情感分析:使用循环神经网络
与词相似度和类比任务一样,我们也可以将预先训练的词向量应用于情感分析。由于 :numref:sec_sentiment中的IMDb评论数据集不是很大,使用在大规模语料库上预训练的文本表示可以减少模型的过拟合。我们将使用预训练的GloVe模型来表示每个词元,并将这些词元表示送入多层双向循环神经网络以获得文本序列表示,该文本序列表示将被转换为情感分析输出。对于相同的下游应用,我们稍后将考虑不同的架构选择。
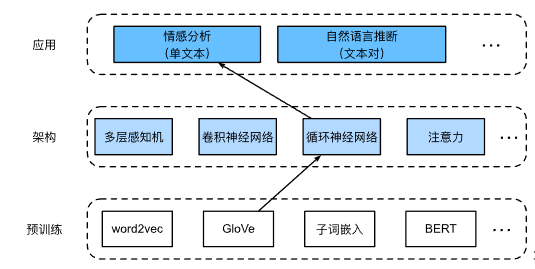
使用循环神经网络表示单个文本
在文本分类任务(如情感分析)中,可变长度的文本序列将被转换为固定长度的类别。在下面的BiRNN类中,虽然文本序列的每个词元经由嵌入层(self.embedding)获得其单独的预训练GloVe表示,但是整个序列由双向循环神经网络(self.encoder)编码。更具体地说,双向长短期记忆网络在初始和最终时间步的隐状态(在最后一层)被连结起来作为文本序列的表示。然后,通过一个具有两个输出(“积极”和“消极”)的全连接层(self.decoder),将此单一文本表示转换为输出类别。
import os
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
d2l.DATA_HUB['aclImdb'] = (
'http:///~amaas/data/sentiment/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz',
'01ada507287d82875905620988597833ad4e0903')
data_dir = d2l.download_extract('aclImdb', 'aclImdb')
def read_imdb(data_dir, is_train):
"""读取IMDb评论数据集文本序列和标签"""
data, labels = [], []
for label in ('pos', 'neg'):
folder_name = os.path.join(data_dir, 'train' if is_train else 'test',
label)
for file in os.listdir(folder_name):
with open(os.path.join(folder_name, file), 'rb') as f:
review = f.read().decode('utf-8').replace('\n', '')
data.append(review)
labels.append(1 if label == 'pos' else 0)
return data, labels
train_data = read_imdb(data_dir, is_train=True)
print('训练集数目:', len(train_data[0]))
for x, y in zip(train_data[0][:3], train_data[1][:3]):
print('标签:', y, 'review:', x[0:60])
train_tokens = d2l.tokenize(train_data[0], token='word')
vocab = d2l.Vocab(train_tokens, min_freq=5, reserved_tokens=['<pad>'])
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.xlabel('# tokens per review')
d2l.plt.ylabel('count')
d2l.plt.hist([len(line) for line in train_tokens], bins=range(0, 1000, 50));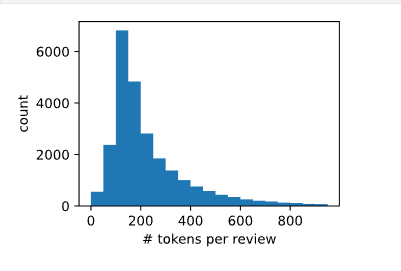
num_steps = 500 # 序列长度
train_features = torch.tensor([d2l.truncate_pad(
vocab[line], num_steps, vocab['<pad>']) for line in train_tokens])
print(train_features.shape)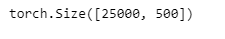
train_iter = d2l.load_array((train_features,
torch.tensor(train_data[1])), 64)
for X, y in train_iter:
print('X:', X.shape, ', y:', y.shape)
break
print('小批量数目:', len(train_iter))
#@save
def load_data_imdb(batch_size, num_steps=500):
"""返回数据迭代器和IMDb评论数据集的词表"""
data_dir = d2l.download_extract('aclImdb', 'aclImdb')
train_data = read_imdb(data_dir, True)
test_data = read_imdb(data_dir, False)
train_tokens = d2l.tokenize(train_data[0], token='word')
test_tokens = d2l.tokenize(test_data[0], token='word')
vocab = d2l.Vocab(train_tokens, min_freq=5)
train_features = torch.tensor([d2l.truncate_pad(
vocab[line], num_steps, vocab['<pad>']) for line in train_tokens])
test_features = torch.tensor([d2l.truncate_pad(
vocab[line], num_steps, vocab['<pad>']) for line in test_tokens])
train_iter = d2l.load_array((train_features, torch.tensor(train_data[1])),
batch_size)
test_iter = d2l.load_array((test_features, torch.tensor(test_data[1])),
batch_size,
is_train=False)
return train_iter, test_iter, vocabimport torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 64
