[word] &= ~bit;
u->flags &= ~USER_FLAG_ALLCOMMANDS;
}
}ACLGetCommandBitCoordinates是将id转为为word和bit
/* Given a command ID, this function set by reference 'word' and 'bit'
* so that user->allowed_commands[word] will address the right word
* where the corresponding bit for the provided ID is stored, and
* so that user->allowed_commands[word]&bit will identify that specific
* bit. The function returns C_ERR in case the specified ID overflows
* the bitmap in the user representation. */
int ACLGetCommandBitCoordinates(uint64_t id, uint64_t *word, uint64_t *bit) {
if (id >= USER_COMMAND_BITS_COUNT) return C_ERR;
*word = id / sizeof(uint64_t) / 8;
*bit = 1ULL << (id % (sizeof(uint64_t) * 8));
return C_OK;
}commandId全局对象的初始化
commandId是用来通过命令名得到命令id的
struct redisCommand {
char *name;
...
int id; /* 命令的id,Command ID. This is a progressive ID starting from 0 that
is assigned at runtime, and is used in order to check
ACLs. A connection is able to execute a given command if
the user associated to the connection has this command
bit set in the bitmap of allowed commands. */
};id初始化是在populateCommandTable函数中,该函数调用ACLGetCommandID得到每个命令的id:
void populateCommandTable(void) {
int j;
int numcommands = sizeof(redisCommandTable)/sizeof(struct redisCommand);
// 所有命令是定义在全局变量redisCommandTable中
for (j = 0; j < numcommands; j++) {
struct redisCommand *c = redisCommandTable+j;
int retval1, retval2;
/* Translate the command string flags description into an actual
* set of flags. */
if (populateCommandTableParseFlags(c,c->sflags) == C_ERR)
serverPanic("Unsupported command flag");
// 得到每个命令的id
c->id = ACLGetCommandID(c->name); /* Assign the ID used for ACL. */
retval1 = dictAdd(server.commands, sdsnew(c->name), c);
/* Populate an additional dictionary that will be unaffected
* by rename-command statements in redis.conf. */
retval2 = dictAdd(server.orig_commands, sdsnew(c->name), c);
serverAssert(retval1 == DICT_OK && retval2 == DICT_OK);
}
}
ACLGetCommandID函数中传入命令名,返回一个偏序递增的命令id,同时将cmdname和id的映射保存到commandId(Command name to id mapping)全局变量中,该变量也是一个rax变量,相同的命令是用固定的一个id(因为是依次对redisCommandTable中的命令进行处理得到id,nextid初始值为0,即id初始值是从0开始的)
unsigned long ACLGetCommandID(const char *cmdname) {
sds lowername = sdsnew(cmdname);
sdstolower(lowername);
if (commandId == NULL) commandId = raxNew();
void *id = raxFind(commandId,(unsigned char*)lowername,sdslen(lowername));
if (id != raxNotFound) { // 如果已存在则直接返回
sdsfree(lowername);
return (unsigned long)id;
}
raxInsert(commandId,(unsigned char*)lowername,strlen(lowername),
(void*)nextid,NULL);
sdsfree(lowername);
unsigned long thisid = nextid;
nextid++;
/* We never assign the last bit in the user commands bitmap structure,
* this way we can later check if this bit is set, understanding if the
* current ACL for the user was created starting with a +@all to add all
* the possible commands and just subtracting other single commands or
* categories, or if, instead, the ACL was created just adding commands
* and command categories from scratch, not allowing future commands by
* default (loaded via modules). This is useful when rewriting the ACLs
* with ACL SAVE. */
if (nextid == USER_COMMAND_BITS_COUNT-1) nextid++;
return thisid;
}
Users全局对象初始化
main函数会调用到ACLInit函数初始化Users
/* Initialization of the ACL subsystem. */
void ACLInit(void) {
Users = raxNew();
UsersToLoad = listCreate();
ACLLog = listCreate();
ACLInitDefaultUser();
}ACLInitDefaultUser是用来创建default用户的:
/* Initialize the default user, that will always exist for all the process
* lifetime. */
void ACLInitDefaultUser(void) {
DefaultUser = ACLCreateUser("default",7);
ACLSetUser(DefaultUser,"+@all",-1);
ACLSetUser(DefaultUser,"~*",-1);
ACLSetUser(DefaultUser,"&*",-1);
ACLSetUser(DefaultUser,"on",-1);
ACLSetUser(DefaultUser,"nopass",-1);
}接着main会调用ACLLoadUsersAtStartup函数,从redis.conf或者aclfile中加载用户信息:
/* This function is called once the server is already running, modules are
* loaded, and we are ready to start, in order to load the ACLs either from
* the pending list of users defined in redis.conf, or from the ACL file.
* The function will just exit with an error if the user is trying to mix
* both the loading methods. */
void ACLLoadUsersAtStartup(void) {
if (server.acl_filename[0] != '\0' && listLength(UsersToLoad) != 0) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Configuring Redis with users defined in redis.conf and at "
"the same setting an ACL file path is invalid. This setup "
"is very likely to lead to configuration errors and security "
"holes, please define either an ACL file or declare users "
"directly in your redis.conf, but not both.");
exit(1);
}
if (ACLLoadConfiguredUsers() == C_ERR) { // 从redis.conf加载user信息
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Critical error while loading ACLs. Exiting.");
exit(1);
}
if (server.acl_filename[0] != '\0') {
sds errors = ACLLoadFromFile(server.acl_filename); // 从aclfile加载user信息
if (errors) {
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Aborting Redis startup because of ACL errors: %s", errors);
sdsfree(errors);
exit(1);
}
}
}
ACLLoadConfiguredUsers和ACLLoadFromFile都会调用ACLCreateUser函数创建user对象并插入到全局变量Users中去
allowed_subcommands初始化
当acl setuser命令中有添加子命令参数时,如:
acl setuser myuser -client +client|getname +client|setname,
会调用到ACLSetUser,接着会调用ACLAddAllowedSubcommand函数,该函数中会初始化allowed_subcommands,保存可以执行的子命令
密码认证
启用用户密码后,用户连接到redis,默认是未认证状态,此时用户访问redis,会提示没有权限:
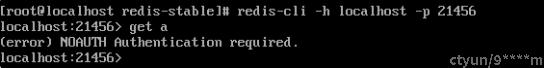
redis是在processCommand函数处理用户普通命令的,判断是否有认证,上面输出就是在该函数中返回的:
int processCommand(client *c) {
...
/* Check if the user is authenticated. This check is skipped in case
* the default user is flagged as "nopass" and is active. */
int auth_required = (!(DefaultUser->flags & USER_FLAG_NOPASS) ||
(DefaultUser->flags & USER_FLAG_DISABLED)) &&
!c->authenticated; // 还未认证
if (auth_required) {
/* AUTH and HELLO and no auth modules are valid even in
* non-authenticated state. */
if (!(c->cmd->flags & CMD_NO_AUTH)) {
rejectCommand(c,shared.noautherr); // 输出NOAUTH Authentication required
return C_OK;
}
}
...
}一旦用户执行auth username password命令认证后,就会设置c->authenticated为1,表示密码认证成功,具体调用流程为:authCommand -> ACLAuthenticateUser -> ACLCheckUserCredentials
int ACLAuthenticateUser(client *c, robj *username, robj *password) {
if (ACLCheckUserCredentials(username,password) == C_OK) {
c->authenticated = 1;
c->user = ACLGetUserByName(username->ptr,sdslen(username->ptr));
moduleNotifyUserChanged(c);
return C_OK;
} else {
addACLLogEntry(c,ACL_DENIED_AUTH,0,username->ptr);
return C_ERR;
}
}会调用ACLCheckUserCredentials校验密码,通过用户名查找到user对象,得到配置的密码列表,然后进行匹配校验
/* Check the username and password pair and return C_OK if they are valid,
* otherwise C_ERR is returned and errno is set to:
*
* EINVAL: if the username-password do not match.
* ENONENT: if the specified user does not exist at all.
*/
int ACLCheckUserCredentials(robj *username, robj *password) {
user *u = ACLGetUserByName(username->ptr,sdslen(username->ptr));
if (u == NULL) {
errno = ENOENT;
return C_ERR;
}
/* Disabled users can't login. */
if (u->flags & USER_FLAG_DISABLED) {
errno = EINVAL;
return C_ERR;
}
/* If the user is configured to don't require any password, we
* are already fine here. */
if (u->flags & USER_FLAG_NOPASS) return C_OK;
/* Check all the user passwords for at least one to match. */
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
listRewind(u->passwords,&li);
// 将用户密码转换为sha256加密密码进行比较,因为u->passwords中保存的也是sha256加密密码
sds hashed = ACLHashPassword(password->ptr,sdslen(password->ptr));
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
sds thispass = listNodeValue(ln);
if (!time_independent_strcmp(hashed, thispass)) {
sdsfree(hashed);
return C_OK;
}
}
sdsfree(hashed);
/* If we reached this point, no password matched. */
errno = EINVAL;
return C_ERR;
}
其中ACLGetUserByName函数就是从全局变量Users中查找到该用户的user对象(保存了权限配置)
/* Return an username by its name, or NULL if the user does not exist. */
user *ACLGetUserByName(const char *name, size_t namelen) {
void *myuser = raxFind(Users,(unsigned char*)name,namelen);
if (myuser == raxNotFound) return NULL;
return myuser;
}访问的命令和key权限认证
权限校验函数:acl.c中的ACLCheckAllPerm,校验是否有权限,在三个地方会被调用:
- scripting.c: luaRedisGenericCommand函数,redis调用lua脚本会调用
- multi.c: execCommand函数, 执行事务命令会调用
- server.c: processCommand函数,执行普通命令会调用
ACLCheckAllPerm会调用ACLCheckCommandPerm函数进行
/* Check if the command is ready to be executed in the client 'c', already
* referenced by c->cmd, and can be executed by this client according to the
* ACLs associated to the client user c->user.
