服务发现-主要流程介绍篇
简述
在使用 Presto 的时候有没有想过这几个问题?
- Presto 是怎么组建集群的?
- Presto 的 Coordinator 与 Worker 是怎么联系起来的?
- 配置了个服务发现,它是怎么工作的?
最后根据文中的内容看看是否能解答这3个问题。
四个主要流程讲解
Presto 的 Coordinator 利用 discovery node manager 注册或更新 worker nodes 来实现集群化。
Coordinator 就相当于主从架构的主,Worker 就是从,由 Coordinator 来做任务接收、解析、查询执行计划生成、任务调度分发等操作,Worker 只是被动接收信息然后干活,Coordinator 要能与 Worker 联系起来的话,就需要 discovery 中的 Worker 信息。
它们之间的流程主要涉及以下四个流程:
- 1、注册流程,每个 worker node 每 8 秒向 discovery server 注册一次;
- 2、缓存更新流程,service selector 以10秒为间隔更新 discovery server 中注册的节点信息缓存;
- 3、健康检查流程,每 0.5 秒执行一次 worker nodes 的健康检查;
- 4、Coordinator 更新 Worker 流程,discovery node manager 更新 worker node 列表;
对上面的四点,画了个大概的时序图
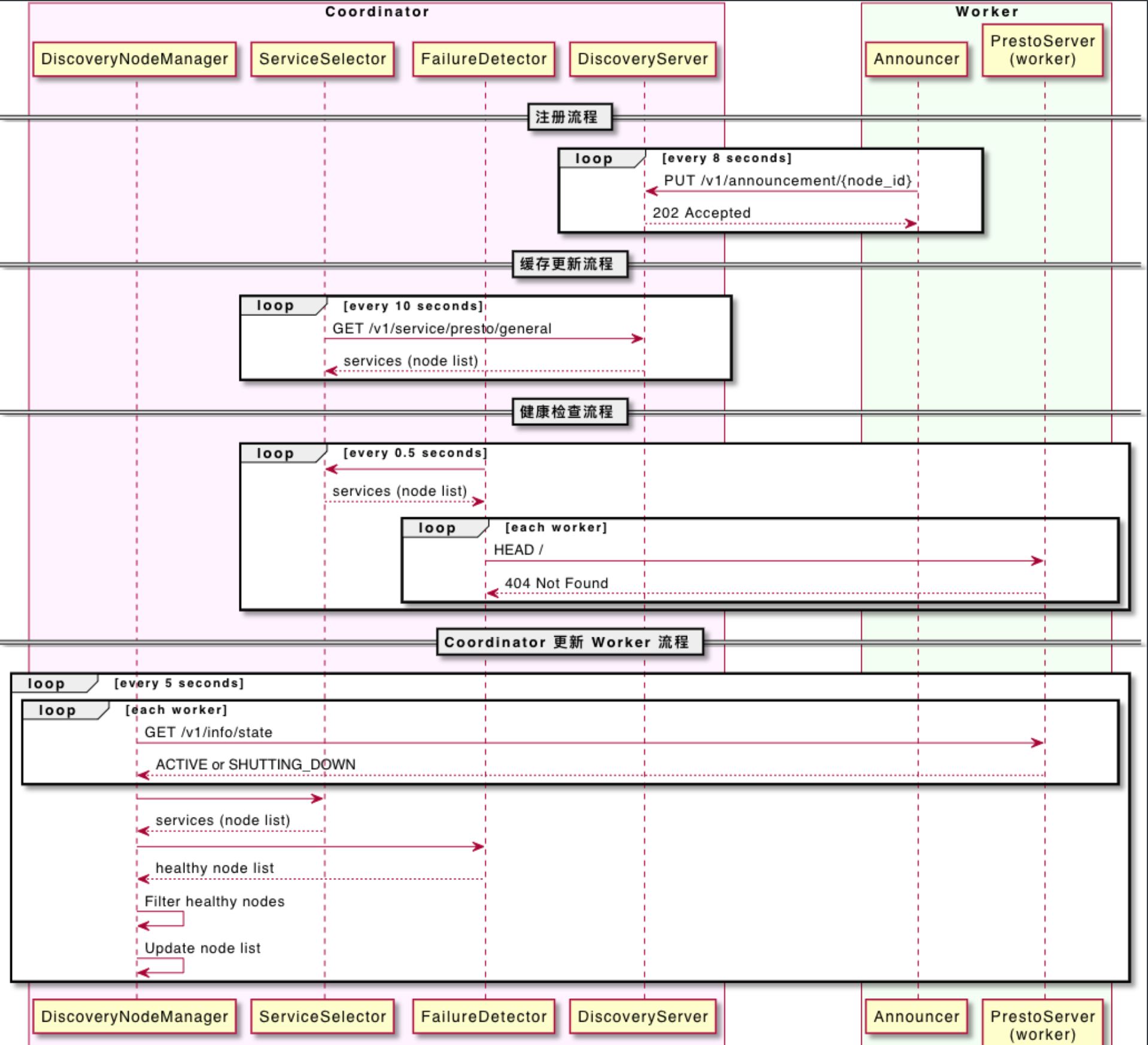
接下来详细解读这4个流程
注册流程
注:以下内容以内嵌服务发现的方式来讲解
Presto 的服务发现的功能,有 Client 与 Server 两个角色。Coordinator 使用 EmbeddedDiscoveryModule 配置了 Server 角色。Coordinator 和 Worker 使用 DiscoveryModule 配置了 Client 角色,然后 Client 主要使用 Announcer 向 Server 发起注册。
再理解这句话之前,需要知道几个细节,是怎么成为 Coordinator 节点或 Worker 节点的,并且怎么注册到 Discovery 服务中的,并且这些角色是如何启动的。
通过查看 Airlift 项目,发现 Airlift 中的 Discovery 是 Client 端,另一个在 discovery-server 项目里。是两个不同的项目。
怎么成为Coordinator/Woker节点的呢?
跟一下代码
// io.trino.server.TrinoServer
...
new Server().start(firstNonNull(version, "unknown")); // 准备启动服务
...
// io.trino.server.Server
public final void start(String trinoVersion)
{
new EmbedVersion(trinoVersion).embedVersion(() -> doStart(trinoVersion)).run();
}
private void doStart(String trinoVersion)
{
...
ImmutableList.Builder<Module> modules = ImmutableList.builder();
modules.add(
new NodeModule(),
new DiscoveryModule(), // 加载注册发现服务,注意这里是 Discovery 的 client 端
new HttpServerModule(),
new JsonModule(),
new JaxrsModule(),
new MBeanModule(),
new PrefixObjectNameGeneratorModule("io.trino"),
new JmxModule(),
new JmxHttpModule(),
new LogJmxModule(),
new TraceTokenModule(),
new EventModule(),
new JsonEventModule(),
new ServerSecurityModule(),
new AccessControlModule(),
new EventListenerModule(),
new CoordinatorDiscoveryModule(), // 加载 Coordinator 专属的注册发现服务,注意这里是 Discovery 的 Server 端
new ServerMainModule(trinoVersion), // 加载节点与服务相关的主 Module 在这里确认是启动 Coordinator 还是 Worker
new GracefulShutdownModule(),
new WarningCollectorModule());
...
injector.getInstance(Announcer.class).start(); // client 端启动
...
// io.trino.server.CoordinatorDiscoveryModule
...
install(new EmbeddedDiscoveryModule()); // 服务端的启动
...
// io.trino.server.ServerMainModule
protected void setup(Binder binder)
{
ServerConfig serverConfig = buildConfigObject(ServerConfig.class); // 根据配置中的内容
if (serverConfig.isCoordinator()) {
install(new CoordinatorModule()); // 成为Coordinator
}
else {
install(new WorkerModule()); // 成为Worker
}
...
