有一次在开发环境做一个接口的压测时,结果很不理想。于是用命令查了一下进程的gc情况,每500毫秒查一次,连续查100次
jstat -gc 2847106 500 100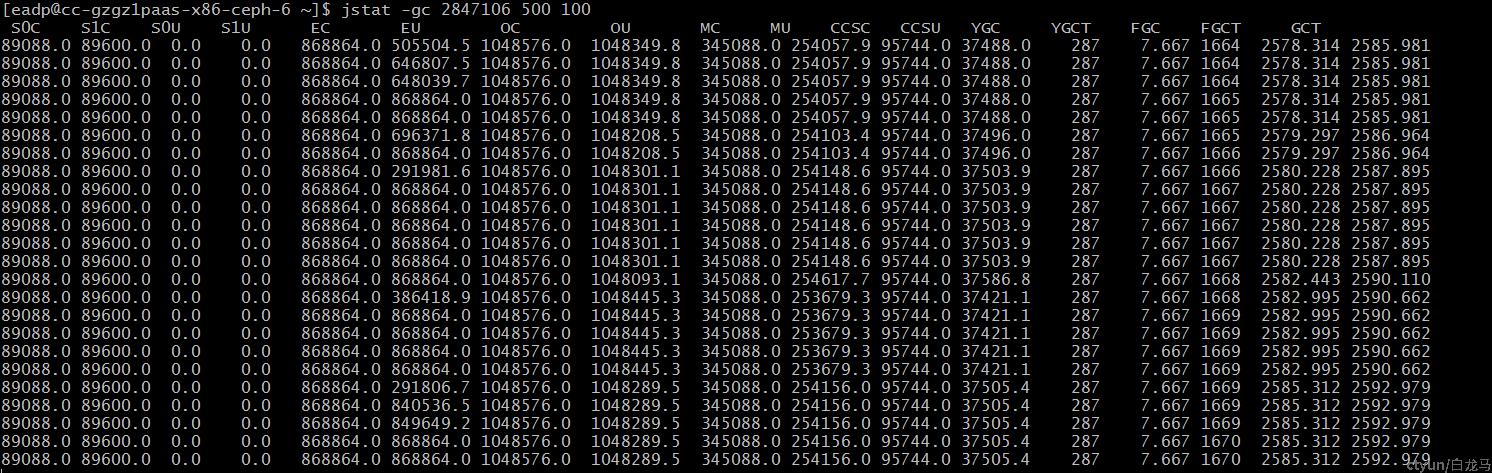
结果发现Full gc次数比Young gc次数多得多,高达1670次,平均每几秒就一次Full gc。
如此频繁的Full gc,可以看出每次Full gc之后都没能清掉堆内的对象释放内存,因此需要打印jvm内存中对象数量来看下是什么对象常驻内存没有释放。执行
jmap -histo 2847106 | less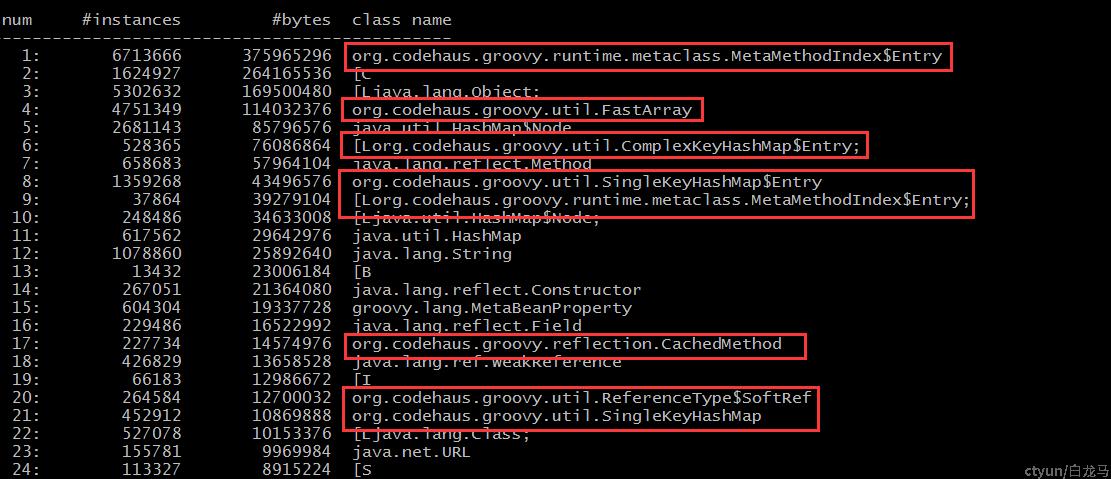
结果可以看出是groovy相关的对象占用了大部分的堆空间,问题是工程中并没有直接使用groovy,需要找出是哪个jar间接使用了groovy

原来是工程中使用了json-path来解释接口请求中的json入参(json-path可以使用搜索路径来直接读取json中的某个字段的值),而json-path使用了groovy脚本来读取json数据。
// json-path 将搜索路径都转成了 JSONAssertion
class JSONAssertion implements Assertion {
String key;
Map<String, Object> params;
def Object getResult(object, config) {
Object result = getAsJsonObject(object)
return result;
}
def getAsJsonObject(object) {
key = escapePath(key, hyphen(), attributeGetter(), integer(), properties(), classKeyword());
def result;
if (key == "\$" || key == "") {
result = object
} else {
def root = 'restAssuredJsonRootObject'
try {
def expr;
if (key =~ /^\[\d+\].*/) {
expr = "$root$key"
} else {
expr = "$root.$key"
}
result = eval(root, object, expr)
} catch (MissingPropertyException e) {
// This means that a param was used that was not defined
String error = String.format("The parameter \"%s\" was used but not defined. Define parameters using the JsonPath.params(...) function", e.property);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(error, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
String error = e.getMessage().replace("startup failed:","Invalid JSON expression:").replace("$root.", generateWhitespace(root.length()));
throw new IllegalArgumentException(error, e);
}
}
return result
}
def String description() {
return "JSON path"
}
private def eval(root, object, expr) {
Map<String, Object> newParams;
// Create parameters from given ones
if(params!=null) {
newParams=new HashMap<>(params);
} else {
newParams=new HashMap<>();
}
// Add object to evaluate
newParams.put(root, object);
// Create shell with variables set
GroovyShell sh = new GroovyShell(new Binding(newParams));
// Run
return sh.evaluate(expr);
}
}那为什么使用groovy会有这样的问题呢?
