cache写机制中的write through 和 write back
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache#Writing_Policies
Write-through- Write is done synchronously both to the cache and to the backing store.
Write-back (or Write-behind) - Writing is done only to the cache. A modified cache block is written back to the store, just before it is replaced.
-
Write-through(直写模式)在数据更新时,同时写入缓存Cache和后端存储。此模式的优点是操作简单;缺点是因为数据修改需要同时写入存储,数据写入速度较慢。
-
Write-back(回写模式)在数据更新时只写入缓存Cache。只在数据被替换出缓存时,被修改的缓存数据才会被写到后端存储。此模式的优点是数据写入速度快,因为不需要写存储;缺点是一旦更新后的数据未被写入存储时出现系统掉电的情况,数据将无法找回。
-
Writearound ats现有cache写入模式
Write-misses写缺失的处理方式
对于写操作,存在写入缓存缺失数据的情况,这时有两种处理方式:
Write allocate (aka Fetch on write) - Datum at the missed-write location is loaded to cache, followed by a write-hit operation. In this approach, write misses are similar to read-misses. No-write allocate (aka Write-no-allocate, Write around) - Datum at the missed-write location is not loaded to cache, and is written directly to the backing store. In this approach, actually only system reads are being cached.
Write allocate方式将写入位置读入缓存,然后采用write-hit(缓存命中写入)操作。写缺失操作与读缺失操作类似。
No-write allocate方式并不将写入位置读入缓存,而是直接将数据写入存储。这种方式下,只有读操作会被缓存。
无论是Write-through还是Write-back都可以使用写缺失的两种方式之一。只是通常Write-back采用Write allocate方式,而Write-through采用No-write allocate方式;因为多次写入同一缓存时,Write allocate配合Write-back可以提升性能;而对于Write-through则没有帮助。
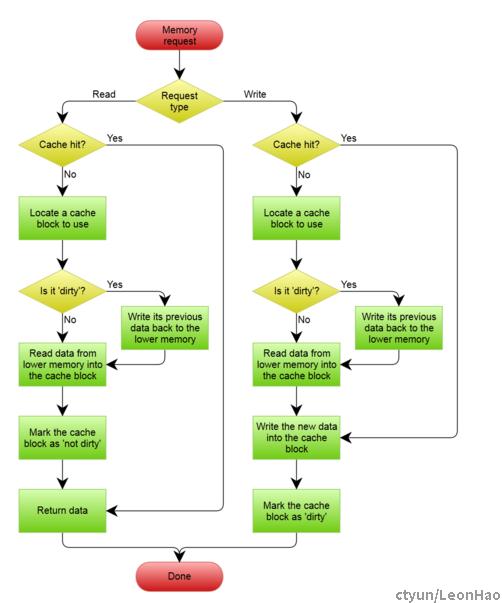
处理流程图
Write-through模式处理流程:
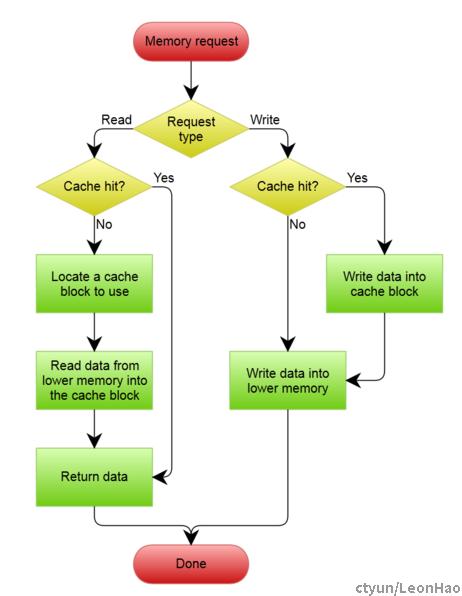
A Write-Through cache with No-Write Allocation
Write-back模式处理流程: