一、/etc/sudoers文件说明
sudo命令的意思是以其他用户身份执行命令,用户是否拥有sudo权限?拥有哪些权限?sudo执行时是否需要输入密码?这些都是通过/etc/sudoers文件进行配置和控制的。普通用户我们可以通过su命令切换到其他用户,但是需要知道其他用户的密码,如果是需要执行管理员命令则需要知道root密码。但是如果普通用户拥有sudo权限则可以只需要输入自己密码或者不输入密码完成管理员命令的执行。既保证了超级管理员的密码的安全性,又满足了普通用户执行特殊命令的需求,这就是/etc/sudoers文件的作用。
二、sudo使用实践
1、输入用户密码执行sudo
- 编辑sudo文件,加入如下内容
[root@s142 etc]# visudo -f sudoers
…
wuhs ALL=(ALL) ALL
…
- 验证测试,在给wuhs用户配置了sudo权限后,wuhs用户可以直接任何root权限才能执行的命令,但是执行命令前需要输入wuhs账户的密码。当然如果是连续执行其他命令,并不需要每次都输入密码。退出会话再次sudo执行root权限命令则需要再次输入wuhs账户密码。
[wuhs@s142 ~]$ sudo yum install -y wget
[sudo] password for wuhs:
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base:
* extras:
* updates:
Package wget-1.14-18.el7_6.1.x86_64 already installed and latest version
Nothing to do
2、免密执行sudo
- 编辑sudo文件,加入如下内容
[root@s142 etc]# visudo -f sudoers
…
wuhs ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
…
- 验证测试,执行直接cat查看shadow文件是被拒绝的,加上sudo则可以查看,而且不需要密码。
[wuhs@s142 ~]$ cat /etc/shadow
cat: /etc/shadow: Permission denied
[wuhs@s142 ~]$ sudo cat /etc/shadow
3、设置运行普通用户可以执行指定命令
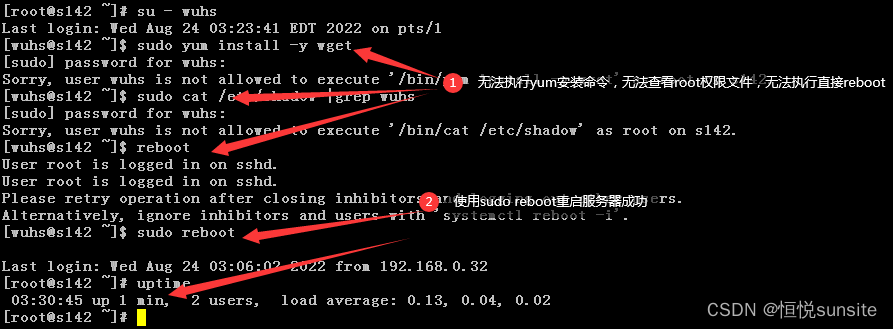
- 以yum命令为例,配置wuhs账户可以免密执行reboot命令,其他root权限命令无法执行。
[root@s142 ~]# visudo -s
…
wuhs ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/sbin/reboot
…
- 验证测试,
[root@s142 ~]# su - wuhs
Last login: Wed Aug 24 03:23:41 EDT 2022 on pts/1
[wuhs@s142 ~]$ sudo yum install -y wget
[sudo] password for wuhs:
Sorry, user wuhs is not allowed to execute ‘/bin/yum install -y wget’ as root on s142.
[wuhs@s142 ~]$ sudo cat /etc/shadow |grep wuhs
[sudo] password for wuhs:
Sorry, user wuhs is not allowed to execute ‘/bin/cat /etc/shadow’ as root on s142.
[wuhs@s142 ~]$ reboot
User root is logged in on sshd.
User root is logged in on sshd.
Please retry operation after closing inhibitors and logging out other users.
Alternatively, ignore inhibitors and users with ‘systemctl reboot -i’.
