一、说明
1、使用场景
当页面需要展示大量数据时,如果直接将大量数据渲染到页面上,会导致网页性能变差,加载时间变长,甚至出现卡顿等问题。此时使用虚拟列表,可以通过动态计算和渲染可见区域内的数据,来优化性能并提高用户体验。
2、虚拟列表实现
可以基于组件库的虚拟滚动组件,如 vue-virtual-scroll-list(https://github.com/tangbc/vue-virtual-scroll-list)、vue-virtual-scroller(https://github.com/Akryum/vue-virtual-scroller/tree/master) 等实现,也可手写实现,基本思路是通过计算可视区域内需要渲染的数据项的索引范围,只对这些数据项进行渲染。
二、手写一个简单的虚拟列表
1、实现步骤
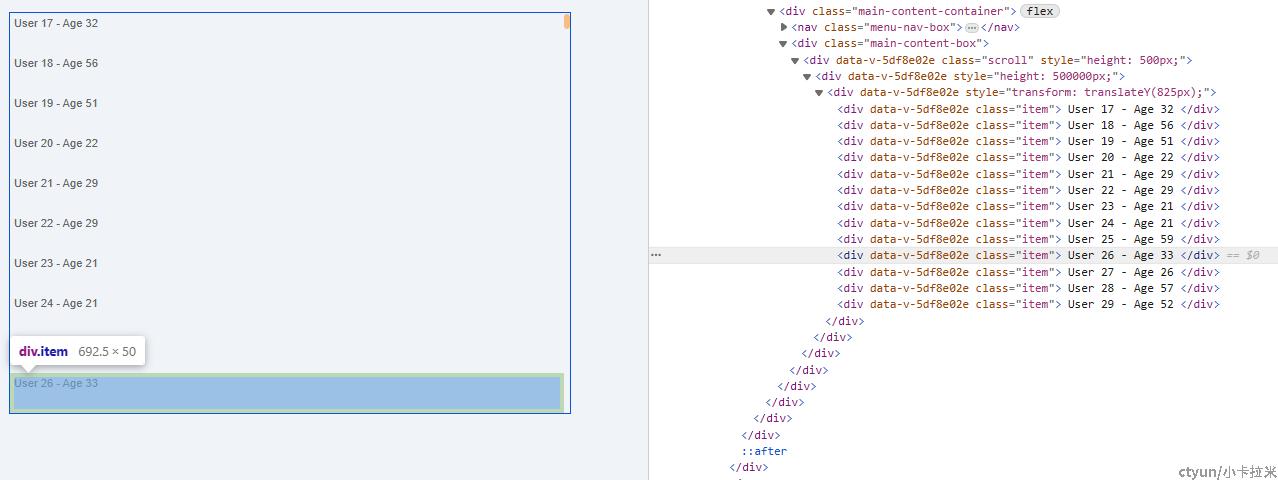
1)定义可视区域div,固定其高度,通过overflow使其允许纵向Y轴滚动。定义整体高度div撑开高度,显示滚动条。遍历可视数据项
2)定义一些基本的数据和参数,如原始数据、每项的高度、可见项数、缓存项数等。
3)计算列表的总高度和初始显示的数据,并将其赋值给相应的变量。
4)在onScroll方法中监听滚动事件,更新滚动距离并重新计算显示的数据。
2、代码
<template>
<div ref="scroll" :style="{ height: `${contentHeight}px` }" class="scroll" @scroll="onScroll">
<!--撑开高度,让滚动条出现-->
<div :style="{ height: totalHeight + 'px' }">
<!--数据项渲染区域-->
<div :style="{ transform: 'translateY(' + offsetY + 'px)' }">
<div v-for="(item, index) in visibleData" :key="index" class="item">
{{ item.name + ' - ' + item.age }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
data: [], // 原始数据
visibleData: [], // 显示的数据
contentHeight: 0, // 可视区域高度
itemHeight: 50, // 每项的高度
visibleCount: 10, // 可见项数
bufferCount: 3, // 缓冲项数,避免滑动太快出现白屏
offsetY: 0, // 滚动距离
totalHeight: 0 // 总高度
}
},
mounted() {
this.contentHeight = this.itemHeight * this.visibleCount
// 测试数据
this.data = [...new Array(10000).keys()].map((i) => ({
id: i + 1,
name: `User ${i + 1}`,
age: `Age ${Math.floor(Math.random() * (60 - 20 + 1)) + 20}`
}))
this.calculateTotalHeight()
this.calculateVisibleData()
},
methods: {
// 计算总高度
calculateTotalHeight() {
this.totalHeight = this.data.length * this.itemHeight
},
// 计算显示的数据
calculateVisibleData() {
const start = Math.floor(this.offsetY / this.itemHeight)
const end = Math.min(start + this.visibleCount + this.bufferCount, this.data.length)
this.visibleData = this.data.slice(start, end)
},
// 监听滚动事件
onScroll() {
this.offsetY = this.$refs.scroll.scrollTop
this.calculateVisibleData()
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.scroll {
overflow: auto;
width: 700px;
border: 1px solid rgb(7, 84, 226);
}
/*每条数据的样式*/
.item {
height: 50px;
padding: 5px;
color: #666;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
</style>
3、效果展示