CSS简介

CSS概念
CSS(Cascading Style Sheets)层叠样式表,又叫级联样式表,简称样式表
CSS文件后缀名为 .css
CSS用于HTML文档中元素样式的定义
为什么需要CSS
使用css的目的就是让网页具有美观一致的页面
CSS和HTML之间的关系

语法
CSS 规则由两个主要的部分构成:选择器,以及一条或多条声明

选择器通常是您需要改变样式的 HTML 元素 每条声明由一个属性和一个值组成属性(property)是您希望设置的样式属性(style attribute)。每个属性有一个值。属性和值被冒号分开
<style>
h1{
color: blue;
font-size: 12px;
}
</style>学习效果反馈
1.下列关于CSS基础语法描述错误的是:属性与属性值之间用分号隔开
CSS的引入方式

内联样式(行内样式)
要使用内联样式,你需要在相关的标签内使用样式(style)属性。 Style 属性可以包含任何 CSS 属性

<p >CSS<p>内部样式
当单个文档需要特殊的样式时,就应该使用内部样式表。你可以使
用 <style> 标签在文档头部定义内部样式表
<head>
<style>
h1 {
background: red;
}
</style>
</head>外部样式(推荐)
当样式需要应用于很多页面时,外部样式表将是理想的选择。在使
用外部样式表的情况下,你可以通过改变一个文件来改变整个站点
的外观。每个页面使用 <link> 标签链接到样式表。 <link> 标签在(文档的)头部<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="xxx.css">导入式(了解)
此种方式使用率比较低,因为会影响加载速度
<style type="text/css">
@import url("css文件路径");
</style>
@import和link的区别

学习效果反馈
1.外部CSS样式的引入方式,以下正确的是:
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="xxx.css">
CSS样式表特征

继承性
指被包含在内部的标签可以拥有外部标签的样式,比如:text-、 font-、line-height,但有些属性不能继承,比如:border、 padding、margin
层叠性
简单的说,层叠就是对一个元素多次设置同一个样式,这将使用最 后一次设置的属性值。例如对一个站点中的多个页面使用了同一套 CSS样式表,而某些页面中的某些元素想使用其他样式,就可以针 对这些样式单独定义一个样式表应用到页面中。这些后来定义的样 式将对前面的样式设置进行重写,在浏览器中看到的将是最后面设 置的样式效果
优先级
样式定义冲突时,按照不同样式规则的优先级来应用样式 行内样式>内部样式(外部样式)

CSS注释
注释是用来解释你的代码,并且可以随意编辑它,浏览器会忽略它
CSS注释以 /* 开始, 以 */ 结束,/* 这是注释 */
学习效果反馈
1.以下哪个不是CSS样式表特征:CSS注释
基础选择器一

全局选择器
可以与任何元素匹配,优先级最低,不推荐使用
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}元素选择器
HTML文档中的元素, p、b、div、a、img、body 等。
标签选择器,选择的是页面上所有这种类型的标签,所以经常描述
“共性”,无法描述某一个元素的“个性”p{
font-size:14px;
}再比如说,我想让“学完前端,继续学Java”这句话中的“前端”两个变
为红色字体,那么我可以用 <span> 标签把“前端”这两个字围起来,然
后给 <span> 标签加一个标签选择器<p>学完了<span>前端</span>,继续学Java</p>
span{
color: red;
}
类选择器
规定用圆点 . 来定义,针对你想要的所有标签使用

<h2 >你好</h2>
/*定义类选择器*/
.oneclass{
width:800px;
}
<h3 >我是一个h3啊</h3>
<h3 >我是一个h3啊</h3> // 错误学习效果反馈
1.下列代码哪个是类选择器使用方式:.title{color:red;}
基础选择器二
 ID选择器
ID选择器
针对某一个特定的标签来使用,只能使用一次。 css 中的 ID选择器 以 # 来定义<h2 id="mytitle">你好</h2>
#mytitle{
border:3px dashed green;
}
合并选择器
语法: 选择器1,选择器2,...{ }作用:提取共同的样式,减少重复代码
.header, .footer{
height:300px;
}
选择器的优先级
CSS中,权重用数字衡量
元素选择器的权重为: 1
class选择器的权重为: 10
id选择器的权重为: 100
内联样式的权重为: 1000
优先级从高到低: 行内样式 > ID选择器 > 类选择器 > 元素选择器
学习效果反馈
1.下列选择器优先级排序正确的是:行内样式 > ID选择器 > 类选择器 > 元素选择器
DIV+CSS布局

