上次说到通过mybatis-collection机制,将数据库中的一对多数据映射为Java对象GenTable,之后又是如何一步一步的生成预览代码的呢?
我们注意到GenTable中有一个字段名为tplCategory,它可取值crud, tree,sub,分别表示
crud:单表;tree:树表操作;sub:主子表。暂未涉及,按下不表[手动狗头]。模板引擎 Velocity
后续代码执行到:
VelocityInitializer.initVelocity();这一句执行中,引入了一个第三方的类库org.apache.velocity.app.Velocity。经过询问度娘与谷哥,我们知道这是一个模板引擎。
通过简单阅读Velocity文档,了解到它可以通过配置模板并配合java代码实现后续内容填充。比如在掘金网站上有一篇博客介绍了如何使用Velocity:Velocity开发指南,例如,模板文件hello.vm中内容为:
Hi! This $name from the $project project.通过对name与project赋值,我们可以生成想要的内容。
/* 首先,初始化运行时引擎,使用默认的配置 */
Velocity.init();
/* 创建Context对象,然后把数据放进去 */
VelocityContext context = new VelocityContext();
context.put("name", "Velocity");
context.put("project", "Jakarta");
/* 渲染模板 */
StringWriter w = new StringWriter();
Velocity.mergeTemplate("testtemplate.vm", context, w );
System.out.println(" template : " + w );然后,自然而然的下一步就是构造Velocity的数据以及获取模板。构造数据代码如下所示:
/**
* 设置模板变量信息
*
* @return 模板列表
*/
public static VelocityContext prepareContext(GenTable genTable)
{
// 省略代码......
VelocityContext velocityContext = new VelocityContext();
velocityContext.put("tplCategory", genTable.getTplCategory());
velocityContext.put("tableName", genTable.getTableName());
velocityContext.put("functionName", StringUtils.isNotEmpty(functionName) ? functionName : "【请填写功能名称】");
velocityContext.put("ClassName", genTable.getClassName());
// 省略代码......
return velocityContext;
}寻找模板代码如下:
List<String> templates = new ArrayList<String>();
templates.add("vm/java/domain.java.vm");
templates.add("vm/java/mapper.java.vm");
templates.add("vm/java/service.java.vm");
templates.add("vm/java/serviceImpl.java.vm");
templates.add("vm/java/controller.java.vm");
templates.add("vm/xml/mapper.xml.vm");
templates.add("vm/sql/sql.vm");
templates.add("vm/js/api.js.vm");
if (GenConstants.TPL_CRUD.equals(tplCategory))
{
templates.add("vm/vue/index.vue.vm");
}
else if (GenConstants.TPL_TREE.equals(tplCategory))
{
templates.add("vm/vue/index-tree.vue.vm");
}
else if (GenConstants.TPL_SUB.equals(tplCategory))
{
templates.add("vm/vue/index.vue.vm");
templates.add("vm/java/sub-domain.java.vm");
}其中特意根据表类型做了区分,我们来看看其中的domain.java.vm长什么样子?
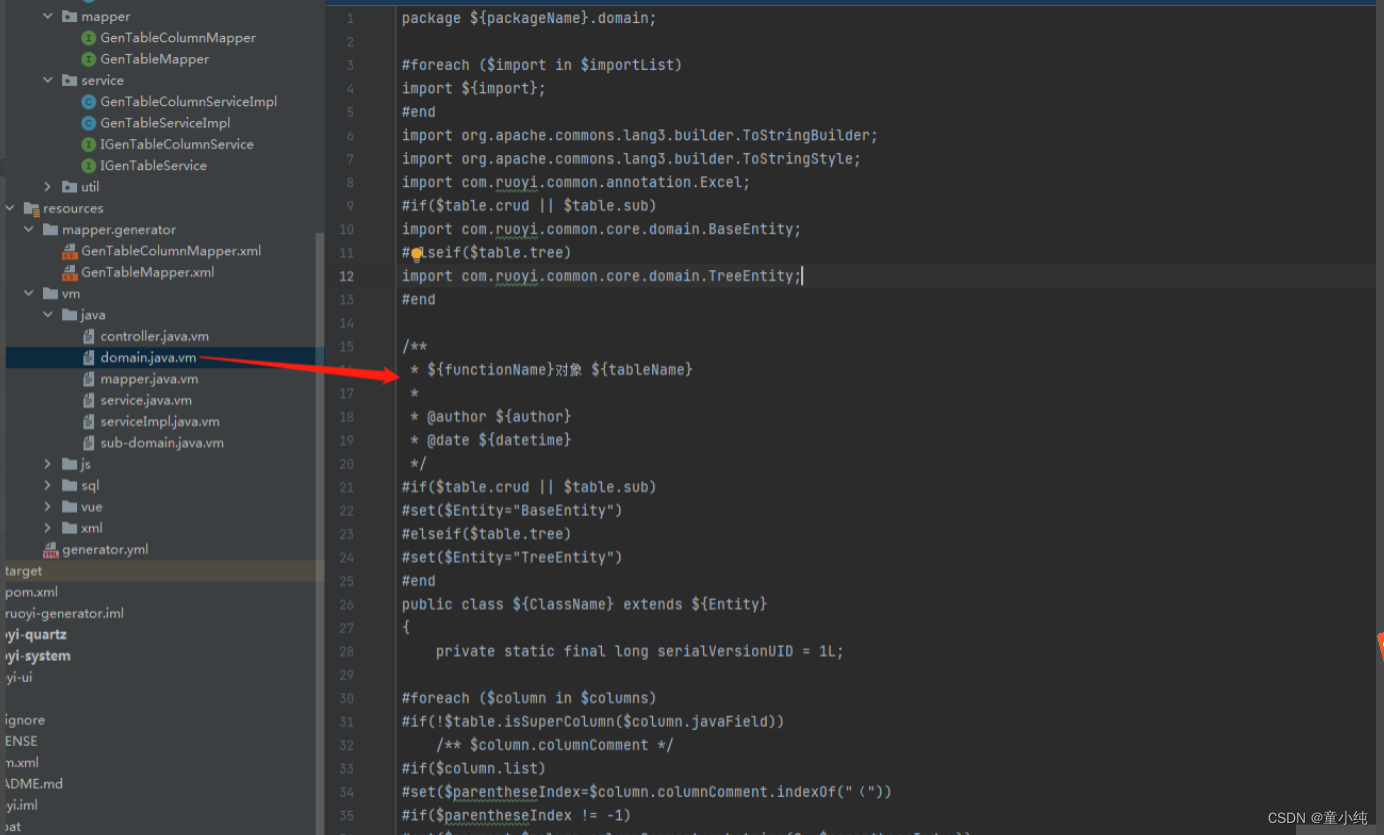
有点复杂的样子。

