Java clone深浅拷贝
对象的clone方法是一个native本地方法,由jvm底层实现,效率高。要想调用对象的clone方法必须实现Cloneable接口,且父类也必须实现,一直向上传递到Object.clone本地方法。
浅拷贝
Object自带了一个protected Object clone()方法,但是我们直接去调用的时候发现是调用不了的,我们需要实现Cloneable接口并调用父类的clone()方法,我建立了一个Animal类进行测试,分别声明了一个基本数据类型的和一个引用类型的成员变量。
class Animal implements Cloneable{
//基本数据类型
String name;
//引用类型
StringBuilder desc = new StringBuilder();
/**
* 浅拷贝(基本数据类型成功(常量),对象是引用拷贝)
* @return
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException
*/
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", desc=" + desc +
'}';
}
}
我们调用clone()方法并进行修改测试
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Animal animal = new Animal();
animal.name = "test animal";
animal.desc.append("test desc");
System.out.println(animal);
Animal cloneObject = null;
try {
cloneObject = (Animal) animal.clone();
System.out.println(cloneObject);
}catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//modify content
animal.name += " modified";
animal.desc.append(" modified");
System.out.println("modified data bellow");
System.out.println(animal);
System.out.println(cloneObject);
}
}
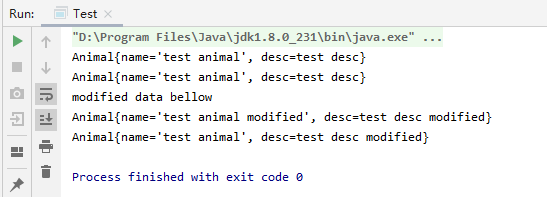
我们可以发现,复制过后,我们修改原始对象,复制出的对象的基本数据类型name是没有改变值的,而引用类型的desc内容跟随着变化了,因为是引用的同一个对象。
深拷贝
由于clone()这个本地方法是浅拷贝的,如果需要进行深拷贝,需要我们进行重写并手动对引用类型的变量进行拷贝(如果这个对象是我们自己写的,那就对这个对象的类也实现clone接口,直接调用这个独享的clone进行复制,不再手动复制,一些系统提供的且没有实现Cloneable接口的我们就手动new复制)。
class Animal implements Cloneable{
//基本数据类型
String name;
//引用类型
StringBuilder desc = new StringBuilder();
/**
* 深拷贝(基本数据类型成功(常量),对象拷贝手动进行)
* @return
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException
*/
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Animal animal = (Animal) super.clone();
//对引用类型的对象手动拷贝
animal.desc = new StringBuilder(animal.desc.toString());
return animal;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", desc=" + desc +
'}';
}
}
我们测试一下
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Animal animal = new Animal();
animal.name = "test animal";
animal.desc.append("test desc");
System.out.println(animal);
Animal cloneObject = null;
try {
cloneObject = (Animal) animal.clone();
System.out.println(cloneObject);
}catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//modify content
animal.name += " modified";
animal.desc.append(" modified");
System.out.println("modified data bellow");
System.out.println(animal);
System.out.println(cloneObject);
}
}

对象流实现深拷贝
对于一些复杂的对象我们直接使用对象流来实现深拷贝
import java.io.*;
class Animal implements Cloneable,Serializable{
//基本数据类型
String name;
//引用类型
StringBuilder desc = new StringBuilder();
/**
* 深拷贝(基本数据类型成功(常量),对象拷贝手动进行)
* @return
* @throws CloneNotSupportedException
*/
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
outputStream.writeObject(this);
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()));
return inputStream.readObject();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", desc=" + desc +
'}';
}
}
测试
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Animal animal = new Animal();
animal.name = "test animal";
animal.desc.append("test desc");
System.out.println(animal);
Animal cloneObject = null;
try {
cloneObject = (Animal) animal.clone();
System.out.println(cloneObject);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//modify content
animal.name += " modified";
animal.desc.append(" modified");
System.out.println("modified data bellow");
System.out.println(animal);
System.out.println(cloneObject);
}
}