优点

布局时常用的属性
布局-上中下结构
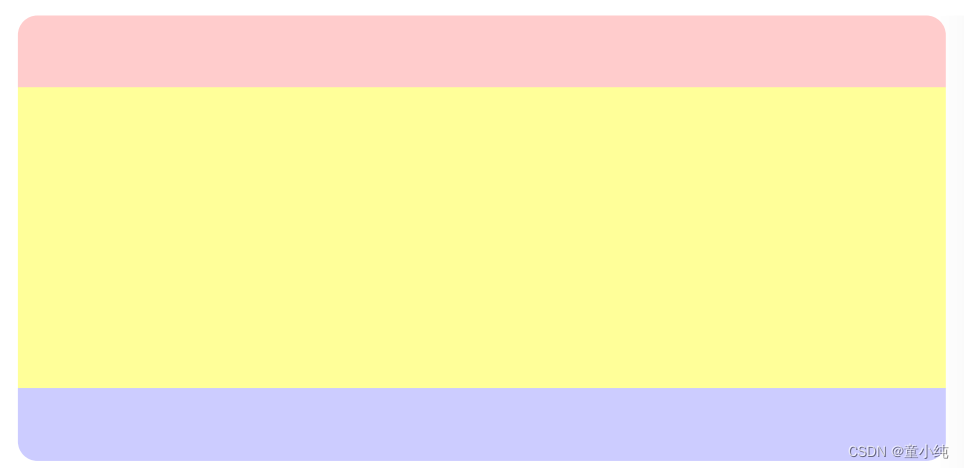

<div ></div>
<div ></div>
<div ></div><style>
.header {
height: 100px;
background-color: #fcc;
}
.content {
height: 400px;
background-color: #ff9;
}
.footer {
height: 100px;
background-color: #ccf;
}
</style>布局-上中下-左右

<div >
<div ></div>
<div ></div>
<div >
<div ></div>
<div ></div>
<div ></div>
</div>
<div ></div>
</div><style>
.header {
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
.nav {
width: 100%;
height: 50px;
background-color: pink;
}
.content {
width:100%;
height: 300px;
background-color: yellow;
}
.footer {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
background-color: deepskyblue;
}
.left {
width: 33.33%;
height: 300px;
background-color: palegoldenrod;
float: left;
}
.center {
width: 33.33%;
height: 300px;
background-color: palegreen;
float: left;
}
.right {
width: 33.33%;
height: 300px;
background-color: palevioletred;
float: left;
}
</style>
学习效果反馈
1.以下哪个不是 DIV+CSS 布局的优点:对搜索引擎不友好
布局实操一