Coordinator/Woker节点如何注册的呢?
从上面的源码我们可以看出,是在启动服务的时候加载 Module,在 ServerMainModule 中通过配置判断启动 Coordinator 还是 Worker。
注意到在加载 Module 的时候,我们既加载了 Discovery 的 Client,也加载了 Server。他们是怎么区分的呢?
这里有同样也有个细节,也是关于配置文件的。
在启动时,通过加载 DiscoveryModule 来注册 Client 端。在加载 CoordinatorDiscoveryModule 时里面有个对配置文件的判断。
相当于如果配置文件中指明了该节点是 Coordinator,那么还会加载一个 EmbeddedDiscoveryModule 来注册 Server 端。
// io.trino.server.CoordinatorDiscoveryModule
protected void setup(Binder binder)
{
// 注意这个判断,这里如果配置文件中设置为 isEnabled 那么就会加载发现服务的 Server 端,如果没指定发现服务可以单独部署
if (buildConfigObject(ServerConfig.class).isCoordinator() && buildConfigObject(EmbeddedDiscoveryConfig.class).isEnabled()) {
install(new EmbeddedDiscoveryModule());
}
}
注意到我们前面说的发现服务是可以单独部署(在官方文档里给出的建议是内嵌),如果发现服务内嵌在 Coordinator 的话,那么 Coordinator 的 Server 中包含发现服务的 Server,发现服务的 Server 会接收所有 Worker 发现服务 Client 端的请求,同时也会接收 Coordinator 的发现服务 Client 端的请求。
**我们可以通过 **/v1/service 接口可以来验证所有的注册信息。(这里的前提是发现服务内嵌在 Coordinator 中)。
准备了一个测试环境,启动了2个节点,1个Coordinator,1个Worker。
在接口中查看到以下数据,并且发现2台节点应该是都注册的 Client,另一个节点因为是 Coordinator 它还多注册了一个 server。
{
"environment": "cdh6_test",
"services": [
{ ... },
{ ... },
{
"id": "25a99b20-bcd4-4f81-881f-8432fdd62557",
"nodeId": "tcdh31",
"type": "presto",
"pool": "general",
"location": "/tcdh31",
"properties": {
"node_version": "",
"coordinator": "false",
"connectorIds": "**"
}
},
{ },
{
"id": "924b4589-1d63-4bbe-a2f5-78a62f91a4fc",
"nodeId": "tcdh29",
"type": "presto-coordinator",
"pool": "general",
"location": "/tcdh29",
"properties": {
}
},
{ ... },
{ ... },
{ ... },
{
"id": "d7147db7-cfba-4c57-9d7f-e10183650471",
"nodeId": "tcdh29",
"type": "presto",
"pool": "general",
"location": "/tcdh29",
"properties": {
"node_version": "",
"coordinator": "true", "connectorIds": "***"
}
}
]
}
**Client 通过向 **/v1/announcement/{node_id} 发送 PUT 请求来向服务器注册自己。注册信息有30秒的生命周期,所以client会定期向服务器发送注册请求。这个间隔是 8 秒,源码如下:
Client角色启动 Airlift工程 discovery模块 客户端的发送
// io.trino.server.Server
...
injector.getInstance(Announcer.class).start();
...
// io.airlift.discovery.client.Announcer 客户端发起注册的代码 发起put
// announce 准备开始
public void start()
{
checkState(!executor.isShutdown(), "Announcer has been destroyed");
if (started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// announce immediately, if discovery is running
ListenableFuture<Duration> announce = announce(System.nanoTime(), new Duration(0, SECONDS));
try {
announce.get(30, SECONDS); // 30秒的生命周期,在服务端设置好了。
}
catch (Exception ignored) {
}
}
}
...