*
* If the user can execute the command ACL_OK is returned, otherwise
* ACL_DENIED_CMD or ACL_DENIED_KEY is returned: the first in case the
* command cannot be executed because the user is not allowed to run such
* command, the second if the command is denied because the user is trying
* to access keys that are not among the specified patterns. */
int ACLCheckCommandPerm(client *c, int *keyidxptr) {
user *u = c->user;
uint64_t id = c->cmd->id;
/* If there is no associated user, the connection can run anything. */
if (u == NULL) return ACL_OK;
/* Check if the user can execute this command or if the command
* doesn't need to be authenticated (hello, auth). */
if (!(u->flags & USER_FLAG_ALLCOMMANDS) && !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_NO_AUTH))
{
/* If the bit is not set we have to check further, in case the
* command is allowed just with that specific subcommand. */
if (ACLGetUserCommandBit(u,id) == 0) { // 如果该命令没有在allowed_commands中设置
/* Check if the subcommand matches. */
if (c->argc < 2 ||
u->allowed_subcommands == NULL ||
u->allowed_subcommands[id] == NULL)
{
return ACL_DENIED_CMD;
}
long subid = 0;
while (1) { // 遍历子命令,判断子命令是否可执行
if (u->allowed_subcommands[id][subid] == NULL)
return ACL_DENIED_CMD;
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[1]->ptr,
u->allowed_subcommands[id][subid]))
break; /* Subcommand match found. Stop here. */
subid++;
}
}
}
/* Check if the user can execute commands explicitly touching the keys
* mentioned in the command arguments. */
// 下面是进行key的pattern判断
if (!(c->user->flags & USER_FLAG_ALLKEYS) &&
(c->cmd->getkeys_proc || c->cmd->firstkey))
{
getKeysResult result = GETKEYS_RESULT_INIT;
int numkeys = getKeysFromCommand(c->cmd,c->argv,c->argc,&result);
int *keyidx = result.keys;
for (int j = 0; j < numkeys; j++) {
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
listRewind(u->patterns,&li);
/* Test this key against every pattern. */
int match = 0;
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
sds pattern = listNodeValue(ln);
size_t plen = sdslen(pattern);
int idx = keyidx[j];
if (stringmatchlen(pattern,plen,c->argv[idx]->ptr,
sdslen(c->argv[idx]->ptr),0))
{
match = 1;
break;
}
}
if (!match) {
if (keyidxptr) *keyidxptr = keyidx[j];
getKeysFreeResult(&result);
return ACL_DENIED_KEY;
}
}
getKeysFreeResult(&result);
}
/* If we survived all the above checks, the user can execute the
* command. */
return ACL_OK;
}int ACLGetUserCommandBit(user *u, unsigned long id) {
uint64_t word, bit;
if (ACLGetCommandBitCoordinates(id,&word,&bit) == C_ERR) return 0;
return (u->allowed_commands[word] & bit) != 0;
}上面代码总结如下:
- ACL限制围绕user的各个字段进行
- 全局的flag优先级最高,例如设置为所有键可用,所有命令可用,会跳过后续的可用命令遍历和可用键Pattern匹配
- 即使在allowed_commands位图中没有被置位,命令也可能可用,因为它是个子命令,而且命令只开放了部分子命令的使用权限
- 键通过遍历所有定义了的Pattern检查,如果有匹配上说明可用
- 先判断操作是否可用,再判断键(包括全局flag也在操作之后)是否可用,两种判断分别对应不同返回整数值:ACL_DENIED_CMD、ACL_DENIED_KEY
其他点说明
- aclfile中密码是用sha256加密的,保存的密码为: echo -n passowrd | sha256sum的输出,前面还加一个#字符,即为aclfile文件中的密码,sha256算法不可逆,aclfile支持明文密码,执行acl save时会将User对象数据保存到acl文件中,因为user对象中密码是一个sha256加密的,所以写到文件中也是加密的
- acl setuser default +set表示可以执行set这个命令,acl setuser default +@set,表示可以执行set集合的所有命令,即acl cat set输出的所有命令
- 注意命令可能同时属于不同的类别,所以ACL规则例如+@geo -@readonly会导致特定的geo命令被排除,因为它们也属于readonly类别。