<div >
<div >
<div ></div>
<div ></div>
</div>
<div ></div>
</div><style>
.box{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
}
.left{
float: left;
width: 250px;
height: 500px;
}
.right{
float: right;
width: 250px;
height: 500px;
background-color: burlywood;
}
.top{
width: 250px;
height: 250px;
background-color: pink;
}
.bottom{
width: 250px;
height: 250px;
background-color: turquoise;
}
</style>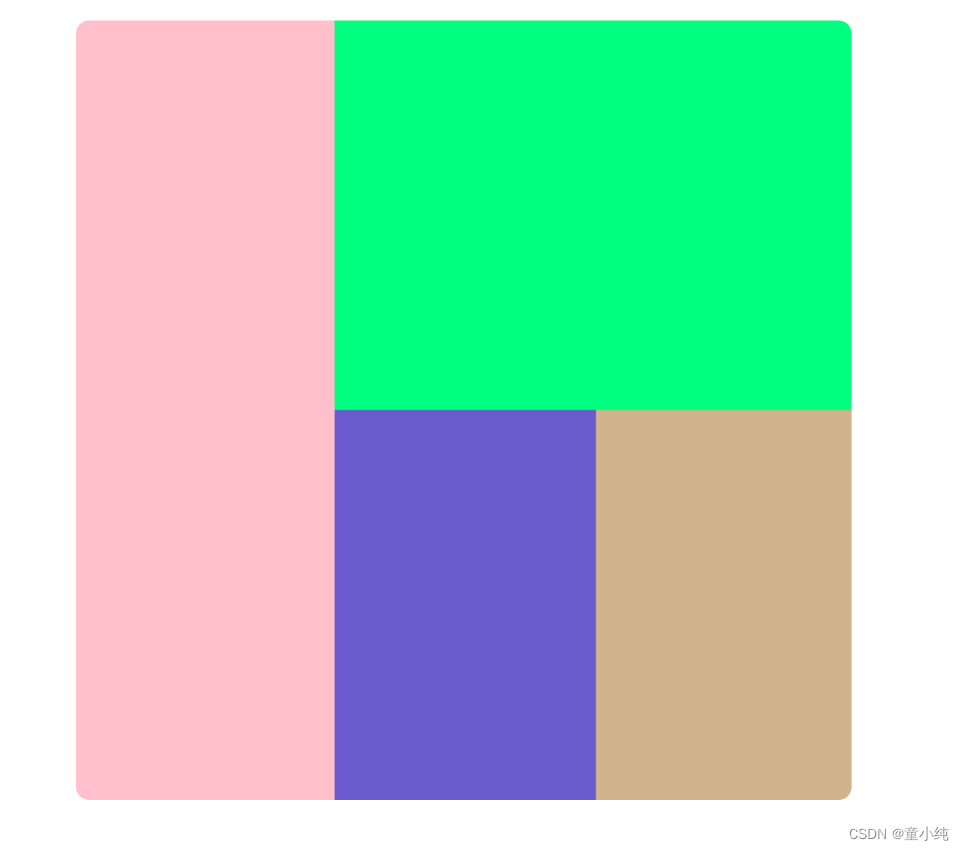
<div >
<div ></div>
<div >
<div ></div>
<div >
<div ></div>
<div ></div>
</div>
</div>
</div><style>
.box{
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
}
.left{
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 600px;
background-color: pink;
}
.right{
float: right;
width: 400px;
height: 600px;
}
.top{
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
background-color: springgreen;
}
.b-left{
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
background-color: slateblue;
}
.b-right{
float: right;
width: 200px;
height: 300px;
background-color: tan;
}
</style>布局实操二

<div >
<div >
<img src="./images/1.webp" alt="">
</div>
<div >
<div >
<img src="./images/2.webp" alt="">
<h3>黑鲨4S</h3>
<p>磁动力升降肩键</p>
</div>
<div >
<img src="./images/2.webp" alt="">
<h3>黑鲨4S</h3>
<p>磁动力升降肩键</p>
</div>
<div >
<img src="./images/2.webp" alt="">
<h3>黑鲨4S</h3>
<p>磁动力升降肩键</p>
</div>
<div >
<img src="./images/2.webp" alt="">
<h3>黑鲨4S</h3>
<p>磁动力升降肩键</p>
</div>
<div >
<img src="./images/2.webp" alt="">
<h3>黑鲨4S</h3>
<p>磁动力升降肩键</p>
</div>
<div >
<img src="./images/2.webp" alt="">
<h3>黑鲨4S</h3>
<p>磁动力升降肩键</p>
</div>
<div >
<img src="./images/2.webp" alt="">
<h3>黑鲨4S</h3>
<p>磁动力升降肩键</p>
</div>
<div >
<img src="./images/2.webp" alt="">
<h3>黑鲨4S</h3>
<p>磁动力升降肩键</p>
</div>
</div>
</div><style>
body{
background-color: #f1f1f1;
}
.phone{
width: 1300px;
height: 680px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.left{
float: left;
width: 234px;
height: 680px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.right{
float: right;
width: 1050px;
}
.item{
width: 250px;
height: 300px;
float: left;
margin-left: 10px;
background-color: #fff;
margin-top: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
</style>

