前沿
Prometheus 是一种开源的监控系统,用于记录和查询系统的各种指标。Prometheus 可以通过其自身的存储方式存储指标数据,也可以通过远程存储实现长期存储。
Prometheus 远程存储允许将指标数据存储到第三方存储系统中,例如 Amazon S3、Google Cloud Storage 或 OpenStack Swift。这种存储方式可以用于长期存储,以便进行更长时间范围内的数据分析。整体架构图如下:
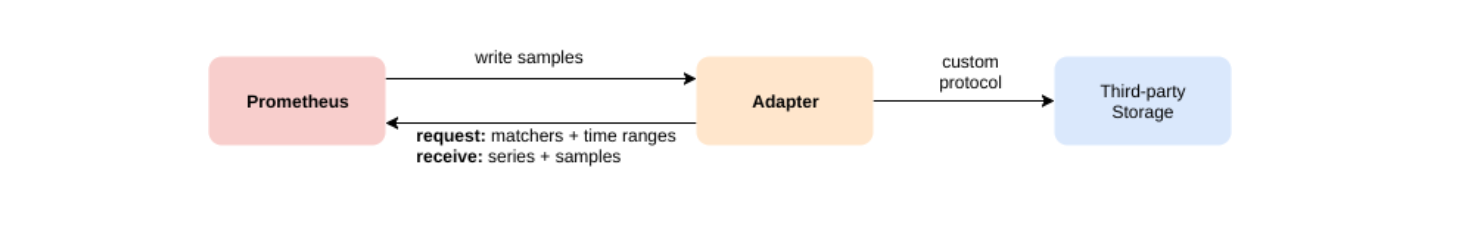
Prometheus接口规范
数据写入

Prometheus 远程写入数据的格式是 protobuf 格式。Prometheus server 将内存数据库中的指标数据按照时间序列进行组织,并将其编码为 protobuf 格式。
protobuf 格式是一种二进制格式,它可以将复杂的数据结构进行高效的编码和解码。在 Prometheus 中,protobuf 格式被用来表示时间序列和标签。时间序列是一组带有相同标签的数据点,其中标签是键值对,用于区分不同的时间序列。
Prometheus server 会将时间序列和标签编码为 protobuf 格式,并通过 HTTP 协议发送到远程存储系统中。远程存储系统接收到请求后,会将请求中的数据解码,并将其存储在其自身的存储系统中。在查询时,Prometheus server 会向远程存储系统发送 HTTP GET 请求,并解码从远程存储系统返回的 protobuf 编码的数据。
总之,Prometheus 远程写入数据的格式是 protobuf 格式,它可以将复杂的数据结构进行高效的编码和解码,并实现了将指标数据存储到第三方存储系统中的功能。
WriteRequest数据格式
type WriteRequest struct {
Timeseries []TimeSeries `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=timeseries,proto3" json:"timeseries"`
Metadata []MetricMetadata `protobuf:"bytes,3,rep,name=metadata,proto3" json:"metadata"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
TimeSeries数据格式
type TimeSeries struct {
// For a timeseries to be valid, and for the samples and exemplars
// to be ingested by the remote system properly, the labels field is required.
Labels []Label `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=labels,proto3" json:"labels"`
Samples []Sample `protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=samples,proto3" json:"samples"`
Exemplars []Exemplar `protobuf:"bytes,3,rep,name=exemplars,proto3" json:"exemplars"`
Histograms []Histogram `protobuf:"bytes,4,rep,name=histograms,proto3" json:"histograms"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
数据读取

远程数据读取是指从Prometheus服务器连接到远程目标,并直接读取其指标数据。当用户发起查询请求后,Promthues将向remote_read中配置的URL发起查询请求(matchers,ranges),Adaptor根据请求条件从第三方存储服务中获取响应的数据。同时将数据转换为Promthues的原始样本数据返回给Prometheus Server。
主要的数据结构如下
type ReadRequest struct {
Queries []*Query `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=queries,proto3" json:"queries,omitempty"`
// accepted_response_types allows negotiating the content type of the response.
//
// Response types are taken from the list in the FIFO order. If no response type in `accepted_response_types` is
// implemented by server, error is returned.
// For request that do not contain `accepted_response_types` field the SAMPLES response type will be used.
AcceptedResponseTypes []ReadRequest_ResponseType `protobuf:"varint,2,rep,packed,name=accepted_response_types,json=acceptedResponseTypes,proto3,enum=prometheus.ReadRequest_ResponseType" json:"accepted_response_types,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
type Query struct {
StartTimestampMs int64 `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=start_timestamp_ms,json=startTimestampMs,proto3" json:"start_timestamp_ms,omitempty"`
EndTimestampMs int64 `protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=end_timestamp_ms,json=endTimestampMs,proto3" json:"end_timestamp_ms,omitempty"`
Matchers []*LabelMatcher `protobuf:"bytes,3,rep,name=matchers,proto3" json:"matchers,omitempty"`
Hints *ReadHints `protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=hints,proto3" json:"hints,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
type ReadHints struct {
StepMs int64 `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=step_ms,json=stepMs,proto3" json:"step_ms,omitempty"`
Func string `protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=func,proto3" json:"func,omitempty"`
StartMs int64 `protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=start_ms,json=startMs,proto3" json:"start_ms,omitempty"`
EndMs int64 `protobuf:"varint,4,opt,name=end_ms,json=endMs,proto3" json:"end_ms,omitempty"`
Grouping []string `protobuf:"bytes,5,rep,name=grouping,proto3" json:"grouping,omitempty"`
By bool `protobuf:"varint,6,opt,name=by,proto3" json:"by,omitempty"`
RangeMs int64 `protobuf:"varint,7,opt,name=range_ms,json=rangeMs,proto3" json:"range_ms,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
type ReadResponse struct {
// In same order as the request's queries.
Results []*QueryResult `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=results,proto3" json:"results,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
type QueryResult struct {
// Samples within a time series must be ordered by time.
Timeseries []*TimeSeries `protobuf:"bytes,1,rep,name=timeseries,proto3" json:"timeseries,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
通过ReadRequest 我们可以知道请求的起始时间,labelMathcer,rangeMs,group等信息,拿到这些信息之后,我们就可以根据远程存储的特点,读取远程存储的数据,返回ReadResponse 给Prometheus。
总结
从上述分析看,实现Prometheus远程存储适配工作量并不大。目前Prometheus社区也提供了部分对于第三方数据库的Remote Storage支持:

VictoriaMetrics、Thanos也可以用来作为Prometheus的远程存储。这些解决方案允许将Prometheus的指标数据存储在远程位置,以实现高可用性、扩展性和持久性。选择适合的远程存储方案取决于你的需求和环境。