// announce 异步发送,在回调函数中进行延迟等待,然后准备下一次的announce
private ListenableFuture<Duration> announce(long delayStart, Duration expectedDelay)
{
// log announcement did not happen within 5 seconds of expected delay
if (System.nanoTime() - (delayStart + expectedDelay.roundTo(NANOSECONDS)) > SECONDS.toNanos(5)) {
log.error("Expected service announcement after %s, but announcement was delayed %s", expectedDelay, Duration.nanosSince(delayStart));
}
long requestStart = System.nanoTime();
// 主要是在announce中发起请求
ListenableFuture<Duration> future = announcementClient.announce(getServiceAnnouncements());
// 通过future的回调函数异步获得结果
Futures.addCallback(future, new FutureCallback<Duration>()
{
@Override
public void onSuccess(Duration expectedDelay)
{
errorBackOff.success();
// wait 80% of the suggested delay
expectedDelay = new Duration(expectedDelay.toMillis() * 0.8, MILLISECONDS); // 在这里计算得出的8秒,我们继续看下面的代码,看 expectedDelay是怎么变成10秒的
log.debug("Service announcement succeeded after %s. Next request will happen within %s", Duration.nanosSince(requestStart), expectedDelay);
scheduleNextAnnouncement(expectedDelay); // 下一次的announce
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t)
{
Duration duration = errorBackOff.failed(t);
// todo this is a duplicate log message and should be remove after root cause of announcement delay is determined
log.error("Service announcement failed after %s. Next request will happen within %s", Duration.nanosSince(requestStart), expectedDelay);
scheduleNextAnnouncement(duration); // 下一次的announce
}
}, executor);
return future;
}
// 下一次的announce
private void scheduleNextAnnouncement(Duration expectedDelay)
{
// already stopped? avoids rejection exception
if (executor.isShutdown()) {
return;
}
long delayStart = System.nanoTime();
executor.schedule(() -> announce(delayStart, expectedDelay), expectedDelay.toMillis(), MILLISECONDS);
}
// 这里有个细节我们需要注意下。通过代码可以看出,expectedDelay为我们每次延迟时间的。但是它是怎么变成8秒的呢?我们看一下announcementClient的实现,它其实是实现了DiscoveryAnnouncementClient接口。
// io.airlift.discovery.client.DiscoveryAnnouncementClient
public interface DiscoveryAnnouncementClient
{
Duration DEFAULT_DELAY = new Duration(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 在接口的定义中,有一个默认延迟时间,这里是10秒
ListenableFuture<Duration> announce(Set<ServiceAnnouncement> services);
ListenableFuture<Void> unannounce();
}
// 一般我们的实现都是基于Http的协议,所以announce的常用实现在HttpDiscoveryAnnouncementClient中
// io.airlift.discovery.client.HttpDiscoveryAnnouncementClient
public class HttpDiscoveryAnnouncementClient
implements DiscoveryAnnouncementClient
{
...
@Override
public ListenableFuture<Duration> announce(Set<ServiceAnnouncement> services)
{
requireNonNull(services, "services is null");
// 获得URI
URI uri = discoveryServiceURI.get();
if (uri == null) {
return immediateFailedFuture(new DiscoveryException("No discovery servers are available"));
}
// 构建Request,准备发现请求
Announcement announcement = new Announcement(nodeInfo.getEnvironment(), nodeInfo.getNodeId(), nodeInfo.getPool(), nodeInfo.getLocation(), services);
Request request = preparePut()
.setUri(createAnnouncementLocation(uri, nodeInfo.getNodeId()))
.setHeader("User-Agent", nodeInfo.getNodeId())
.setHeader("Content-Type", MEDIA_TYPE_JSON.toString())
.setBodyGenerator(jsonBodyGenerator(announcementCodec, announcement))
.build();
// 发起请求
return httpClient.executeAsync(request, new DiscoveryResponseHandler<Duration>("Announcement", uri)
{
@Override
public Duration handle(Request request, Response response)
throws DiscoveryException
{
int statusCode = response.getStatusCode();
if (!isSuccess(statusCode)) {
throw new DiscoveryException(String.format("Announcement failed with status code %s: %s", statusCode, getBodyForError(response)));
}
Duration maxAge = extractMaxAge(response);
// 返回最大时延
return maxAge;
}
});
}
// 可以看到在进行请求发送时最后会去返回一个 maxAge 最大年龄,应该可以理解为最大的时延,具体我们看extractMaxAge里的实现
private static Duration extractMaxAge(Response response)
{
String header = response.getHeader(HttpHeaders.CACHE_CONTROL);
if (header != null) {
CacheControl cacheControl = CacheControl.valueOf(header);
if (cacheControl.getMaxAge() > 0) {
return new Duration(cacheControl.getMaxAge(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
return DEFAULT_DELAY; // 这个地方对应了接口中定义的默认值,10秒,通过上面的代码可以看出,如果没有特殊配置的下,请求发出去后,都会返回一个10秒的时延。最后对应到启动时的onSuccess回调函数中 * 0.8 计算得出是8秒。
}
这个每隔8秒发一次注册请求的逻辑,是一个值得学习的细节。小总结一下,这块代码多次使用了 ListenableFuture,我们记住2个宗旨,先看 future 对应的启动实现逻辑是什么(这里可能会对应接口然后接入多个实现,也可能是其他),然后再看回调函数的逻辑。流程为先启动再回调
discovery工程 discovery-server模块 服务端的接收
// io.airlift.discovery.server.DynamicAnnouncementResource 服务端接收注册的代码 接收put
@PUT
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Response put(@PathParam("node_id") Id<Node> nodeId, @Context UriInfo uriInfo, DynamicAnnouncement announcement)
{
if (!nodeInfo.getEnvironment().equals(announcement.getEnvironment())) {
return Response.status(BAD_REQUEST)
.entity(format("Environment mismatch. Expected: %s, Provided: %s", nodeInfo.getEnvironment(), announcement.getEnvironment()))
.build();
}
String location = firstNonNull(announcement.getLocation(), "/somewhere/" + nodeId.toString());
DynamicAnnouncement announcementWithLocation = DynamicAnnouncement.copyOf(announcement)
.setLocation(location)
.build();
dynamicStore.put(nodeId, announcementWithLocation);
return Response.status(ACCEPTED).build();
}
服务端从注册接口收到注册信息后,存入到 store 后他们是怎么控制这个30秒的生命周期呢?
// io.airlift.discovery.server.ReplicatedDynamicStore 注册的内容只有30秒有效
@Override
public void put(Id<Node> nodeId, DynamicAnnouncement announcement)
{
List<Service> services = FluentIterable.from(announcement.getServiceAnnouncements())
.transform(toServiceWith(nodeId, announcement.getLocation(), announcement.getPool()))
.toList();
byte[] key = nodeId.getBytes();
byte[] value = codec.toJsonBytes(services);
// 30秒设置到maxAge这个变量中了。服务端的DiscoveryConfig中默认设置了maxAge为30秒,所以每次生命周期 // 为30秒
store.put(key, value, maxAge);
}
看代码,这个 store 是一个分布式kv存储。
相当于在启动这个分布式kv存储时,会启动一个过期检查,定时检查 PUT 过来的注册信息,根据里面的生命周期条件来判断是否进行过期释放。
/**
* A simple, eventually consistent, fully replicated, distributed key-value store.
*/
public class DistributedStore {
...
@Managed
public void removeExpiredEntries()
{
for (Entry entry : localStore.getAll()) {
if (isExpired(entry)) { // 获取每个注册信息进行是否过期的判断,判断通过则在 store 中执行 delete
localStore.delete(entry.getKey(), entry.getVersion());
}
}
lastGcTimestamp.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
private boolean isExpired(Entry entry)
{
long ageInMs = timeSupplier.get().getMillis() - entry.getTimestamp();
return entry.getValue() == null && ageInMs > tombstoneMaxAge.toMillis() || // TODO: this is repeated in StoreResource
entry.getMaxAgeInMs() != null && ageInMs > entry.getMaxAgeInMs();
}
...
}