[wuhs@s142 ~]$ sudo reboot
三、sudoer文件说明
[root@s142 etc]# cat /etc/sudoers
## Sudoers allows particular users to run various commands as
## the root user, without needing the root password.
##该文件允许特定用户像root用户一样使用各种各样的命令,而不需要root用户的密码
##
## Examples are provided at the bottom of the file for collections
## of related commands, which can then be delegated out to particular
## users or groups.
## 在文件的底部提供了很多相关命令的示例以供选择,这些示例都可以被特定用户或
## ## 用户组所使用
## This file must be edited with the 'visudo' command.
## 该文件必须使用"visudo"命令编辑
## Host Aliases
#主机别名
## Groups of machines. You may prefer to use hostnames (perhap using
## wildcards for entire domains) or IP addresses instead.
## 对于一组服务器,你可能会更喜欢使用主机名(可能是全域名的通配符)
## 或IP地址代替,这时可以配置主机别名
# Host_Alias FILESERVERS = fs1, fs2
# Host_Alias MAILSERVERS = smtp, smtp2
## User Aliases
#用户别名
## These aren't often necessary, as you can use regular groups
## (ie, from files, LDAP, NIS, etc) in this file - just use %groupname
## rather than USERALIAS
## 这并不很常用,因为你可以通过使用组来代替一组用户的别名
# User_Alias ADMINS = jsmith, mikem
## Command Aliases
## These are groups of related commands...
## 指定一系列相互关联的命令(当然可以是一个)的别名,通过赋予该别名sudo权限,
## 可以通过sudo调用所有别名包含的命令,下面是一些示例
## Networking
#网络操作相关命令别名
Cmnd_Alias NETWORKING = /sbin/route, /sbin/ifconfig, /bin/ping, /sbin/dhclient,
/usr/bin/net, /sbin/iptables, /usr/bin/rfcomm, /usr/bin/wvdial, /sbin/iwconfig,
/sbin/mii-tool
## Installation and management of software
#软件安装管理相关命令别名
Cmnd_Alias SOFTWARE = /bin/rpm, /usr/bin/up2date, /usr/bin/yum
## Services
#服务相关命令别名
Cmnd_Alias SERVICES = /sbin/service, /sbin/chkconfig
## Updating the locate database
#本地数据库升级命令别名
Cmnd_Alias LOCATE = /usr/sbin/updatedb
## Storage
#磁盘操作相关命令别名
Cmnd_Alias STORAGE = /sbin/fdisk, /sbin/sfdisk, /sbin/parted, /sbin/partprobe, /bin/mount, /bin/umount
## Delegating permissions
#代理权限相关命令别名
Cmnd_Alias DELEGATING = /usr/sbin/visudo, /bin/chown, /bin/chmod, /bin/chgrp
## Processes
#进程相关命令别名
Cmnd_Alias PROCESSES = /bin/nice, /bin/kill, /usr/bin/kill, /usr/bin/killall
## Drivers
#驱动命令别名
Cmnd_Alias DRIVERS = /sbin/modprobe
...
## Next comes the main part: which users can run what software on
## which machines (the sudoers file can be shared between multiple
## systems).
## 下面是规则配置:什么用户在哪台服务器上可以执行哪些命令(sudoers文件可以在多个系统上共享)
## Syntax:
##语法
## user MACHINE=COMMANDS
## 用户 登录的主机=(可以变换的身份) 可以执行的命令
##
## The COMMANDS section may have other options added to it.
## 命令部分可以附带一些其它的选项
##
## Allow root to run any commands anywhere
## 允许root用户执行任意路径下的任意命令
root ALL=(ALL) ALL
## Allows members of the 'sys' group to run networking, software,
## service management apps and more.
# %sys ALL = NETWORKING, SOFTWARE, SERVICES, STORAGE, DELEGATING, PROCESSES, LOCATE, DRIVERS
## 允许sys中户组中的用户使用NETWORKING等所有别名中配置的命令
## Allows people in group wheel to run all commands
## 允许wheel用户组中的用户执行所有命令
%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
## 允许wuhs用户不输入密码执行reboot命令,允许wuhs用户不输入密码执行查看/etc/shadow文件命令
wuhs ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/sbin/reboot
wuhs ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/cat /etc/shadow
## Same thing without a password
## 允许wheel用户组中的用户在不输入该用户的密码的情况下使用所有命令
# %wheel ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
## Allows members of the users group to mount and unmount the
## cdrom as root
## 允许users用户组中的用户像root用户一样使用mount、unmount、chrom命令
# %users ALL=/sbin/mount /mnt/cdrom, /sbin/umount /mnt/cdrom
## Allows members of the users group to shutdown this system
## 允许users用户组中的用户像root用户一样使用shutdown命令
# %users localhost=/sbin/shutdown -h now
四、visudo命令简介
1、使用语法
用法:
#visudo [-chqsV] [-f sudoers]
2、参数说明
| 参数 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|
| -c, --check | 检查sudoers配置文件 |
| -f, --file=sudoers | 修改sudoers配置文件 |
| -h, --help | 获取命令帮助 |
| -q, --quiet | 静默输出 |
| -s, --strict | 严格语法检查 |
| -V, --version | 查看命令版本 |
四、visudo命令使用示例
1、查看命令版本
[root@s142 ~]# visudo -V
visudo version 1.8.23
visudo grammar version 46
…
2、获取命令帮助
[root@s142 ~]# visudo -h
visudo - safely edit the sudoers file
…
3、检查sudoers文件
[root@s142 ~]# visudo -c
/etc/sudoers: parsed OK
4、修改sudoers文件
[root@s142 ~]# cd /etc/
[root@s142 etc]# visudo -f sudoers
## Sudoers allows particular users to run various commands as
## the root user, without needing the root password.
…
5、严格执行语法检查编辑
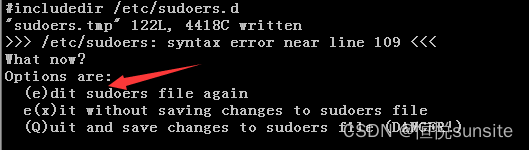
实际上我们可以直接编辑/etc/sudoers文件,直接编辑不会进行语法检查。使用visudo -s可以执行sudoers文件的编辑,编辑国产中实际编辑的是/etc/sudoers.tmp文件,编辑完成后必须wr保存后才会存入sudoers文件。保存前会进行语法检查,如果语法检查失败,会进程错误提示,告知是哪一行有语法错误。如果强制保存会有危险。这就是visudo方式编辑sudo文件的好处。
[root@s142 etc]# visudo -s