每次groovy都会根据脚本内容生成一个class对象和生成一个新的classloader,由这个classloader去加载class
public GroovyShell(ClassLoader parent, Binding binding, final CompilerConfiguration config) {
if (binding == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Binding must not be null.");
}
if (config == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Compiler configuration must not be null.");
}
final ClassLoader parentLoader = (parent!=null)?parent:GroovyShell.class.getClassLoader();
this.loader = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<GroovyClassLoader>() {
public GroovyClassLoader run() {
return new GroovyClassLoader(parentLoader,config);
}
});
this.context = binding;
this.config = config;
}继续查看GroovyClassLoader的源码,发现有两个用于缓存的map,sourceCache用来缓存groovy脚本文件名,classCache用来缓存已编译的class。从源码中看出,脚本没有缓存到sourceCache,但会缓存到classCache,导致class对象没有及时被full gc回收。
/**
* this cache contains the loaded classes or PARSING, if the class is currently parsed
*/
protected final Map<String, Class> classCache = new HashMap<String, Class>();
/**
* This cache contains mappings of file name to class. It is used
* to bypass compilation.
*/
protected final Map<String, Class> sourceCache = new HashMap<String, Class>(); /**
* Parses the groovy code contained in codeSource and returns a java class.
*/
private Class parseClass(final GroovyCodeSource codeSource) throws CompilationFailedException {
// Don't cache scripts
return loader.parseClass(codeSource, false);
} /**
* Parses the given code source into a Java class. If there is a class file
* for the given code source, then no parsing is done, instead the cached class is returned.
*
* @param shouldCacheSource if true then the generated class will be stored in the source cache
* @return the main class defined in the given script
*/
public Class parseClass(GroovyCodeSource codeSource, boolean shouldCacheSource) throws CompilationFailedException {
synchronized (sourceCache) {
Class answer = sourceCache.get(codeSource.getName());
if (answer != null) return answer;
answer = doParseClass(codeSource);
if (shouldCacheSource) sourceCache.put(codeSource.getName(), answer);
return answer;
}
}
private Class doParseClass(GroovyCodeSource codeSource) {
validate(codeSource);
Class answer; // Was neither already loaded nor compiling, so compile and add to cache.
CompilationUnit unit = createCompilationUnit(config, codeSource.getCodeSource());
if (recompile!=null && recompile || recompile==null && config.getRecompileGroovySource()) {
unit.addFirstPhaseOperation(TimestampAdder.INSTANCE, CompilePhase.CLASS_GENERATION.getPhaseNumber());
}
SourceUnit su = null;
File file = codeSource.getFile();
if (file != null) {
su = unit.addSource(file);
} else {
URL url = codeSource.getURL();
if (url != null) {
su = unit.addSource(url);
} else {
su = unit.addSource(codeSource.getName(), codeSource.getScriptText());
}
}
ClassCollector collector = createCollector(unit, su);
unit.setClassgenCallback(collector);
int goalPhase = Phases.CLASS_GENERATION;
if (config != null && config.getTargetDirectory() != null) goalPhase = Phases.OUTPUT;
unit.compile(goalPhase);
answer = collector.generatedClass;
String mainClass = su.getAST().getMainClassName();
for (Object o : collector.getLoadedClasses()) {
Class clazz = (Class) o;
String clazzName = clazz.getName();
definePackageInternal(clazzName);
setClassCacheEntry(clazz);
if (clazzName.equals(mainClass)) answer = clazz;
}
return answer;
}找到原因后,项目中就将json-path去掉了。因为json的搜索路径是固定的,之前用json-path就是想少写点代码,现在知道有性能问题只能去掉了。
去掉json-path之后就没有频繁的Full gc了。