train_iter, test_iter, vocab = d2l.load_data_imdb(batch_size)
class BiRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_size, num_hiddens,
num_layers, **kwargs):
super(BiRNN, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_size)
# 将bidirectional设置为True以获取双向循环神经网络
self.encoder = nn.LSTM(embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers=num_layers,
bidirectional=True)
self.decoder = nn.Linear(4 * num_hiddens, 2)
def forward(self, inputs):
# inputs的形状是(批量大小,时间步数)
# 因为长短期记忆网络要求其输入的第一个维度是时间维,
# 所以在获得词元表示之前,输入会被转置。
# 输出形状为(时间步数,批量大小,词向量维度)
embeddings = self.embedding(inputs.T)
self.encoder.flatten_parameters()
# 返回上一个隐藏层在不同时间步的隐状态,
# outputs的形状是(时间步数,批量大小,2*隐藏单元数)
outputs, _ = self.encoder(embeddings)
# 连结初始和最终时间步的隐状态,作为全连接层的输入,
# 其形状为(批量大小,4*隐藏单元数)
encoding = torch.cat((outputs[0], outputs[-1]), dim=1)
outs = self.decoder(encoding)
return outs
embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers = 100, 100, 2
devices = d2l.try_all_gpus()
net = BiRNN(len(vocab), embed_size, num_hiddens, num_layers)
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
if type(m) == nn.LSTM:
for param in m._flat_weights_names:
if "weight" in param:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m._parameters[param])
net.apply(init_weights);
glove_embedding = d2l.TokenEmbedding('glove.6b.100d')
embeds = glove_embedding[vocab.idx_to_token]
embeds.shape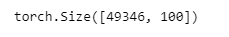
net.embedding.weight.data.copy_(embeds)
net.embedding.weight.requires_grad = False
lr, num_epochs = 0.01, 5
trainer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction="none")
loss_acc_value_list = d2l.train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs,
devices)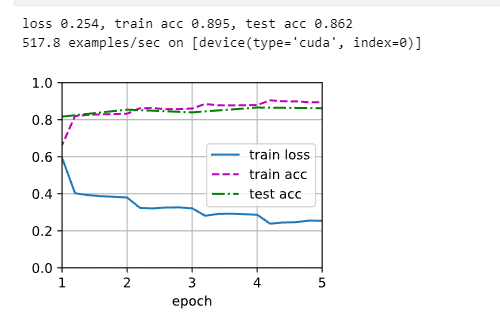
此外,本文将画图放在一个新的visdom中
查看教程pytorch训练可视化包visdom的使用
import numpy as np
import visdom
viz = visdom.Visdom(env='main-12')
name_1 = 'train loss'
name_2 = 'train acc'
name_3 = 'test acc'
window_loss_acc = viz.line(
X=[0], # x坐标
Y=[0], # y值
win="train_acc_1", # 窗口id
name= name_1, # 线条名称
update='append', # 以添加方式加入
opts={
'showlegend': True, # 显示网格
'title': "Bi-RNN LOSS & ACC",
'xlabel': "epoch", # x轴标签
'ylabel': "value", # y轴标签
},)
#[
# [epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches, (metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[3], None) ]
# [epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc) ]
# ]
vaa = "replace"
for i in loss_acc_value_list:
x_value = i[0]
if i[1][-1] == None:
loss_value = i[1][0]
train_value = i[1][1]
# 画图
viz.line(X=[x_value], Y=[loss_value],name=name_1, win=window_loss_acc, update=vaa)
viz.line(X=[x_value], Y=[train_value],name=name_2, win=window_loss_acc, update=vaa)
else:
test_value = i[1][-1]
# 画图
viz.line(X=[x_value], Y=[test_value],name=name_3, win=window_loss_acc, update=vaa)
vaa = 'append'为了让上面得工作顺利进行,还需要更改函数:
def train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs,
devices=d2l.try_all_gpus()):
"""Train a model with mutiple GPUs (defined in Chapter 13).
Defined in :numref:`sec_image_augmentation`"""
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0, 1],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
net = nn.DataParallel(net, device_ids=devices).to(devices[0])
# 新增----------下面
epoch_idx_list = []
# 新增----------上面
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# Sum of training loss, sum of training accuracy, no. of examples,
# no. of predictions
metric = d2l.Accumulator(4)
for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
l, acc = train_batch_ch13(
net, features, labels, loss, trainer, devices)
metric.add(l, acc, labels.shape[0], labels.numel())
timer.stop()
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,(metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[3],None))
# 新增----------下面
epoch_idx_list.append([epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,(metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[3],None)])
# 新增----------上面
test_acc = d2l.evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
# 新增----------下面
epoch_idx_list.append([epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc)])
# 新增----------上面
print(f'loss {metric[0] / metric[2]:.3f}, train acc '
f'{metric[1] / metric[3]:.3f}, test acc {test_acc:.3f}')
print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec on '
f'{str(devices)}')
# 新增----------下面
return epoch_idx_list
# 新增----------上面在虚拟环境中,通过python -m visdom.server启动visdom
最后visdom中结果显示为:
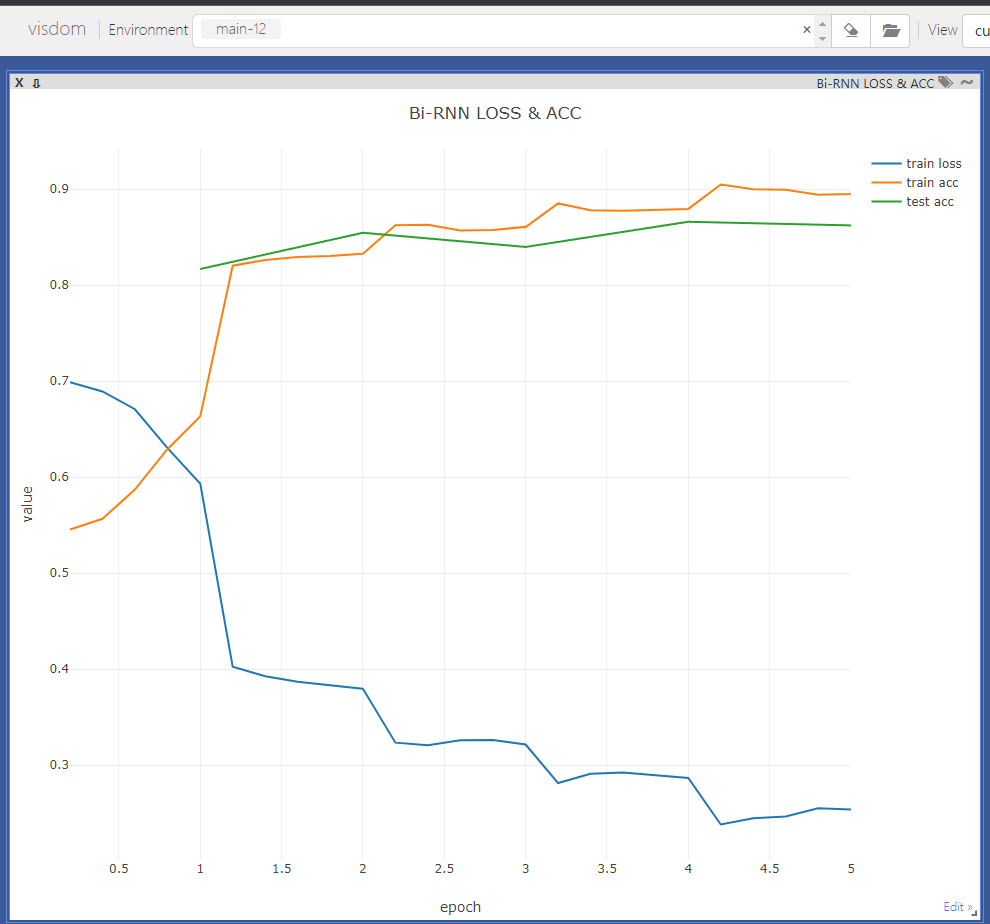
#@save
def predict_sentiment(net, vocab, sequence):
"""预测文本序列的情感"""
sequence = torch.tensor(vocab[sequence.split()], device=d2l.try_gpu())
label = torch.argmax(net(sequence.reshape(1, -1)), dim=1)
return 'positive' if label == 1 else 'negative'
predict_sentiment(net, vocab, 'this movie is so great')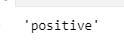
predict_sentiment(net, vocab, 'this movie is so bad')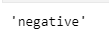
小结
- 预训练的词向量可以表示文本序列中的各个词元。
- 双向循环神经网络可以表示文本序列。例如通过连结初始和最终时间步的隐状态,可以使用全连接的层将该单个文本表示转换为类别。

